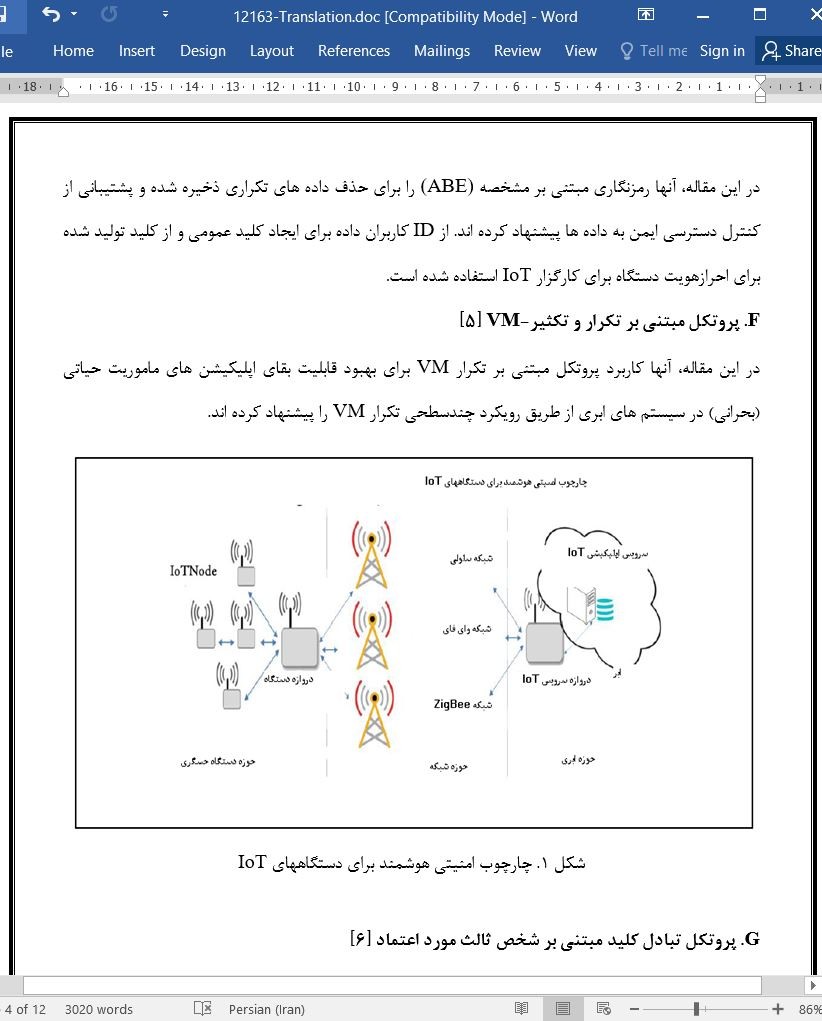
چارچوب امنیتی هوشمند برای دستگاههای IoT
چکیده
اینترنت اشیاء (IoT) با پیوند بین دستگاههای (دیوایس) مختلف پلتفرم، سرویس ها را فراهم می کند. آنها در زمینه ارائه سرویس های هوشمند (خدمات) محدودیت دارند. دستگاههای IoT ناهمگن بوده و شامل حسگرهای بی سیم برای دستگاههایی با محدودیت کمتر منابع می باشند. این دستگاهها مستعد حملات سخت افزاری/ نرم افزاری و شبکه هستند. اگر به درستی ایمن نشوند، آنگاه برخی مسائل امنیتی نظیر حریم خصوصی و محرمانگی پدید می آید. برای حل مسئله فوق، در این مقاله، یک چارچوب امنیتی هوشمند برای دستگاههای IoT پیشنهاد شده است. روش پیشنهادی از 2 بخش ساخته شده است (1) رمزنگاری نامتقارن سبک وزن برای ایمن سازی دستگاههای سرتاسر که از دروازه سرویس IoT و گره های حسگر کم توان محافظت می کند و (2) رمزنگاری مبتنی بر شبکه را برای ایمن سازی دستگاهها/ دروازه Broker و سرویس های ابری پیاده می نماید. معماری پیشنهادی رمزنگاری کلید نامتقارن را برای به اشتراک گذاشتن کلید جلسه بین گره ها پیاده نموده، و سپس از این کلید جلسه برای انتقال پیام استفاده می کند. این کار از سیستم در برابر حملات منع سرویس توزیع شده، استراق سمع، و حملات الگوریتم کوانتومی محافظت می نماید. پروتکل پیشنهادی از ID دستگاه منحصر به فرد حسگرها برای تولید جفت کلید و احراز هویت متقابل بین دستگاهها و سرویس ها استفاده می کند. بالاخره، مکانیسم احراز هویت متقابل در دروازه پیاده شده است.
1. مقدمه
در منبع [3] آنها یک چارچوب IoT ایمن برای تضمین امنیت سرتاسر از یک اپلیکشن IoT به دستگاههای IoT پیشنهاد کردند. ترکیب رایانش ابری و IoT، سرویس های حسگری فراگیر (همه جا حاضر) و پردازش قدرتمند جریانات داده حسگری را توانمند می سازد [13]. IoT معمولاً دارای یک معماری سه لایه متشکل از ادراک (حوزه دستگاه حسگری)، شبکه (حوزه شبکه بندی) و لایه کاربرد (حوزه ابر) می باشد. هر لایه IoT مستعد تهدیدات و حملات فعال یا غیر فعال است که می توانند از منابع خارجی یا شبکه داخلی سرچشمه بگیرند. اینترنت اشیاء (IoT) از یک ساختار متمرکز به سمت شبکه ای پیچیده از دستگاههای هوشمند غیر متمرکز حرکت می کند. در منابع [12]، [14]، دستگاهها و سرویس های IoT مستعد حملات منع سرویس (DoS) هستند. تبانی استراق سمع کننده، تهدیدی بزرگ و مهم برای امنیت ارتباطات بی سیم به شمار می رود. در سرتاسر دوره عمر دستگاه، از طراحی اولیه گرفته تا محیط عملیاتی، امنیت بایستی خطاب قرار داده شود. چالش های سختی که راه حل های اینترنت اشیاء با آن مواجه می شوند، عبارتنداز: نحوه دستیابی به یک بیت اضافی از عمر باتری برای راه حل های نوآورانه IoT و محدودیت های توان در ارتباطات. اولاً، چارچوب امنیت هوشمند برای امنیت سرتاسر را پیشنهاد می کنیم [16]. ثانیاً، مقاله یک نظر کلی (کلیاتی) راجع به روش رمزنگاری مرتبط ارائه می دهد.
Abstract
Internet of Thing (IoT) provide services by linking the different platform devices. They have the limitation in providing intelligent service. The IoT devices are heterogeneous which includes wireless sensors to less resource constrained devices. These devices are prone to hardware/software and network attacks. If not properly secured, it may lead to security issues like privacy and confidentiality. To resolve the above problem, an Intelligent Security Framework for IoT Devices is proposed in this paper. The proposed method is made up of (1) the light weight Asymmetric cryptography for securing the End-To-End devices which protects the IoT service gateway and the low power sensor nodes and (2) implements Lattice-based cryptography for securing the Broker devices/Gateway and the cloud services. The proposed architecture implements Asymmetric Key Encryption to share session key between the nodes and then uses this session key for message transfer This protects the system from Distributed Denial of Service Attacks, eavesdropping and Quantum algorithm attacks. The proposed protocol uses the unique Device ID of the sensors to generate key pair to establish mutual authentication between Devices and Services. Finally, the Mutual authentication mechanism is implemented in the gateway.
I. INTRODUCTION
In [3] they proposed a secure IoT framework to ensure an End-To-End security from an IoT application to IoT devices. The combination of cloud computing and IoT enables ubiquitous sensing services and powerful processing of sensing data streams [13]. The IoT typically has a three-layer architecture consisting of Perception (sensing Device Domain), Network (networking Domain), and Application layers (Cloud Domain). Each IoT layer is susceptible to either active or passive threats and attacks, that can originate from external sources or internal network. The Internet of Things (IoT) is moving from a centralized structure to a complex network of decentralized smart devices. In [12], [14] IoT devices and services are susceptible to Denial of Service attacks (DoS). Eavesdropper collusion is a significant threat to wireless communication security. Security must be addressed throughout the device lifecycle, from the initial design to the operational environment. the tough challenges of the Internet of Things solutions face are how to get extra bit of battery life for the innovative IoT solutions and the power constraints in communication. First, we propose the Intelligent Security Framework for End -To- End security [16]. Second, the paper gives an overview of the cryptography method associated with.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
A. رمزنگاری کلید متقارن و نامتقارن
2. مرور کارهای پیشین
B. پروتکل BRP IoT [1]
C. پروتکل مسیریابی و ویژگیهای امنیتی اش
D. پروتکل مبتنی بر امنیت سرتاسر [3]
E. مدیریت داده ها و حذف داده های تکراری در رایانش ابری [4]
F. پروتکل مبتنی بر تکرار و تکثیر-VM [5]
G. پروتکل تبادل کلید مبتنی بر شخص ثالث مورد اعتماد [6]
H. پروتکل تبادل کلید ماشین به ماشین (M2M) [7]
I. معرفی خودآموز [8]
J. پروتکل تبادل کلید مبتنی بر شخص ثالث قابل اعتماد [10]
K. پروتکل تبادل کلید مبتنی بر شخص ثالث قابل اعتماد [11]
L. حملات برروی سیستمهای IoT [15]
M. امنیت، حریم خصوصی و اعتماد [16]
3. چارچوب امنیتی هوشمند
A. رمزنگاری کلید متقارن
B. رمزنگاری مبتنی بر شبکه
C. چارچوب امنیتی هوشمند. الگوریتم پیشنهادی
گام 1: پیش نیازها
گام 2: تولید جفت کلید گره های IoT
گام 3: تولید کلید جلسه رمزی (سری) دستگاه
گام 4: تولید کلید جلسه سرویس رمزی
گام 5: انتقال داده ها از گره های IoT و دروازه دستگاه پس از اکتساب کلید جلسه رمزی (سری) دستگاه
گام 6: انتقال داده ها از دروازه دستگاه و دروازه سرویس IoT پس از کلید جلسه سرویس رمزی
گام 7: تراکنش ایمن سرتاسر
4. نتیجه گیری
منابع
Abstract
I. INTRODUCTION
A. Symmetric and Asymmetric Key Encryption
II. REVIEW OF PREVIOUS WORK
B. The IoT Broker Registration Protocol [1]
C. Routing Protocol and its security features [2]
D. End -To- End security based Protocol [3]
E. Data management and deduplication in cloud computing[4]
F. VM-replication-based Protocol [5]
G. Trusted-third-party-based key exchange protocol [6]
H. Machine-to-Machine (M2M) key exchange protocol [7]
I. A Tutorial Introduction [8]
J. Trusted-third-party-based key exchange protocol [10]
K. Trusted-third-party-based key exchange protocol [11]
L. Attacks on IoT Systems [15]
M. Security, privacy and trust [16]
III. INTELLIGENT SECURITY FRAMEWORK
A. ASymmetric Key Cryptography
B. Lattice-based cryptography
C. Intelligent Security Framework a Proposed Algorithm
Step 1: Pre-requisites
Step 2: IoT nodes Key pair generation
Step 3: Secret Device Session Key generation
Step 4: Secret Service Session Key generation
Step 5: Data transfer from IoT nodes and Device gateway after acquiring Secret Device Session Key.
Step 6: Data transfer from Device gateway and IoT Service gateway after Secret Service Session Key.
Step 7: End-To-End secure transaction.
IV. CONCLUSION
References
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه