حسابرسی پیوسته: ایجاد قابلیت حسابرسی خودکار
خلاصه
اقتصاد دیجیتال به طور قابلتوجهی شیوه انجام کسبوکار و اطلاعات مالی را تغییر دادهاست. تعداد رو به رشدی از سازمانها در حال انجام کسبوکار و انتشار گزارشهای مالی آنلاین در آن واحد هستند. گزارش مالی در آن واحد به احتمال زیاد مستلزم حسابرسی مستمر است تا اطمینان مستمر در مورد کیفیت حاصل شود. اعتبار اطلاعات ارائهشده، فرآیند حسابرسی با ضرورت ، از حسابرسی معمولی متعارف به حسابرسی مبتنی بر کامپیوتر تکامل یافته است و در حال حاضر با ایجاد حسابرسیهای مداوم الکترونیکی مواجه شدهاست. اطلاعات جدید در حال ظهور فنآوری اطلاعات، و تقاضا برای برقراری ارتباط به موقع تر اطلاعات به سهامداران کسبوکار، نیازمند ایجاد راههای جدید برای نظارت مداوم، جمعآوری و تجزیه و تحلیل مدارک حسابرسی میباشد. حسابرسی پیوسته در اینجا به عنوان "یک فرآیند حسابرسی الکترونیکی جامع" تعریف شدهاست که حسابرسان را قادر میسازد تا درجهای از اطمینان را در خصوص اطلاعات پیوسته و یا کمی بعد از آن افشا کنند. این مقاله مبتنی بر مروری بر ادبیات مربوطه، برنامههای حسابرسی مستمر ، و تجربیات نویسندگان است. روشی برای ایجاد قابلیت حسابرسی پیوسته ارائه و انبارهای داده و دادههای اطلاعاتی مورد بررسی قرار میگیرد.
تاکنون، فنآوری پیشرفته حاکی از آن است که تبادل در آن واحد دادههای مالی حساس، فشار ثابتی بر حسابرسان برای به روز رسانی تکنیکهای حسابرسی اعمال خواهد کرد. نویسندگان از حمایت دانشکده تحقیقاتی تجارت و اقتصاد در دانشگاه ممفیس و نظرات مفید منتقدان و آرنولد رایت (سردبیر) قدردانی کردهاند.
مقدمه
تجارت الکترونیک، تبادل داده الکترونیکی (EDI)، و اینترنت به طور چشمگیری شیوههای کسبوکار و نگهداری سوابق را تغییر میدهند. انجام کسبوکار در وب گسترده جهانی، سازمانها را قادر میسازد تا به دنیای آنلاین متصل شوند و تمام جنبههای کسبوکار خود را بهبود بخشند. در این محیط با فنآوری گسترده ، معاملات تجاری به طور کامل به صورت الکترونیکی انجام میشوند. پیشرفتهای تکنولوژیکی، نوعی انتقال داده دیجیتال با سرعت بالا، با استفاده از سختافزاری که اطلاعات را به سرعت و به راحتی تولید میکند، و استفاده از نرمافزاری که در بسیاری از موارد زمان، فضا و محدودیتهای دیگر را برای اطلاعات از بین میبرد، اتخاذ کردهاست. پیشرفت در فنآوری اطلاعات، در حالی که هزینههای معامله و مشکلات اطلاعات نامتقارن را کاهش میدهد، اقتصادها مقیاس و دامنه را در تمام بخشهای تجاری (آلبرشت و ساک ۲۰۰۰)افزایش دادهاست. پروژه سال ۱۹۹۸ موسسه حسابداران رسمی عمومی (AICPA) بیان میکند که پیشرفتهای تکنولوژیکی نیروهای مهمی هستند که بر حرفه حسابداری تاثیر میگذارند (AICPA ۱۹۹۸ a).
Summary
The digital economy has significantly altered the way business is conducted and financial information is communicated. A rapidly growing number of organizations are conducting business and publishing business and financial reports online and in real-time. Real-time financial reporting is likely to necessitate continuous auditing to provide continuous assurance about the quality and credibility of the information presented. The audit process has, by necessity, evolved from a conventional manual audit to computer-based auditing and is now confronted with creating continuous electronic audits. Rapidly emerging information technology and demands for more timely communication of information to business stakeholders requires auditors to invent new ways to continuously monitor, gather, and analyze audit evidence. Continuous auditing is defined here as “a comprehensive electronic audit process that enables auditors to provide some degree of assurance on continuous information simultaneously with, or shortly after, the disclosure of the information.” This paper is based on a review of related literature, innovative continuous auditing applications, and the experiences of the authors. An approach for building continuous audit capacity is presented and audit data warehouses and data marts are described. Ever improving technology suggests that the real-time exchange of sensitive financial data will place constant pressure on auditors to update audit techniques. Most of the new techniques that will be required will involve creation of new software and audit models. Future research should focus on how continuous auditing could be constantly improved in various auditing domains including assurance, attestation, and audit services.
The authors acknowledge the research support of the Fogelman College of Business and Economics at The University of Memphis and the helpful comments of the reviewers and Arnold Wright (editor).
Introduction
Electronic commerce, electronic data interchange (EDI), and the Internet are dramatically changing business practices and record keeping. Doing business on the World Wide Web enables organizations to connect into the online world and improve all aspects of their business. In this high-technology environment business transactions are conducted entirely in electronic form. Technological advances have taken the form of low-cost, high-speed digital data transmission by utilizing hardware that produces information quickly and easily, and using software that reduces and, in many cases, eliminates much time, space, and other constraints to information. The progress in information technology, while reducing both transaction costs and asymmetric information problems, has increased economies of scale and scope in all business sectors (Albrecht and Sack 2000). The 1998 Vision Project of the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) states that technological advances are significant forces affecting the accounting profession (AICPA 1998a).
خلاصه
مقدمه
حسابداری در آن واحد و گزارش الکترونیکی مالی
تعریف حسابرسی پیوسته
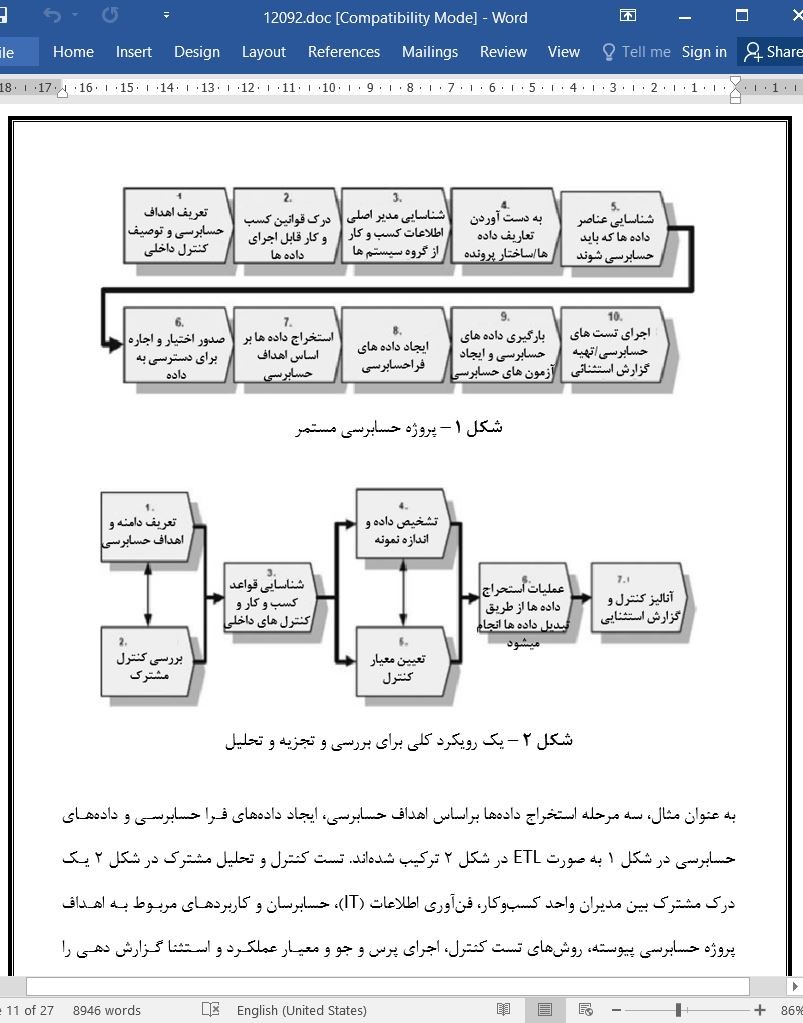
فرآیند حسابرسی پیوسته
حسابرسی پیوسته مدارک حسابرسی را در رابطه با پرسشهای زیر جمعآوری میکند:
روش حسابرسی پیوسته
ایجاد قابلیت حسابرسی پیوسته
برنامههای حسابرسی پیوسته
خلاصه و نتیجهگیری
تحقیقات آینده
منابع
Summary
Introduction
Real-Time Accounting and Electronic Financial Reporting
Continuous Auditing Definition
Continuous Auditing Process
Continuous Auditing Methodology
Building Continuous Auditing Capability
Continuous Auditing Applications
Summary and Conclusion
References
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه