موفقیت هوش تجاری به کار برده شده در سیستم های اطلاعات مراقبت بهداشتی
چکیده
ما در این مقاله مدل موفقیت سیستم های اطلاعات دیلون و مَکلین بصورت تجربی بر روی یک سیستم هوش تجاری آزمایش میشود که برای سیستم های اطلاعات مراقبت بهداشتی در 12 بیمارستان عمومی در دانمارک مورد استفاده قرار گرفته است. هدف مطالعه حاضر این است که بررسی کند که کدام عوامل به موفقیت هوش تجاری کمک میکنند. بطور کلی 1351 کاربر نهایی به پرسشنامه ما پاسخ دادند و میزان پاسخدهی آن 32 درصد بود. هشت رابطه در این مدل مورد آزمایش قرار گرفت که مشخص شد چهار رابطه از آنها مهم است. نتایج ما بشرح روبرو است: کیفیت سیستم رابطه مثبت و مهمی با کاربرد و رضایت کاربر دارد. کیفیت اطلاعات رابطه مثبت و مهمی با رضایت کاربر دارد اما چنین رابطه ای را با «کاربرد» ندارد. همچنین رضایت کاربر رابطه مهمی با کاربرد ندارد و بالعکس. رضایت کاربر رابطه مثبت و مهمی با تأثیر فردی دارد اما کاربرد رابطه مهمی با تأثیر فردی ندارد.
1. مقدمه
در بسیاری از سازمان ها مهمترین اولویت مدیریت تکنولوژی اطلاعات این است که مقادیر تصاعدی داده های تولید شده داخلی و خارجی را مدیریت کند و این داده ها را در اختیار تحلیل گران و تصمیم گیرندگان در تمام سطوح سازمان قرار دهد. این پیشرفت حاصل تمایل مدیریت برای ایجاد یک سازمان داده-محور است. همانطور که مادسِن میگوید: داده-محوری به این معناست که اطلاعات باید محتوایی و قابل مصرف باشند تا اقداماتی ترغیب شوند که رفتار را به مرور زمان اصلاح میکنند. از لحاظ تاریخی، بخش مراقبت بهداشتی داده های مهمی را ایجاد کرده است که حاصل تقاضا برای ثبت «نگهداری، مطلوبیت، الزامات مقرراتی و مراقبت از بیمار» بوده است. بنابراین بهتر است از هوش تجاری (BI) به کار برده شده در سیستم های اطلاعات مراقبت بهداشتی (HIS) استفاده کنیم. پارنیت و بونبار پی بردند که سازمان های مراقبت بهداشتی با سیستم های اطلاعات (IS) در مقایسه با سازمان های مراقبت بهداشتی که سیستم های اطلاعات ندارند، حاشیه های کلی و حاشیه های عملیاتی بالاتری دارند.
Abstract
In this paper, DeLone and McLean’s IS Success Model is empirically tested on a Business Intelligence System applied to Healthcare Information Systems at 12 public hospitals in Denmark. The purpose of the study is to investigate which factors contribute to BI Success. A total of 1351 end-users replied to the questionnaire, and the response rate was 32%. Eight relationships in the model were tested, and four relationships were found to be significant. Our results are as follows: System Quality is positively and significantly associated with Use and User Satisfaction. Information Quality is positively and significantly associated with User Satisfaction but not Use, and User Satisfaction is not significantly associated with Use and vice versa. User Satisfaction is positively and significantly associated with Individual Impact, but Use is not significantly associated with Individual Impact.
1. Introduction
In many organisations, the IT manager's top priority is to handle the increasing amounts of data produced internally and externally and make the data available to analysts and decision makers at all levels of the organisation1 . This development results from the management's desire to create a data-driven organisation. According to Madsen: ‘Datadriven means that information must be consumable and contextual, to encourage action that will modify behaviour over time’2 .The healthcare sector has historically generated a significant amount of data, driven by the demand for record keeping, compliance, regulatory requirements and patient care3 . Therefore, it is relevant to use Business Intelligence (BI) applied to Healthcare Information Systems (HIS). Parente and Dunbar found that healthcare organisations with Information Systems (IS) have higher total margins and operating margins than those that do not have IS4 .
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. مدل موفقیت سیستم های اطلاعات
3. روش شناسی
3.1 زمینه مطالعه
3.2 طراحی پرسشنامه
3.3 تحلیل داده ها
3.4 برآورد مدل سنجش
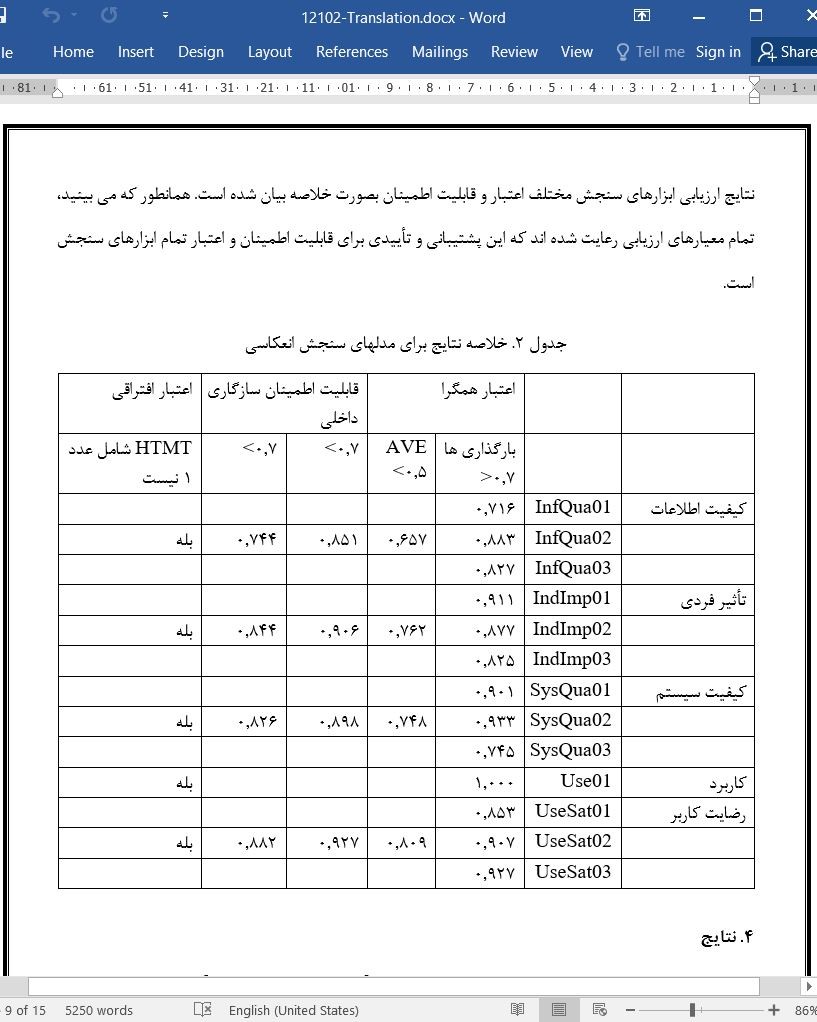
4. نتایج
5. بحث
6. نتیجه گیری
منابع
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. IS Success Model
3. Methodology
3.1. The context of study
3.2. The questionnaire design
3.3. Analysis of the data
3.4. Estimation of measurement model
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusion
References
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه