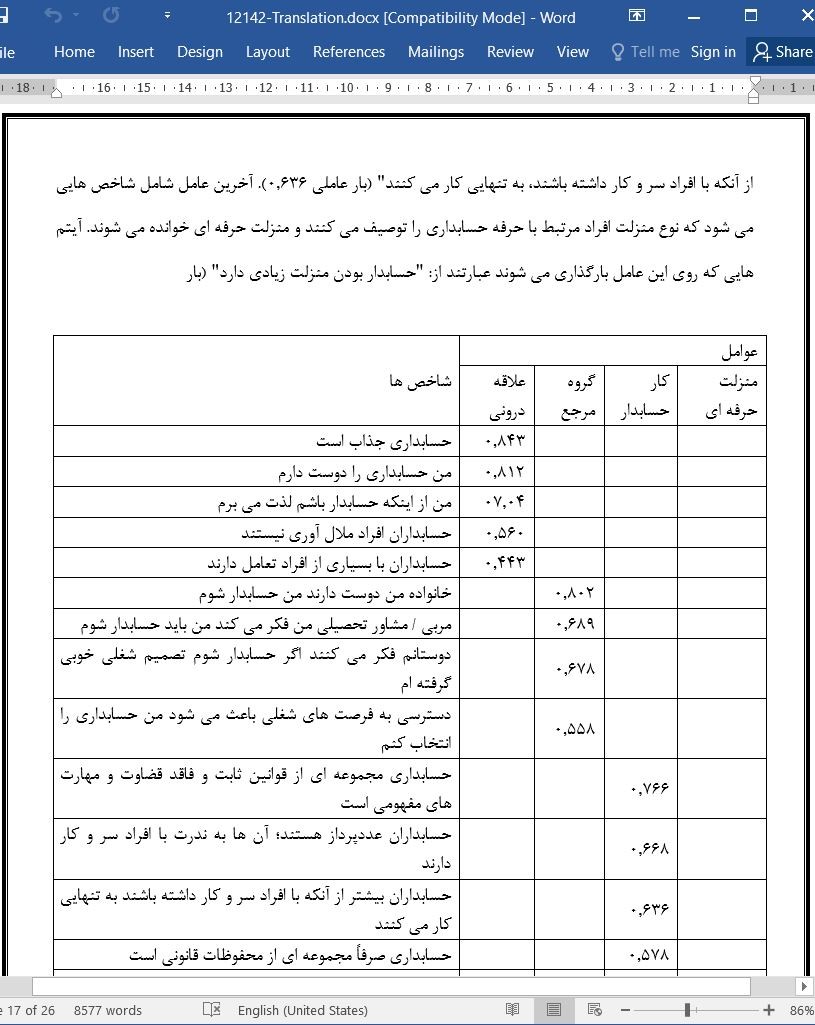
نگرش ها نسبت به حسابداری و قصد تحصیل در رشته حسابداری
چکیده
هدف - هدف مقاله حاضر بررسی نگرش دانشجویان کسب و کار نسبت به حرفه حسابداری و تحقیق درباره رابطه بین نگرش دانشجویان و قصد آن ها برای اخذ مدرکی در حسابداری است.
طرح / روش شناسی / رویکرد - از نظرسنجی خودگردان یا خودایفاء برای گردآوری داده ها از دانشجویان آموزشگاه کسب و کار غنا (UGBS) استفاده شد. مجموعاً از 457 پرسشنامه در تجزیه و تحلیل تجربی استفاده گردید. از تکنیک تجزیه و تحلیل رگرسیون منطقی باینری برای تجزیه و تحلیل داده ها بهره گرفته شد.
یافته ها - تجزیه و تحلیل رگرسیون منطقی نشان داد که علاقه درونی به رشته حسابداری، آشنایی قبلی با حسابداری در مقطع پیش دانشگاهی و تمایل برای اخذ مدرک حرفه ای حسابداری در آینده، شاخص های پیش بینی کننده خوبی برای قصد دانشجویان جهت تحصیل در رشته حسابداری محسوب می شوند. نتایج نیز نشان دادند که اعضای خانواده، مربیان دوره و سایر گروه های مرجع نقش حیاتی در تاثیرگذاری بر قصد دانشجویان برای اتخاذ یک حرفه در حسابداری ایفا می نمایند.
پیامدهای عملی - یافته های مطالعه حاضر پیامدهای مهمی برای نهاد حسابرسی حرفه ای و آموزگاران کسب و کار علاقمند به بررسی کمبود مهارت در حرفه حسابداری دارند.
اصالت / ارزش - مطالعه حاضر نه تنها نگرش دانشجویان نسبت به رشته حسابداری را مورد بررسی قرار داده بلکه به بررسی نحوه تاثیرگذاری چنین نگرش هایی بر قصد تحصیل در رشته حسابداری نیز می پردازد.
مقدمه
یک مساله موضوعی که توجه فراوان تحقیقات حسابداری را به خصوص در زمینه آموزش حسابداری معطوف خود نموده، کمبودها در عرضه حسابداران حرفه ای برای برآوردن تقاضای همواره رو به رشد است. مطالعات گذشته نشان داد که تقاضا برای حسابداران حرفه ای در بسیاری از نقاط جهان در طی سالیان گذشته از عرضه پیشی گرفته است (چن، ۲۰۱۲؛ نور و همکاران، ۲۰۱۳؛ ون زیل و دی ویلیرز، ۲۰۱۱). شگفت آور آنکه، در حالی که کشورها همچنان در تقلا برای مواجهه با کمبود حسابداران حرفه ای هستند، انتظار می رود که تقاضا برای حسابداران در سطح جهانی به دلیل رشد سریع فعالیت های کسب و کار در آینده افزایش یابد (کو، ۲۰۱۶). با توجه به پیامد مزبور، چالش برآوردن تقاضای حسابداران در سطح جهان می تواند در صورتی وخیم تر خواهد شد که که اقدام های لازم برای رفع کمبود در عرضه حسابداران اتخاذ نگردد. در حالی که دلایل مربوط به کمبود جهانی عرضه حسابداران همچنان یک پرسش باز است، مضمون مشترکی که از آثار تجربی پیشین منشا می گیرد، گرایش تاسفبار افت مداوم تعداد دانشجویانی است که حسابداری را به عنوان یک رشته تحصیلی دنبال کرده و عدم تمایل برخی از فارغ التحصیلان حسابداری برای اتخاذ حسابداری به عنوان یک حرفه است (جکلینگ و کالرو، ۲۰۰۶؛ کاپلتو، ۲۰۱۰).
نتیجه گیری
مقاله حاضر به بررسی نگرش دانشجویان نسبت به حرفه حسابداری و قصد دانشجویان برای اتخاذ یک شغل در حسابداری می پردازد. نتایج مطالعه حاضر آشکار ساخت دانشجویانی که آشنایی قبلی از پیش دانشگاهی با حسابداری دارند و کسانی که خواهان اخذ مدرک حرفه ای حسابداری در آینده هستند در قیاس با همتایان خود معمولاً برداشت مثبتی نسبت به حسابداری دارند. هم چنین نتایج نشان دادند که علاقه شخصی دانشجویان و تاثیر گروه مرجع دیگر، شاخص های پیش بینی کننده کلیدی قصد دانشجویان برای اتخاذ یک شغل در حسابداری محسوب می شوند. بنابراین، برخلاف آنچه در حوزه های دیگر رخ داد (انجی و همکاران، ۲۰۱۷)، در بافت غنا، اشخاص ثالث نقش حیاتی را در اثرگذاری بر قصد دانشجویان برای اتخاذ یک شغل در حسابداری ایفاء می نمایند. هم چنین، دانشجویانِ برخوردار از آشنایی قبلی با رشته حسابداری نسبت به همتایانِ فاقد چنین پیشینه ای دارای انگیزه بیشتری برای اخذ مدرک حسابداری هستند. به علاوه، دانشجویان خواهان اخذ مدرک حرفه ای حسابداری در آینده نسبت به همتایان خود که قصدی برای اخذ مدرک حرفه ای حسابداری ندارند، به احتمال زیاد در سطح دانشگاهی به تحصیل در رشته حسابداری می پردازند.
Abstract
Purpose – The purpose of this paper is to examine the attitude of business students towards the accounting profession and investigate the relationship between students’ attitude and their intention to pursue a degree in accounting.
Design/methodology/approach – A self-administered survey was used to collect data from students from the University of Ghana Business School (UGBS). A total of 457 questionnaires were used in the empirical analysis. A binary logistic regression analysis technique was employed to analyse the data.
Findings – The logistic regression analysis demonstrates that intrinsic interest in the accounting discipline, prior exposure to accounting at the senior high level and the desire to pursue professional accounting qualification in future are good predictors of students’ intention to major in accounting. The results also indicate family members, course instructors and other referent group play a crucial role in influencing students’ intention to pursue a career in accounting.
Practical implications – The findings of this study have important implications for the professional accountancy body and business educators interested in addressing the skill shortage in the accounting profession.
Originality/value – This study does not only examine students’ attitude towards the accounting discipline but also investigates how such attitudes influence intentions to major in accounting.
Introduction
One topical issue that has received considerable interest in accounting research, particularly in the field of accounting education is the shortages in the supply of professional accountants to meet the ever-growing demand. Prior studies have shown that the demand for professional accountants in many parts of the world, have over the years, exceeded the supply (Chen, 2012; Nor et al., 2013; Van Zyl and de Villiers, 2011). Interestingly, while countries are still struggling to deal with the shortages in the supply of professional accountants, it is expected that the demand for accountants globally will increase in the future due to the rapid growth in business activities (Coe, 2016). By implication, the challenge of meeting the demand of accountants globally could worsen if urgent steps are not taken to address the deficit in the supply of accountants. While the reasons for the global shortage in the supply of accountants remain an open question, a common theme emerging from prior empirical works attribute the unfortunate trend to the continuous decline in the number of university students who pursue accounting as a course major and the unwillingness of some accounting graduates to pursue accounting as a career ( Jackling and Calero, 2006; Cappelletto, 2010).
Conclusions
This paper examined the attitude of students towards the accounting profession and the intention of students to pursue a career in accounting. Results of this study reveal that students with prior exposure to accounting in the senior high school and those with the desire to pursue professional accounting qualification in future usually have a positive perception about accounting than their peers. The results further suggest that the personal interest of students and the influence of other referent group are key predictors of students’ intention to pursue a career in accounting. Thus, unlike what pertains in other jurisdictions (Ng et al., 2017), within the Ghanaian context, third parties play a crucial role in influencing students’ intention to pursue a career in accounting. Also, students with prior exposure to accounting course have greater motivation to pursue a degree in accounting than their peers with no such background. Further, students with the desire of pursuing professional accounting qualification in future are more likely to major in accounting at the university level than their counterparts with no intention of earning a professional accounting qualification.
چکیده
مقدمه
بررسی نظری
بررسی ادبیات و طرح فرضیات
عامل گروه مرجع
عامل علاقه درونی
کار حسابداران
عامل منزلت حرفه ای
روش شناسی
نمونه برداری، ابزار تحقیق و گردآوری داده ها
روند تجزیه و تحلیل داده ها
نتایج
خصوصیات پاسخ دهنده
آماره های توصیفی نگرش نسبت به حرفه حسابداری
تجزیه و تحلیل عاملی اکتشافی AAS
تجزیه و تحلیل رگرسیون منطقی
نتایج رگرسیون منطقی و بحث
نتیجه گیری
منابع
Abstract
Introduction
Theoretical review
Referent group factor
Intrinsic interest factor
Accountants’ work
Professional prestige factor
Methodology
Sampling, research instrument and data collection
Data analysis procedures
Results
Characteristics of respondent
Characteristics of respondent
Descriptive statistics on attitudes towards the accounting profession
Exploratory factor analysis of AAS
Logistic regression analysis
Logistic regression results and discussions
Conclusions
References
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه