پیش بینی میزان بارش برای منطقه کلارا در هند با بهره گیری از روش های هوش مصنوعی
چکیده
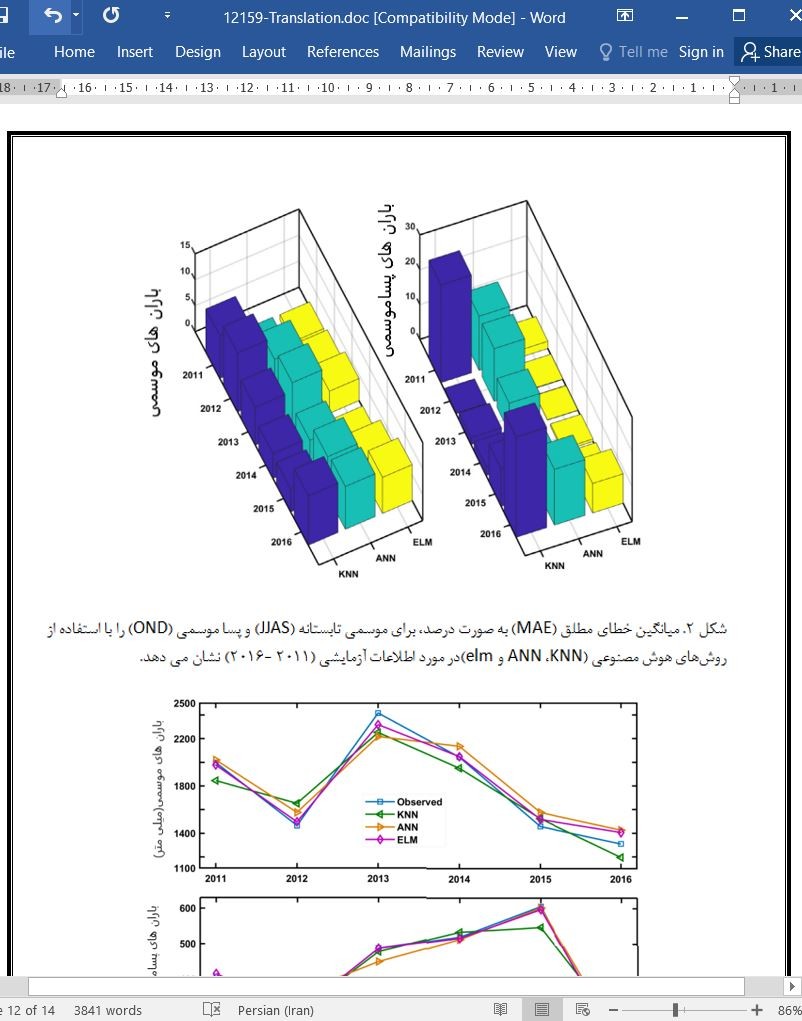
سه روش هوش مصنوعی، نزدیکترین همسایه K (KNN)، شبکه عصبی مصنوعی (ANN)، و دستگاه های یادگیری سریع (ELM)، برای پیش بینی فصلی میزان بارش باران موسمی در ماه های ژوئن تا سپتامبر و در نیز پساموسمی در ماه های اکتبر تا دسامبر از سال 2011 تا 2018 در منطقه کرالای هندوستان مورد استفاده قرار گرفته است؛ و عملکرد این روشها با مشاهداتی، ارزیابی شده است. تمامی روش های فوق عملکرد خوبی را از خود نشان داده اند. در مقایسه با دیگر روش ها، روش ELM عملکرد بهتری را نشان داده است و میانگین خطای مطلق کمتری داشته است. که برای دوره اول 057/3 و دوره دوم 149/3 بوده است. دقت پیش بینی نیز به شدت متاثر از تعداد گره های پنهان در لایه های پنهان است؛ و همچنین نتایج بهتری از ساختار ELM بدست آمده است. مطالعه حاضر نشان می دهد که روش های پیشنهادی، قابلیت نمایش دقیق میزان بارندگی در دوره های زمانی فوق را با حداقل میزان خطای میانگین دارند.
1. مقدمه
پیش بینی دقیق و صحیح بارش باران در ایالاتی مانند کرالا، که در آن اقتصاد کشور و معیشت مردم، به بارش باران بستگی دارد، از اهمیت بالایی برخوردار است. منطقه کلارا حدودا بارشی بالغ بر دو و نیم برابر بیشتر از میانگین کل هندوستان را دریافت می کند، با این وجود، ایالات نیاز به حل مساله کمبود آب در سال های آینده خواهد داشت، چراکه اکثر مقادیر آب باران در عرض 48 تا 72 ساعت به دریای عمان می ریزد (1). بارش های موسمی و پساموسمی دو فصل با بیشترین بارندگی در منطقه شناخته می شوند. باران های موسمی تابستانی از ماه ژوئن تا سپتامبر (JJAD) است و نخستین فصل بارانی در این منطقه محسوب می گردد. به دلیل برگشت باد، این منطقه شاهد بارش های پساموسمی که از اکتبر تا دسامبر (OND) به طول می انجامد، نیز می باشد.
4. نتیجه گیری
عملکرد سه روش هوش مصنوعی نزدیکترین همسایه K (KNN)، شبکه عصبی مصنوعی (ANN) و دستگاه های یادگیری سریع (ELM)، برای پیش بینی میزان بارش در فصول موسمی و پساموسمی تابستان در منطقه کرالای هندوستان مورد ارزیابی قرار گرفت. عملکرد این سه روش با آزمون های آماری متعدد سنجیده شد. در نهایت استنباط شد، که دستگاه های یادگیری سریع ELM، دارای عملکرد بهتری نسبت به شبکه عصبی مصنوعی (ANN)و نزدیکترین همسایهK KMM است. گره های پنهان تاثیر زیادی بر صحت پیش بینی ها دارند. ساختار دستگاه های یادگیری سریع (ELM) نتایج پیش بینی شده بهتری را برای دو فصل موسمی و پساموسمی نسبت به دو روش شبکه عصبی مصنوعی (ANN)و نزدیکترین همسایه K (KNN)، ارائه می دهد. در آینده، الگوریتم های یادگیری بیشتری را برای پیش بینی فصول مهم موسمی و پساموسمی جنوب هند به کار خواهیم برد. اثر تغییرات و ناپایداری های اقلیمی و وقایع آب و هوایی شدید نیز با در نظر گرفتن عوامل محیطی صورت خواهد پذیرفت
Abstract
Three artificial intelligence approaches - K-nearest neighbor (KNN), artificial neural network (ANN), and extreme learning machine (ELM) - are used for the seasonal forecasting of summer monsoon (June-September) and post-monsoon (October-December) rainfall from 2011 to 2016 for the Kerala state of India and performance of these techniques are evaluated against observations. All the aforesaid techniques have performed reasonably well and in comparison, ELM technique has shown better performance with minimal mean absolute percentage error scores for summer monsoon (3.075) and post-monsoon (3.149) respectively than KNN and ANN techniques. The prediction accuracy is highly influenced by the number of hidden nodes in the hidden layer and more accurate results are provided by the ELM architecture (8-15-1). This study reveals that the proposed artificial intelligence approaches have the potential of predicting both summer monsoon and post-monsoon of the Kerala state of India with minimal prediction error scores.
1. Introduction
Accurate prediction of rainfall is highly desirable for states like Kerala where economy of the state and livelihood of people are highly sensitive to rainfall. Kerala receives approximately 2.5 times higher annual mean rainfall than the average of all India rainfall, nevertheless the state needs to resolve water scarcity issues in the upcoming years as the majority of the rainwater flows into the Arabian Sea within 48 to 72 hours of rainfall [1]. Summer monsoon and post-monsoon are the two rainfall seasons occur in the state. Summer monsoon occurs from June to September (JJAS) and is the primary rainy season of the state. Owing to wind reversal, the state has also received rainfall during the post-monsoon period which occurs from October to December (OND) [2].
4. Conclusion
Performances of three artificial intelligence techniques such as K-nearest neighbor (KNN), artificial neural network (ANN), and extreme learning machine (ELM) were evaluated for the prediction of summer monsoon (JJAS) and post-monsoon (OND) rainfall for the Kerala state of India. The performance of the aforementioned approaches has been gauzed by different statistical tests. ELM approach is found to be more accurate than KNN and ANN approaches for the prediction task. There is substantial impact of hidden nodes on the prediction accuracy. ELM structure (8-15-1) provides more accurate results for both JJAS and OND seasons than KNN and ANN techniques in the currently used rainfall dataset. In future, we will further apply different machine learning algorithms for prediction of the chaotic monsoon of southern India. The impacts of climate variability and extreme weather events will also be studied by taking different environmental parameters into consideration.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. روش انجام پژوهش
2.1. مجموعه اطلاعات مورد استفاده
2.1.1. یکسان سازی اطلاعات
2.1.2. آموزش و آزمایش
2.2. روش های هوش مصنوعی استفاده شده
2.2.1. نزدیکترین همسایه K (KNN)
2.2.2. شبکه عصبی مصنوعی. (ANN)
2.2.3. دستگاه یادگیری سریع
2.3. محاسبه عملکرد
3. نتایج و بحث
3.1. اطلاعات توصیفی
3.2 تاثیر گره های پنهان بر دقت و صحت
3.3. پیش بینی عملکرد مدل های هوش مصنوعی
4. نتیجه گیری
منابع
ABSTRACT
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Dataset used
2.1.1. Data normalization
2.1.2. Training and testing
2.2. Artificial intelligence approaches used
2.2.1. K-nearest neighbor (KNN)
2.2.2. Artificial neural network (ANN)
2.2.3. Extreme learning machine (ELM)
2.3. Computation of performance
3. Result and discussion
3.1. Descriptive statistics
3.2. Impact of hidden nodes on accuracy
3.3. Prediction performance of artificial intelligence models
4. Conclusion
References
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه