یک مدل برای یکپارچگی یادگیری الکترونیکی
چکیده
تاکنون نظریه جامعی برای اطلاع رسانی در مورد چگونگی درک و بهینه سازی فاکتورهای مختلف محیط های یادگیری مثل طراحی، کاربرد و ارائه مطرح نشده است. یک تحقیق اصلی که برای معرفی یادگیری الکترونیکی در ارتش امریکا انجام شده است امکان توسعه مدل نظریه اولیه را فراهم آورده است. این مدل، فاکتورهای کلیدی از جمله اولویت های سازمانی، نقش مربی، نیازهای یادگیرنده و محیط یادگیری را به عنوان فرهنگ یادگیری یکپارچه شناسایی می کند. به علاوه، این تحقیق بیان می کند که با پذیرش اینکه محیط یادگیری الکترونیکی بدون ارزش نیست، امکان درک اولویت ها و مباحث رقابتی تاثیر گذار برکارایی و مزایای یادگیری الکترونیکی وجود دارد.
مقدمه
درک کارایی یادگیری الکترونیکی به دلیل وجود اولویت های رقابتی و مطالب متنوع در موقعیت های آموزشی و یادگیری مسئله ساز است. سازمان هایی که آموزش را به عنوان هدف اصلی خود قرار نداده اند اما آموزش را یکی از مهارت های نیروی کاری در نظر می گیرند در تعیین متغیر های نشان دهنده کارایی آموزش به دلیل تعامل فاکتورهای فناوری و یادگیری با مشکلاتی مواجه هستند. مروری بر ادبیات مرتبط با کارایی یادگیری الکترونیکی در سازمان ها (دو روئین – فریتکز & سالاس 2005) نیز شکاف های قابل توجهی را نشان داده اند که از جمله آنها می توان وجود تحقیقات محدود، تاخیر زمانی بین تحقیق و عمل و عدم انسجام در روشهای تحقیقی را نام برد.
نتیجه گیری ها
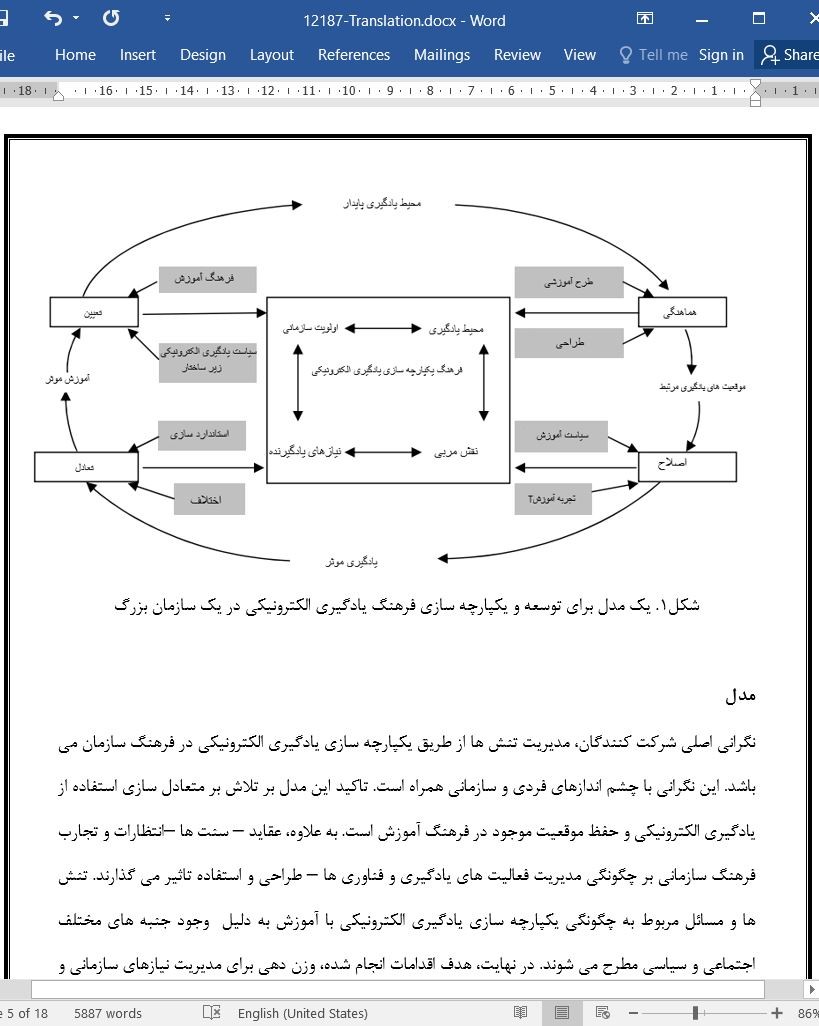
این تحقیقی مدلی را ارائه می کند که برگرفته از تجارب شرکت کنندگان در یک دوره یادگیری الکترونیکی در یک سازمان بزرگ است. این مدل بیان کرد که تصمیمات تاثیر گذار بر یادگیری الکترونیکی در یک سازمان منعکس کننده ویژگی های تلویحی و شفاف فرهنگ سازمانی می باشند. فرهنگ یکپارچه سازی یادگیری الکترونیکی با متعادل سازی انتظارات از فرهنگ سازمانی و تجربه های یادگیری الکترونیکی مطرح شده است. بنابراین، درک تعاملات بین اولویت های سازمانی، نیازهای یادگیرندگان، قوانین مربی و محیط یادگیری برای اطلاع رسانی مباحث و مهفوم سازی یادگیری الکترونیکی ضروری می باشد. با در نظر گرفتن این روش که محیط یادگیری الکترونیکی بدون ارزش نیست، امکان درک اولویت ها و مباحث رقابتی تاثیر گذار برکارایی و مزایای یادگیری الکترونیکی وجود دارد. بنابراین، در این تحقیق بعضی از شکاف های تعریف شده در ادبیات کارایی یادگیری الکترونیکی مطرح شده اند که توسط دروئین و همکارانش در سال2005 نیز بیان شدند و از جمله آنها می توان این نکته را اشاره کرد که " می دانیم که هیچ نظریه ای وجود ندارد که تاثیرات اصلی در طراحی ، ارائه و کاربرد سیستم های یادگیری الکترونیکی را بیان کند" (صفحه 934). " و مطالب زیادی باید در مورد طراحی محیط یادگیری الکترونیکی و چگونگی بهینه سازی اجرای آن و دلایل استفاده از آن آموخت (صفحه 937). تحقیقات آینده به بررسی این مدل در ارتباط با ادبیات گسترده تر و تجارب یایر سازمان ها برای توسعه و بازیابی مفهوم فرهنگ یکپارچه یادگیری خواهند پرداخت.
Abstract
As yet there is no comprehensive theory to inform how the various elements of elearning environments, such as design, implementation and delivery can be understood and optimised. A major study of the introduction of e-learning into the Australian Army has allowed a preliminary grounded theory model to be developed. This model identifies key factors, including organisational priorities, instructors’ roles, learners’ needs and the learning environment as contributing to an integrated e-learning culture. Furthermore, the study highlights that by accepting that e-learning environments are not value-free, it is possible to understand the competing priorities and discourses that influence how e-learning effectiveness is constructed and defined.
Introduction
Understanding e-learning effectiveness is problematic and contested due to the wide range of competing priorities and discourses across a range of education and training situations. Organisations which do not have training as their main purpose but rely on training to maintain a skilled and competent workforce have added difficulties in determining the variables that reflect training effectiveness due to the interactions of organisational, technological and learning factors. A recent literature review of e-learning effectiveness in workplace organisations (DeRouin, Fritzche, & Salas, 2005) also identified significant gaps, including the limited research available, the time lag between research and practice and inconsistencies in research approaches.
Conclusions
This study has provided a model grounded in the experiences of e-learning participants in a large workplace organisation. It was found that decisions influencing e-learning in an organisation reflected implicit and explicit features of the organisational culture. An integrated e-learning culture developed by balancing expectations from the organisational culture with experiences of e-learning. Therefore, it is necessary to understand the interactions between organisational priorities, learners’ needs, instructors’ roles and the learning environment to inform the discussion and conceptualisation of effective e-learning. By taking the approach that the e-learning environment is not value free it is possible to understand the competing priorities and discourses that influence how e-learning effectiveness is constructed and defined. Therefore, this study informs some of the gaps identified in the e-learning effectiveness literature which were summarised by Derouin et al (2005), including: “…we are aware of no theory that has been the major influence in the design, delivery, and implementation of e-learning systems” (p. 934); “And much remains to be learnt about how to best design the e-learning environment, how to optimise its delivery, and what works when and why” (p. 937). Further research will review this model in relation to the broader literature and experiences in other organisations to further extend and refine the concept of developing an integrated e-learning culture.
چکیده
مقدمه
روش تحقیق
مدل
اولویت های سازمانی
محیط یادگیری
نقش مربی
نیازهای یادگیرندگان
نتیجه گیری ها
منابع
Abstract
Introduction
Methodology
The Model
Organisational Priorities
Learning Environment
Instructors’ Role
Learners’ Needs
Conclusions
References
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه