سامانه انتقال تراپوستی انسولین بر اساس نیاز برای درمان دیابت نوع 1
چکیده
دیابت یک بیماری متابولیک است که به صورت فزایندهای افراد بیشتری را در سراسر جهان گرفتار میکند و باعث افزایش فشار بر نظامهای سلامت و جوامع میشود. برای پیشگیری از عوارض جدی و حتی مرگبار، پایش مداوم سطوح قند خون ضروری است. استفادۀ ساده و به موقع از انسولین برای تسهیل تنطیم قند خون و کاهش بروز افت قند خون، یکی از چالشهای عمدۀ مدیریت دیابت است. در این پژوهش یک سامانۀ انتقال انسولین را ساختیم که از نانوذرات سیلیکای مزوپور به عنوان مخزن انسولین، نانوذرات اکسید زینک به عنوان دروازهبان و کاوشگرهای فلورسنت مبتنی بر فنیلبورونیک اسید با نقش پاسخدهندگی به انسولین تشکیل شدهاست. این سامانه با پیونددهندۀ پاسخدهنده به گلوکز، دارای خاصیت رهایش کنترلشدۀ انسولین در غلظتهای بالای گلوکوز است که مدت زمان تنظیم قند خون را افزایش میدهد و خطرات افت قند خون را ندارد. به علاوه، سامانه با پچ ریزسوزنی مبتنی بر هیالورونیک اسید ترکیب شدهاست که برای انتقال تراپوستی، به خوبی در پوست نفوذ میکند. نانوذرات در سامانۀ ما با تزریق زیرجلدی یا پچ ریزسوزنی تراپوستی، به طرز ممتازی باعث تنظیم گلوکوز در شرایط درونتنی شدند. پیشبینی میکنیم که پچ ریزسوزنی هوشمند زیستسازگار و پاسخدهنده به گلوکوز (SGRM patch) ما، باعث تسهیل ساختن سامانههای مفید بالینی میشود.
1. مقدمه
دیابت شیرین یک اختلال متابولیک مزمن با ویژگی سطوح بالای قند خون (BGLs) است که از تولید ناکافی انسولین یا مقاومت به انسولین ناشی میشود و در حال حاضر میلیونها نقر را در جهان مبتلا کردهاست [1و2]. پیشبینی میشود که تعداد بیماران دیابتی از 425 میلیون در سال 2019 به 700 میلیون در سال 2045 خواهد رسید [3]. بیماران دیابتی در معرض خطر بیشتری از عوارض تهدیدکنندۀ حیات هستند که شامل اختلالات قلبی-عروقی، بیماریهای کلیوی و عفونتهای پا است و حتی میتواند منجر به قطع عضو شود [4-7]. با این حال، تزریق انسولین پس از وعدۀ غذایی با استفاده از سرنگ دردناک است و برای بیماران دیابت نوع 1 و دیابت نوع 2 پیشرفته راحت نیست و به همکاری ضعیف در درمان منجر میشود. به علاوه، پمپهای گرانقیمت انسولین باید به صورت دورهای تعویض شوند که ممکن است خطر عفونت را افزایش دهد [8].
4. نتیجهگیری
ما به طور موفق یک سامانۀ انتقال انسولین G-MSN@Insulin@ZnO-PBA-2 را برای درمان دیابت نوع 1 ساختیم. فنیلبورونیک اسید نوع ولف برای اولین بار به عنوان پیونددهندۀ واکنشدهنده به گلوکوز در سامانۀ انتقال انسولین استفاده شد که در شرایط درونتنی در مقایسه با سایر سیستمهای انتقال انسولین مبتنی بر PBA، هم باعث تنظیم طولانی BGLs و هم پیشگیری از هایپوگلایسمی شد [30، 31، 33-37]. فنیلبورونیک اسید منحصربهفرد PBA-2 در ZnO-PBA-2 در شرایط فیزیولوژیک، میتواند با دیولهای G-MSN، بورونیک استر پایدار بسازد؛ درحالیکه، در BGLs بالا، بورونیک استر به طور کامل شکسته میشود و بنابراین عامل پوشاننده از G-MSN جداشده و انسولین از حفرهها آزاد میشود. به علاوه، G-MSN@Insulin@ZnO-PBA-2 درون پچ ریزسوزنی حلشوندۀ مبتنی بر هیالورونیک اسید قرار گرفت تا درد تزریق کاهش یابد و استفاده آسان شود که میتواند به ساخت سامانۀ هوشمد و مطلوب انتقال انسولین منجر شود که مستعد استفادۀ بالینی است. مطالعههای آینده بر روی ایمنیزیستی طولانیمدت و توزیعزیستی G-MSN@Insulin@ZnO-PBA-2 تمرکز میکنند.
Abstract
Diabetes is a metabolic disease that is affecting an ever-increasing number of people worldwide, resulting in increased burdens on healthcare systems and societies. Constant monitoring of blood glucose levels is required to prevent serious or even deadly complications. One major challenge of diabetes management is the simple and timely administration of insulin to facilitate consistent blood glucose regulation and reduce the incidence of hypoglycemia. With this research, we construct an insulin delivery system, the delivery system is comprised of phenylboronic acid based fluorescent probes, which is used as glucose responsive linkers, mesoporous silica nanoparticles providing an insulin reservoir, and zinc oxide nanoparticles used as gate keepers. The system with glucose sensitive responsive linker exhibits controlled release of insulin under high glucose concentrations, providing prolonged blood glucose regulation and no risks of hypoglycemia. Furthermore, the system is combined with a hyaluronic-acid based microneedle patch, which exhibit efficient skin penetration for transdermal delivery. With our system, the nanoparticles provide outstanding in vivo glucose regulation when administrated by subcutaneous injection or via transdermal microneedle patch. We anticipate that our biocompatible smart glucose responsive microneedle patch (SGRM patch) will facilitate the development of clinically useful systems.
1. Introduction
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by high blood glucose levels (BGLs), and is caused by insufficient insulin supply or insulin resistance, and currently affects millions of people worldwide [1,2]. Importantly, the number of diabetic patients worldwide is expected to soar from 425 million in 2019 to 700 million by 2045 [3]. People with diabetes have a higher risk of developing life-threatening complications, including cardiovascular disorders, renal diseases, foot infectious, and can even lead to amputation [4–7]. However, postprandial injection of insulin using a syringe is painful and inconvenient for patients with type 1 diabetes and advanced type 2 diabetes, which leads to poor treatment compliance. In addition, costly insulin pumps need periodic replacement, which may increase the risk of infection [8].
4. Conclusions
We have successfully constructed an insulin delivery system GMSN@Insulin@ZnO-PBA-2 for type 1 diabetic treatments. Wulfftype phenylboronic acid was firstly used as the glucose responsive linker in an insulin delivery system, achieving both prolonged BGLs regulation and avoided of hypoglycemia in vivo compared with other PBAs based insulin delivery systems [30,31,33–37]. The unique Wulff-type phenylboronic acid PBA-2 on ZnO-PBA-2 could forms stable boronic ester with diols on G-MSN under physiological condition, while the boronic ester was completely broken under high BGLs, thus the capping agent was detached from G-MSN and insulin was released from the pores. Furthermore, GMSN@Insulin@ZnO-PBA-2 was incorporated into hyaluronic-acid based dissolving microneedle patch to reduce the pain of injection and achieve convenient administration, which could result in the development of desirable smart insulin delivery system with the potential for clinical application. Further studies would focus on the long-term biosafety and biodistribution of GMSN@Insulin@ZnO-PBA-2.
چکیده تصویری
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. مواد و روشها
2.1 مواد
2.2 آمادهسازی G-MSN
2.3 آمادهسازی انسولین FITC
2.4 آمادهسازی ZnO-PBA-1 و ZnO-PBA-2
2.5 آمادهسازی G-MSN@Insulin@ZnO-PBA-1 و G-MSN@Insulin@ZnO-PBA-2
2.6 اندازهگیری واکنش برونتنی به گلوکوز
2.7 حیوانات آزمایشگاهی
2.8 مطالعات درونتنی بر موشهای صحرایی
2.9 ساختن پچهای ریزسوزنی دارای نانوذرات
2.10 آزمایش استحکام مکانیکی
2.11 آزمایش کارایی نفوذ به پوست
2.12 مطالعات درونتنی بر موشها
3. یافتهها و بحث
3.1 آمادهسازی و تعیین ویژگیهای G-MSN@Insulin@ZnO-PBA-1 و G-MSN@Insulin@ZnO-PBA-2
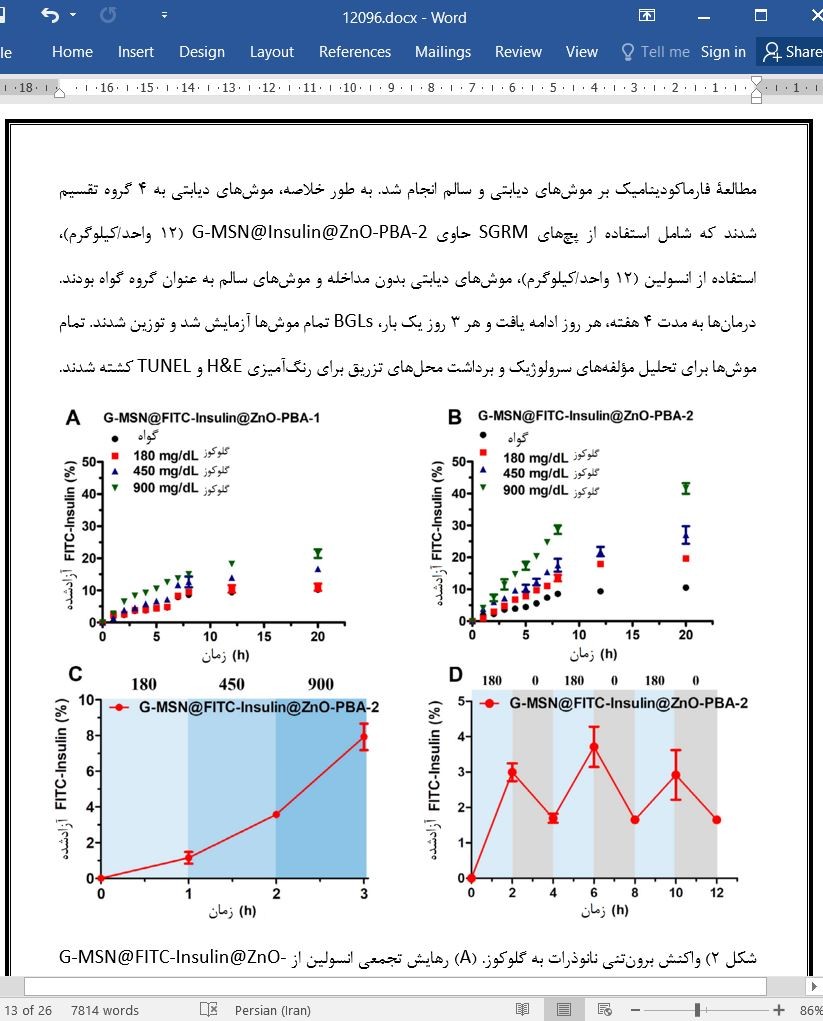
3.2 واکنش برونتنی نانوذرات ساختهشده به گلوکوز
3.3 مطالعات درونتنی G-MSN@Insulin@ZnO-PBA-2 بر موشهای صحرایی دچار دیابت نوع 1
3.4 ساخت و تعیین ویژگیهای پچهای ریزسوزنی
3.5 مطالعات درونتنی اثر پچهای SGRM بر موشهای دیابت نوع 1
4. نتیجهگیری
منابع
Abstract
Graphical abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of G-MSN
2.3. Preparation of FITC-Insulin
2.4. Preparation of ZnO-PBA-1 and ZnO-PBA-2
2.5. Preparation of the G-MSN@Insulin@ZnO-PBA-1 and G-MSN@Insulin@ZnO-PBA-2
2.6. In vitro glucose response measurements
2.7. Experimental animals
2.8. In vivo studies on rats
2.9. Fabrication of nanoparticle-loaded microneedle patches
2.10. Mechanical strength test
2.11. Skin penetration efficiency test
2.12. In vivo studies on mice
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Preparation and characterization of G-MSN@Insulin@ZnO-PBA-1 and G-MSN@Insulin@ZnO-PBA-2
3.2. In vitro glucose response of constructed nanoparticles
3.3. In vivo studies of G-MSN@Insulin@ZnO-PBA-2 on type 1 diabetic rats
3.4. Fabrication and characterization of microneedle patches
3.5. In vivo studies of SGRM patches on type 1 diabetic mice
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgement
References
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه