مطالعه موردی مدل صف بندی بانک
چکیده
این مقاله به بررسی نظریه صف و تجزیه و تحلیل سیستم صفبندی با استفاده از منحنیهای احتمال میپردازد. با شروع با مبنای توزیعها و مفاهیم مهم نظریه صف، از منحنیهای احتمال توزیه گاما برای تجزیه و تحلیل سیستم بانکداری استفاده میشود.
3. نتیجهگیری
این مقاله به مطالعه نظریه صف میپردازد و با استفاده از منحنیهای احتمال، سیستم صف را تجزیه و تحلیل میکند. از کار نظرسنجی شده در بالا کشف کردیم که نرخهای ورود و خدمت در بانک، در هفتههای مختلف متفاوت هستند. نتیجهگیریها از کاربرد توزیع احتمال گاما به دست آمدند. نرخ ورود در هفته 1 بالاتر است. با این حال، این نرخ ورود بالاتر توسط سودآوری بالاتر خدمت تعدیل میشود. بنابراین، احتمال تکمیل خدمت در 5 دقیقه در هفته 1 برابر با 060361/0 است. فاکتور کارایی ثابت نیست. سودآوری خدمت کاهش مییابد، و در نتیجه، احتمال در هفته دوم به 054344/0 تقلیل مییابد. در هفته سوم، نرخ ورود کاهش مییابد. نتیجه، با حفظ نرخ خدت یکسان با نرخ خدمت در هفته دوم، این احتمال به 074055/ افزایش مییابد. نرخ خدمت در هفته آخر ماه کمتر است همچنان که نرخهای ورود به طور قابل توجهی کاهش مییابند. بنابراین، احتمال تکمیل خدمت در زمان کمتر در مقایسه با هفتههای باقیمانده افزایش مییابد، یعنی 087442/0.
Abstract
This paper deals with the Queueing theory and the analysis of queueing system by using probability curves. Starting with the basis of the distributions and important concepts of queueing theory, probability curves of Gamma distribution are used to analyse the banking service.
II. CONCLUSION
This paper studies the Queueing theory and by the use of probability curves the analysis of the queueing system. From the work surveyed above we have found arrival and service rates at the bank are different in different weeks. The conclusions are developed from the application of Gamma probability distribution. The arrival rate is higher in week 1. However, the higher arrival rate is offset by higher service productivity. Therefore, the probability of completing the service in 5 minutes in week 1 is 0.060361. The efficiency factor is not constant. The service productivity diminishes and as a result the probability in the second week drops to 0.054344. In the third week the rate of arrival decreases. Consequently, maintaining the same service rate as in the second week, the probability goes up to 0.074055. The service rate is less in the last week of the month as the arrival rates decrease considerably, the probability of completing the service with in less time peaks as compared to the remaining weeks.i.e0.087442.
چکیده
1. پیشگفتار
مفاهیم مهم
متغیرهای تصادفی گسسته [4]
متغیر تصادفی پیوسته
توزیع احتمال یک متغیر تصادفی
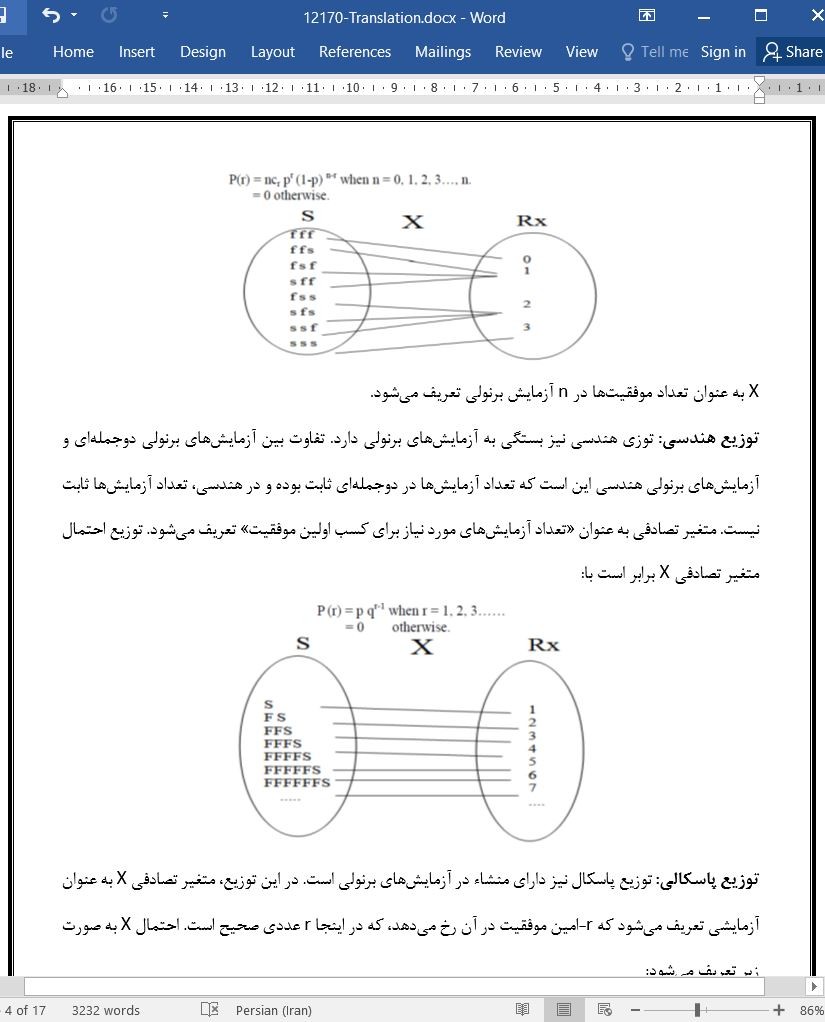
مشخصات برخی توزیعهای گسسته
2. ردهبندی سیستمهای صفبندی
3. نتیجهگیری
منابع
Abstract:
I. INTRODUCTION
Important concepts
Discrete Random variables [4]
Continuous random variable
Probability Distribution of a Random variable
Characteristics of some discrete distributions:
II. CLASSIFICATION OF QUEUING SYSTEMS
III. CONCLUSION
REFERENCES
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه