بهینه سازی پیکربندی گیرنده لوله ای مرکزی با نصب محیط متخلخل برای افزایش انتقال حرارت
چکیده
در این مقاله، افزایش انتقال همرفت جریان آشفته حرارت در یک گیرنده لوله ای مرکزی که با محیط متخلخل و تحت شار حرارتی پیرامونی غیریکنواخت پر شده است بصورت عددی مورد بررسی قرار گرفت. درباره اثرات برخی پارامترهای محیط متخلخل (طرح اولیه، رسانایی گرمایی/حرارتی و تخلخل) و عدد رینولدز (Re) بر روی عملکرد حرارتی و عملکرد حرارتی-هیدرولیکی بحث شده است. نتایج نشان داد هنگامی که نسبت رسانایی حرارتی محیط متخلخل به سیال عامل/متحرک (λs / λf) کمتر از 1000 باشد پر کردن بالا و پایین لوله گیرنده لوله تقویت شده (ERT) با محیط متخلخل، موجب عملکرد حرارتی مناسب گیرنده میشود. زمانیکه λ s / λ f > 100 باشد لوله گیرنده تقویت شده با محیط متخلخل در بالا و پایین، عملکرد حرارتی-هیدرولیکی مناسبی را از خود نشان می دهد. تخلخل (ε) و عدد رینولدز نیز بر عملکرد حرارتی و عملکرد حرارتی-هیدرولیکی تأثیر میگذارند؛ عدد نوزلت (Nu) و شاخص های ارزیابی عملکرد (PEC) افزایش انتقال حرارت از طریق پمپاژ کردن مداوم در اکثر با افزایش ε، کاهش مییابد؛ اما شاخص های ارزیابی عملکرد لوله گیرنده ای که بالای آن با محیط متخلخل پر شده است با افزایش ε، افزایش پیدا می کند. عدد نوزلت تمام لوله های گیرنده تقویت شده، با افزایش عدد رینولدز افزایش مییابد، اما شاخص-های ارزیابی عملکرد با افزایش عدد رینولدز کاهش پیدا میکند.
1. مقدمه
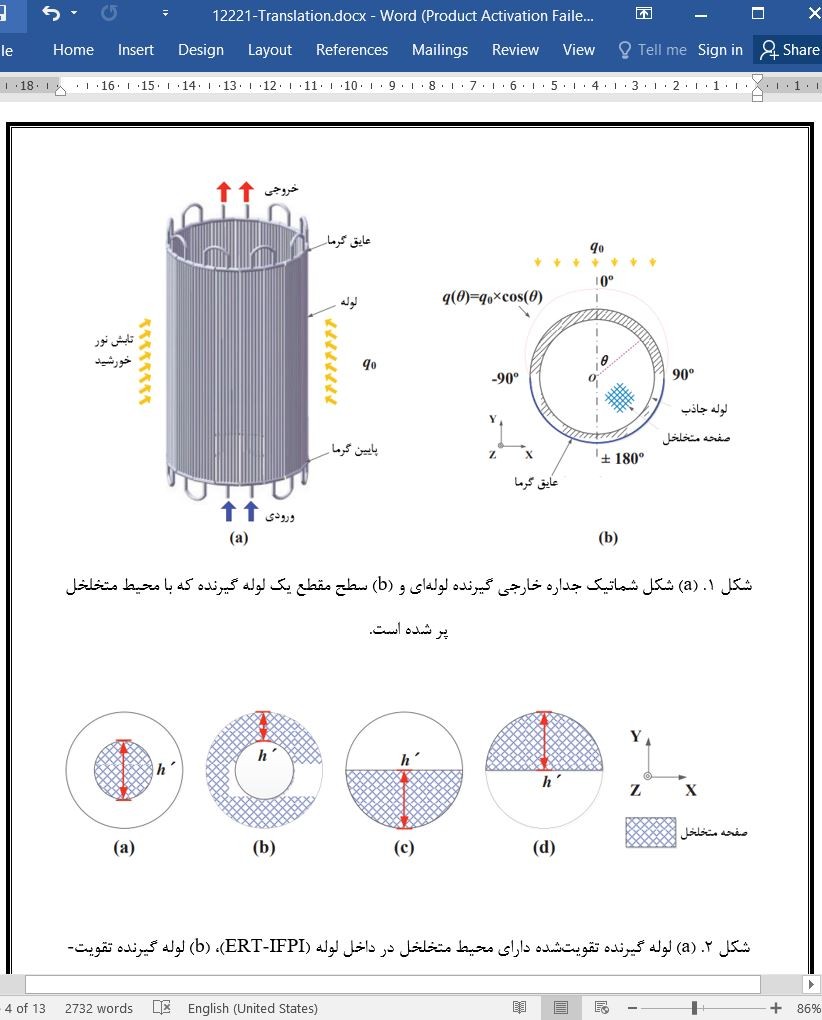
سیستم برج خورشیدی (SPTS)، انرژی اولیه متمرکز خورشیدی است که دارای مزایای بسیار آشکاری از جمله هزینه تقریباً کم و تولید برق در مقیاس وسیع میباشد [1]. گیرنده (receiver)، مؤلفه اصلی سیستم برج خورشیدی است. برای سیستم برج خورشیدی از دو نوع گیرنده اصلی استفاده میشود: گیرنده حجمی و گیرنده لوله ای. گیرنده لوله ای میتواند فشار و درجه حرارت بالا را کاملاً تحمل کند و برای بسیاری از سیالات هادی حرارت (HTF) مانند آب/ بخار، فلز مایع و نمک مذاب، قابل استفاده است.
5- نتیجه گیری
در این مقاله، افزایش انتقال حرارت در لوله گیرنده مرکزی که بصورت جزئی یا کلی با محیط متخلخل پر شده است برحسب اعداد و ارقام مورد بررسی قرار گرفت. در مورد اثر برخی پارامترهای محیط متخلخل(H، λs ، ε) و عدد رینولدز بر عملکرد حرارتی و عملکرد حرارتی-هیدرولیکی نیز بحث شد. از مجموع مطالب گفته شده میتوان به نتیجه زیر رسید.
Abstract
In this paper, the heat transfer enhancement for convection heat transfer of turbulent flow in a central receiver tube filled with porous medium under non-uniform circumferential heat flux was numerically investigated. The effects of some parameters of porous medium (layout, thermal conductivity and porosity) and the Reynolds number (Re) on the thermal and thermo-hydraulic performance were discussed. The results showed that the enhanced receiver tube (ERT) with down-filling porous inserts and in-filling porous inserts have good thermal performance when the ratio of thermal conductivity of porous medium to working fluid (λs/λf) is less than 1,000. The ERT with out-filling porous inserts and up-filling porous inserts have good thermo-hydraulic performance when λs/λf >100. The porosity (ɛ) and Re also affect the thermal and thermo-hydraulic performance, the Nusselt number (Nu) and performance evaluation criteria (PEC) of heat transfer enhancement under constant pumping power of most kinds of ERTs decrease with the increase of ɛ, but the PEC of the ERT with in-filling porous inserts increases with the increase of ɛ. The Nu of all kinds of ERTs increases with the increase of Re, but the PEC decreases with the increase of Re.
1. Introduction
Solar power tower system (SPTS) is a primal concentrating solar power, which has many obvious advantages including low average cost and large-scale power generation [1]. The receiver is the key component of the SPTS. There are two main kinds of receivers used to SPTS: volumetric receiver and tubular receiver. The tubular receiver can well bear pressure and high temperature, and is applicable to various heat transfer fluid (HTF), such as water/steam, liquid metal, and molten salt.
5. Conclusion
In this paper, a numerical investigation was carried to study the heat transfer enhancement in a central receiver tube partially or completely filled with porous medium. The effects of some parameters of porous medium (H, λs, ε) and the Re on the thermal and thermo-hydraulic performance were also discussed. The following conclusions can be made.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. مدل فیزیکی/خارجی
3. فرمول ریاضی و روش عددی
4- نتیجه و بحث
5- نتیجه گیری
منابع
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Physical model
3. Mathematical formulation and numerical procedure
4. Result and Discussion
5. Conclusion
References
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه