طرح مدیریت توزیع اعتماد برای انتقال اطلاعات در ارتباطات اضطراری ماهواره ای شبكه DTN
چکیده
زمانی که ساير سیستم های ارتباطی خراب شده یا داراي ترافيك شديد باشند، ارتباطات ماهواره ای می توانند استفاده شوند. ماهواره های ديده¬باني زمين و شبکه های مقاوم در برابر تاخیر / خرابي، فناوری هایی هستند که می توانند براي ارتباطات اضطراری به هم پيوستهاي به منظور عملیاتهاي جبران فاجعه فراهم آورند. شبكههاي DTN از مکانیزم ذخيره- حمل - انتقال براي ارسال پیام ها از طریق گره های واسطه به گره مقصد استفاده می کنند. قابلیت اطمینان پیام های رله از طریق گره های چند هاب مشکل بزرگی در شبكههاي DTN به علت عدم اتصال پايدار است. این ویژگی های شبکه باعث می شود تا شبكههاي DTN به سختي به همکاری گره های مجاور برای تحویل موفقیت آمیز بسته ها اعتماد نمايند. با این حال، وجود گره های داراي عملكرد بدخواهانه و خودخواهانه تأثیر زیادی بر عملکرد شبکه دارد. در این مقاله، ما یک طرح مدیریت اعتماد غیرمتمرکز (DTMS ) را براي فیلتر کردن گره های مخرب در شبكههاي DTN طراحي نموده ايم. در ابتدا، تعداد مدارک انتقال يافته با میزان مصرف انرژی گره ها برای قاعدهمند ساختن اعتماد مستقیم ترکیب شده است. سپس، يك اعتماد توصيه شده از روي اعتماد غیر مستقیم، اعتبار توصیه شده و آشنایی توصیه شده محاسبه شده است. اعتبار و آشنایی توصیه شده، اعتماد توصیه های کلی را توسط فيلتر توصيههاي نادرست بهبود می بخشند. تجزیه و تحلیل تطبیقی طرح DTMS بر خلاف طرح نظارت تعاونی ( CWS)، مدل اعتماد مبتنی بر توصیه (RBTM) و پروتکل پخش و انتظار Spray& انجام شده است. نتایج نشان می دهد که طرح DTMS می تواند به طور موثر به رفتارهای مخرب در شبكه هاي DTN، از جمله حملات نسبت به اعتماد، بپردازد.
شبکه های مقاوم در برابر تأخير/ تداخل (DTNs) معماریهاي شبکه ای هستند که برای مقابله با اتصال متناوب و تاخیر طولانی در شبکه های بی سیم توسعه یافته اند. بر خلاف شبكه سنتی كه در آن بسته ها در امتداد لینک های ثابت بارگذاری می شوند، شبكه هاي DTN از رویکرد ذخیره و انتقال برای غلبه بر فقدان مسیرهای انتها به انتها استفاده ميكنند [1]، [2]. شبکه های DTN داراي گره هایی با منابع محدود مانند فضای بافر و قدرت هستند. این محدودیت ها در منابع، علاوه بر پراكندگي و تحرک این گره ها اغلب باعث اتصالات متناوب می شود. این کاربرد شبکه DTN طیف گسترده ای از حوزه ها از جمله شبکه زیر آب (UWNs )، شبکه های سوئیچ بسته (PSNS )، شبکه های ادهاک وسائل نقلیه ، کاربردهای نظامی موقت و بازیابی از حادثه و عملیات های نجات را پوشش می دهد [3]، [4].
5. نتیجه گيري
در شبكه هاي DTN، مدل اعتماد در کاهش رفتارهای مسیریابی از گره های آسیب دیده مهم است. شایع ترین سوء رفتار مسیریابی در DTN، رهاسازي پیام است که عملکرد شبکه را کاهش می دهد. بنابراین، برای مقابله با این سوء رفتار مسیریابی، یک مکانیزم تشخیص مناسب و کارآمد مورد نیاز است.در این مقاله، یک طرح مدیریت اعتماد غیرمتمرکز برای شبكه هاي DTN اطلاع رساني حادثه طراحی و تأیید شده است. طرح پیشنهادی، رفتار ارسال گره ها و میزان مصرف انرژی آنها را برای محاسبه اعتماد مستقیم ترکیب می کند. اطلاعات ثانويه از گره های محل حادثه نیز در مدل اعتماد به عنوان اعتماد توصيه شده گنجانده ميشود. اعتماد توصيه شده شامل اعتماد غیرمستقیم، اعتبار و آشنایی توصيه شده است که يك رويداد مبتني بر اعتماد است. نتایج شبیه سازی گسترده نشان می دهد که طرح DTMS به طور موثری سوء رفتار مسیریابی مانند حملات رهاسازي بسته و حملات تباني را کاهش می دهد. در كار تحقيقاتي آینده ، ما از راه حلهايي مانند با استفاده از مدخل شبكه DTN برای کاهش مصرف انرژی در طول محاسبات اعتماد مستقیم و توصیه شده استفاده مينماييم.
Abstract
Satellite communications can be used when other communication systems are either destroyed or overloaded. Observation satellites and delay/disruption tolerant networks (DTNs) are technologies that can be interconnected to provide emergency communication for disaster recovery operations. DTNs use a store-carry-forward mechanism to forward messages through intermediary nodes to the destination node. The reliability of relaying messages through multi-hop nodes poses a significant problem in DTNs due to lack of consistent connectivity. These network characteristics make DTNs to heavily rely on the cooperation of neighboring nodes for the successful delivery of packets. However, the presence of malicious or selfish nodes will have a great impact on the network performance. In this paper, we design a decentralized trust management scheme (DTMS) to filter out malicious nodes in DTNs. First, the number of forwarding evidence is combined with the energy consumption rate of the nodes to formulate direct trust. Then, a recommendation trust is computed from the indirect trust, recommendation credibility, and recommendation familiarity. Recommendation credibility and familiarity improve the overall recommendation trust by filtering out dishonest recommendations. A comparative analysis of DTMS is performed against a cooperative watchdog scheme, recommendation based trust model, and spray and wait protocol. The results show that DTMS can effectively deal with malicious behaviors in DTNs including trust related attacks.
Delay/Disruption Tolerant Networks (DTNs) are network architectures developed to cope with intermittent connectivity and long delays in wireless networks. Unlike traditional networks where packets are forwarded along fixed links, DTNs use a store-and-forward approach to overcome the lack of endto-end paths [1], [2]. DTNs comprise of nodes with limited resources such as buffer space and power. These constraints in resources, in addition to the sparsity and mobility of these nodes often result in intermittent connectivities. The application of DTN spans across a wide range of domains including Under-Water Networks (UWNs), Pocket Switched Networks (PSNs), Vehicular Ad-hoc Networks, Military applications and Disaster recovery and rescue operations [3], [4].
V. CONCLUSION
In DTNs, trust models have become important in mitigating routing behaviour from compromised nodes. The most common routing misbehaviour in DTN is message dropping which degrades the network performance. Therefore, an adequate and efficient detection mechanism is required to mitigate this routing misbehaviour. In this paper, a decentralised trust management scheme has been designed and validated for mobility-aware DTNs. The proposed scheme combines the forwarding behaviour of nodes and their energy consumption rate to compute direct trust. Second-hand information from neighbouring nodes are also incorporated into the trust model as recommendation trust. The recommendation trust incorporates indirect trust, recommendation credibility and familiarity which is an event based trust. Extensive simulation results show that DTMS effectively mitigates routing misbehaviour such as packet dropping attacks and colluding attacks. In our future work, we will exploit solutions such as using DTN gateways to reduce energy consumption during the computation of direct and recommendation trust.
چکیده
1. آثار مرتبط
الف. مدیریت اعتماد در شبكه هاي نظير به نظير و WSN
ب. مدیریت اعتماد در شبکه های ادهاک
ج. مدیریت اعتماد در شبكه هاي DTN
د. خلاصه و چالش های تحقیق
2. مقدمات
الف .مدل سیستم
ب. مدل حمله
3. مدل اعتماد پیشنهادی
الف. اعتماد برخورد مستقیم
ب .اعتماد توصیه شده
ج. ارزش اعتماد كلي
د. تصمیم گیری ارسال
4. ارزیابی عملكرد
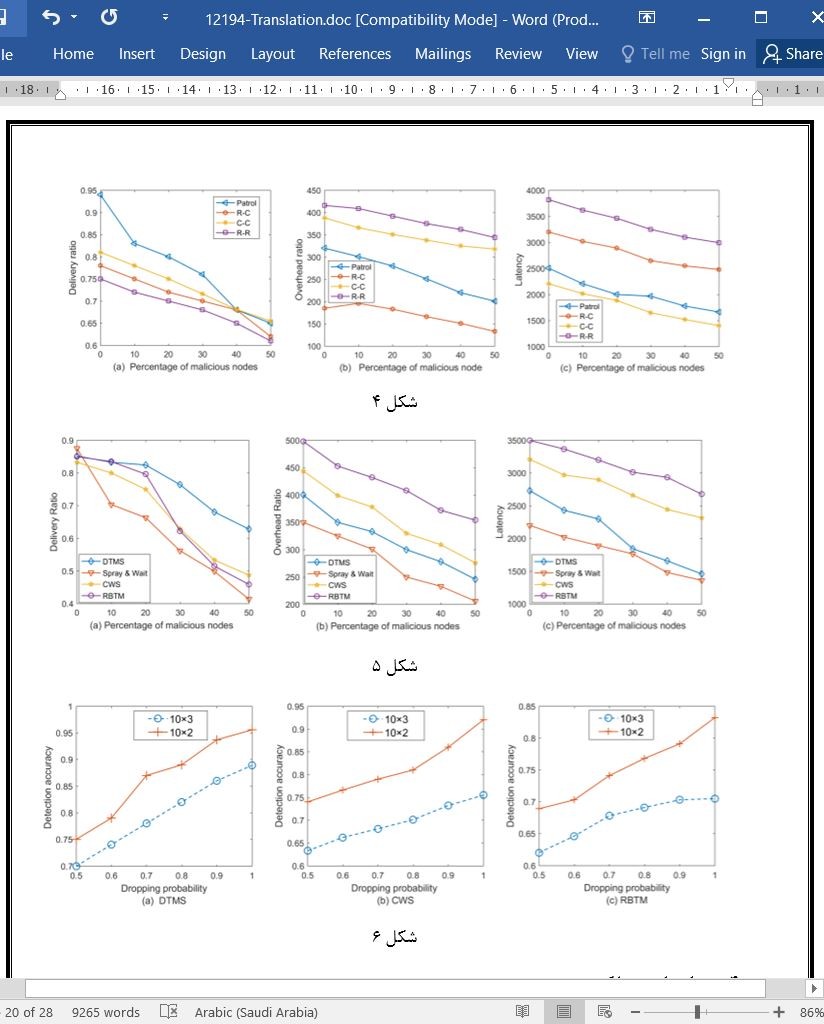
الف. تاثیر سوء رفتار پیام بر الگوهای انگیزش در PDM
ب. مقایسه سوء رفتار رهاسازي پیام با رویکردهای متفاوت
ج. به روز رسانی ارزش اعتماد
5. نتیجه گيري
منابع
Abstract
1. RELATED WORK
A. Trust Management in P2P and WSNs
B. Trust Management in Ad-Hoc Networks
C. Trust Management in DTNs
D. Summary and research challenges
2. PRELIMINARY
A. System Model
B. Attack Model
3. PROPOSED TRUST MODEL
A. Direct Encounter Trust
B. Recommendation Trust
C. Overall Trust Value
D. Forwarding Decision
4. PERFORMANCE EVALUATION
A. Impact of message dropping misbehaviour on various mobility patterns in the PDM
B. Comparison of message dropping misbehaviour with different approaches
C. Updating trust value
5. CONCLUSION
REFERENCES
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه