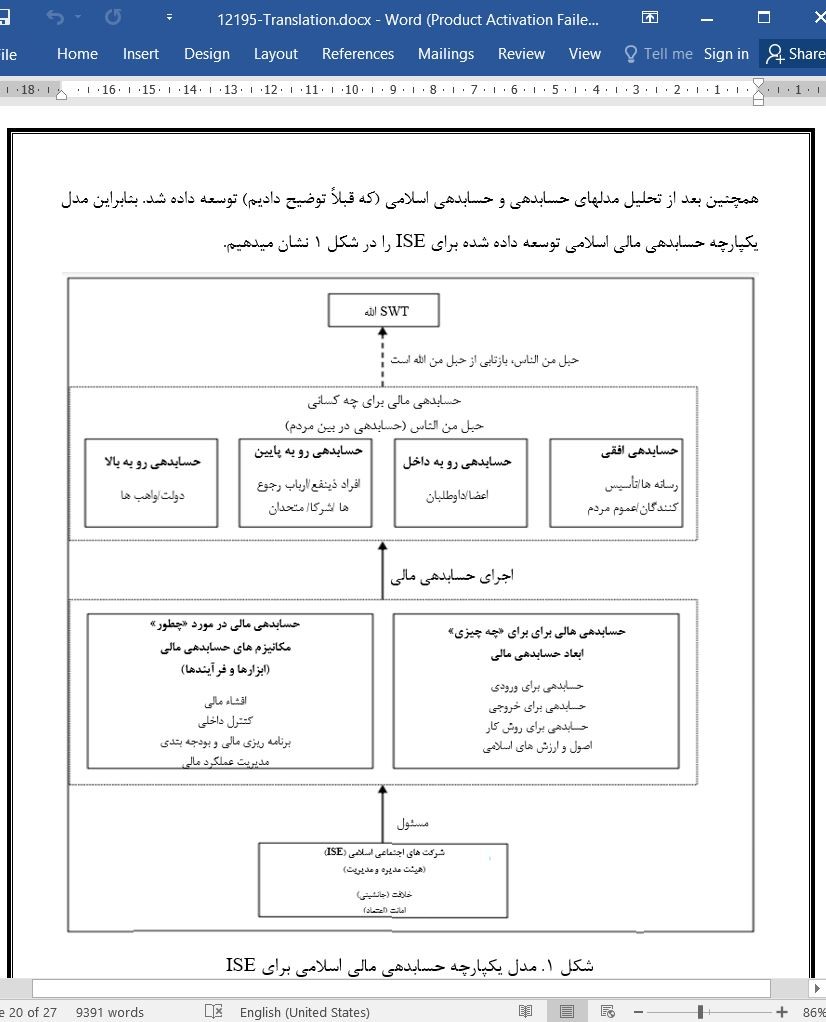
مدل یکپارچه حسابدهی مالی اسلامی برای کسب و کارهای اجتماعی اسلامی (ISE)
چکیده
هدف مطالعه حاضر این است که یک مدل یکپارچه حسابدهی (مسئولیت) مالی اسلامی را معرفی کند که با مدلها و چارچوب های حسابدهی قبلی تفاوت دارد. در این مورد، هر سه جنبه حسابدهی را ترکیب می کنیم و آنرا به یک مدل واحد یکپارچه تبدیل می کنیم. این سه جنبه حسابدهی عبارتند از: (1) حسابدهی به چه کسانی (گروه های حسابدهی)؛ (2) حسابدهی برای چه چیزی (ابعاد حسابدهی)؛ و (3) نحوه حسابدهی (ابزارها و فرآیندهای حسابدهی). مدل حاضر با استفاده از این سه جنبه حسابدهی، بصورت اختصاصی بر حوزه حسابدهی مالی تمرکز می کند، با عناصر اسلامی اضافی که با کسب و کارهای اجتماعی اسلامتی (ISE) متناسب هستند. مطالعه حاضر برای توسعه این مدل، روش مقایسه مدلهای قبلی پاسخدهی و پاسخدهی اسلامی را با ورودی های مقالات دیگر از جنبه های حسابدهی مالی و دیدگاه های حسابدهی اسلامی مقایسه می کند. مطالعه حاضر بر اساس یافته ها، یک مدل یکپارچه حسابدهی مالی اسلامی را بصورت مختص برای ISE معرفی می کند که یکی از انواع سازمانهای نوظهور در بخش غیرانتفاعی است. ما امیدوار هستیم که مدل یکپارچه حسابدهی مالی اسلامی که در این مطالعه توسعه داده شده است، توسط مدیریت و ISE مورد اجرا قرار بگیرد تا حسابدهی آنها خصوصاً برای واهب ها، افراد ذینفع و سهامداران دیگر حل شود.
مقدمه
حسابدهی یکی از عناصر حیاتی برای سازمان های غیرانتفاعی است. دلیل این مسئله این است که حسابدهی رابطه نزدیکی با مسئولیت های سازمان های غیرانتفاعی (از جمله ISE) نسبت به سهامداران خود (مانند واهب ها، افراد ذینفع و عموم مردم) دارد. بعبارت دیگر حسابدهی، چرخه ای از رابطه بین سهامداران ISE (مالک اصلی) و هیئت مدیره ISE (BOD) و مدیریت (نماینده) دارد. در این حالت، سهامداران ISE همواره اطلاعاتی را از ISE BOD و مدیریت تقاضا می کنند، و منابع لازم برای آنها را تأمین می کنند. در حالیکه ISE BOD (هیئت مدیره ISE) و مدیریت همواره منابعی را تقاضا می کنند و اطلاعات لازم را برای سهامداران ISE تأمین می کنند.
نتیجه گیری
تکنیک های مدیریت مالی خوب، می توانند یکی از مکانیزم ها برای تکنیک های خوب حسابدهی مالی باشند تا از اثربخشی و کارایی سازمان های غیرانتفاعی اسلامی – خصوصاً در رابطه با جنبه های مالی – اطمینان حاصل کنند. ما در این مطالعه یک مدل جدید حسابدهی مالی اسلامی را معرفی می کنیم که بر جنبه های مالی از دیدگاه های اسلامی مانند مفاهیم امانت (اعتماد) و خلافت (قدرت) تأکید دارد. این دو مفهوم بر عهده ISE BOD و مدیریت گذاشته می شود تا اطمینان حاصل گردد که تمام فعالیت ها و اعمال اتخاذ شده در مسائل مالی، طبق تکنیک های خوب هستند. این مدل یکپارچه جدید حسابدهی مالی اسلامی همچنین دو حسابدهی اسلامی را اتخاذ میکند که حبل من الله (حسابدهی به الله) و حبل من الناس (حسابدهی در بین مردم) هستند. انتظار می رود که ISE ها با اجرای این مدل، قادر باشند حسابدهی مالی اسلامی خود را از طریق مکانیزم های مدیریت مالی و با تمرکز بر چندین بُعد پیشنهاد شده حسابدهی برای گروه های خاص حسابدهی، اجرا کنند.
ABSTRACT
This study aims to present an integrated Islamic financial accountability model, which is different from previous accountability models and frameworks. In this case, all three accountability aspects which are: (i) accountability to whom (accountability groups); (ii) accountability for what (accountability dimensions); and (iii) accountability on how (accountability tools and processes) were integrated into a single model. By using these three accountability aspects, this model is specifically focused on financial accountability area with additional Islamic elements that suits Islamic Social Enterprise (ISE). In order to develop this model, this study applies the comparison method on previous accountability and Islamic accountability models with additional literature inputs from financial accountability aspects and Islamic accountability perspectives. Based on the findings, this study introduces an integrated Islamic financial accountability model specifically for ISE, one of the emerging institution types under the non-profit sector. It is hoped that the integrated Islamic financial accountability model developed in this study will be implemented by the management of ISE in order to discharge their accountability especially to donors, beneficiaries and other stakeholders.
INTRODUCTION
Accountability is one of the crucial elements for non-profit organisations. This is because accountability is closely related to responsibilities of non-profit organisations including Islamic social enterprise (ISE) to their stakeholders such as donors, beneficiaries and public. In other word, accountability is a cycle of relationship between ISE stakeholders (principal) and ISE board of directors (BOD) and management (agent). In this case, ISE stakeholders are continuously demanding the information from and supplying the resources needed by ISE BOD and management. While, ISE BOD and management are continuously demanding the resources and supplying the information needed by ISE stakeholders.
CONCLUSION
A good financial management practices could be one of the mechanisms for a good financial accountability practices in order to ensure the effectiveness and the efficiency of Islamic non-profit organisations especially in relation to financial aspects. This study presents a new Islamic financial accountability model that emphasise financial aspects from Islamic perspectives such as amanah (trust) and khilafah (power) concepts. These two concepts are entrusted upon ISE BOD and management to ensure that all activities and actions taken in financial matters are in good practices. In addition, this new integrated Islamic financial accountability model also adopted dual Islamic accountability which are hablum minallah (accountability to Allah) and hablum minannas (accountability among people). By implementing this model, it is hoped that ISE will be able to discharge its Islamic financial accountability through financial management mechanisms by focusing on several suggested accountability dimensions towards specific accountability groups.
چکیده
مقدمه
کسب و کارهای اجتماعی اسلامی (ISE)
حسابدهی
مروری بر حسابدهی
حسابدهی مالی
حسابدهی در بخش غیرانتفاعی
حسابدهی اسلامی
مدل های حسابدهی و حسابدهی اسلامی
مدل یکپارچه حسابدهی مالی اسلامی
نتیجه گیری
منابع
ABSTRACT
INTRODUCTION
ISLAMIC SOCIAL ENTERPRISE (ISE)
ACCOUNTABILITY
Overview of Accountability
Financial Accountability
Accountability in Non-Profit Sector
Islamic Accountability
ACCOUNTABILITY AND ISLAMIC ACCOUNTABILITY MODELS
INTEGRATED ISLAMIC FINANCIAL ACCOUNTABILITY MODEL
CONCLUSION
REFERENCES
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه