حریم خصوصی، امنیت و سیاست ها: مرور مشکلات و راه حل های کابردهای اینترنت اشیاء
چکیده
هدف اینترنت اشیاء (IoT) ساده سازی مجموعه داده های توزیع شده در کسب و کارهای تولید جهانی، به اشتراک گذاری و پردازش اطلاعات و معلومات در بین بسیاری از شرکا با استفاده از ساختار مناسب سیستم اطلاعاتی است. همگرایی با فناوری بلاک چین که داده ها، حریم خصوصی و مسائل مرتبط با امنیت و سیاست های داده (به عنوان مثال همخوانی با مقررات) را پردازش می کند، همانند IoT (اینترنت اشیاء) می تواند بر روی داده ها و موضوعات نرم افزاری اعمال شود. علاوه بر این، فناوری بلاک چین می تواند از طریق همگرایی مناسب با فناوری IoT در پشتیبانی از یکپارچه سازی و پردازش داده ها، به مدیریت هوشمندانه تر و منعطف تر داده های مبادله ای کمک کند. این مقاله، مسائل ترکیبی مرتبط با حریم خصوصی، امنیت و سیاست ساختار را بررسی می کند تا همگرایی درک شود و یکپارچه سازی IoT و فناوری بلاک چین فهمیده شود. این مقاله در ابتدا روندهای معمولی متمرکز بر موضوعات مرتبط را در تحقیقات فناوری IoT مبتنی بر بلاک چین را شناسایی نموده و نیاز به بررسی بیشتر مسائل امنیتی- به عنوان مثال چالش های حریم خصوصی داده ها در صنعت تولید- را مشخص می کند.
1. مقدمه
صنعت جدید تولید و زنجیر تامین آن، جهشی را از اتوماسیون سنتی تر به سمت عملیات تولید کاملا مرتبط و قابل انعطاف ارائه می کند. این سیستم قابل انعطاف می تواند جریان ثابتی از داده ها را از عملیات مرتبط و سیستم های تولید برای فراگیری و تطبیق با نیازهای جدید استفاده کند. این روندی است که بر کسب و کارها و رشد اقتصادی اثر می گذارد؛ بسیاری از ماشین های شبکه ای به صورت فزاینده ای برای اجرای عملیات تولید مورد استفاده قرار می گیرند. این ماشین ها می توانند عملیات یا وظایف مشابه یا متفاوتی انجام داده و برخی ماشین ها به شدت به خروجی سایر ماشین ها وابسته هستند (که با عنوان «خط تولید لوله ای» معروف است). ارتباط بین ماشین های شبکه ای می تواند به صورت پویا سازمان دهی شود تا قابلیت انعطاف و تطبیق با وظایف سفارشی شده را افزایش دهد. در نتیجه، همکاری هوشمند ماشین های شبکه ای برای بهبود عملکرد سیستم های تولیدی جدید، ضروری است.
6. نتیجه گیری
سیستم مبتنی بر IoT یک شبکه هوشمند، جامع تر از اشیاء مرتبط به هم است که از طریق طرح های آدرس منحصر به فرد ( به عنوان مثال آدرس مبتنی بر EPC) می توانند با اشیاء مجاور خود همکاری نموده و تعامل کنند تا داده ها را جمع آوری نموده، داده ها را پردازش کنند و آن را به تصمیمات مرتبط با کسب و کار روزانه تبدیل کنند. داده های به دست آمده از کابردهای IoT به همراه فرایندهای کسب و کار تولیدی می توانند تصمیم گیری عملیاتی را راحت تر کنند. با این حال، سیستم کاربردی IoT مستقل با مشکلات امنیتی مختلفی از حمله به تجهیزات IoT گرفته تا حمله به انتقال داده ها روبرو می شوند. علاوه بر این، ادغام شدید دنیای دیجیتال با دنیای فیزیکی با استفاده از سیستم های اطلاعاتی سبب ایجاد سیستم های IoT بیشتر با قابلیت خطرپذیری شده است.
Abstract
Internet of Things (IoT) aims to simplify the collection of the distributed data in a global manufacturing business, sharing and processing of information and knowledge across many collaborating partners using appropriate information system architecture. As with the IoT, convergence with blockchain technology that processes data, privacy and security-related issues, and data policies (e.g., regulatory compliance) may apply to data and software artefacts. Besides, blockchain technology could contribute to the more intelligent and flexible handling of transactional data through appropriate convergence with IoT technology in supporting data integration and processing. This paper examines this hybrid architecture’s privacy, security, and policy-related issues to appreciate the convergence and understand the integration of IoT and blockchain technology. This paper primarily identifies common trends focusing on relevant topics in blockchain-based IoT technology research and by highlighting the need to explore security issues further – for example, data privacy challenges in the manufacturing industry.
1. Introduction
The modern manufacturing industry and its supply chain represent a leap forward from more traditional automation to fully connected and flexible manufacturing operations. This flexible system can use a constant stream of data from connected operations and production systems to learn and adapt to new demands. It becomes a trend impacting business and economic growth; many networked machines are used increasingly to carry out manufacturing operations. These machines may carry out the same or different functions or tasks, and some machines rely heavily on the output from other machines (known as a ‘pipelined product line’). The connection between networked machines may also be configured dynamically to increase flexibility and adaptation to customized tasks. As a result, the smart synergy of networked machines is critical to improving the performance of modern manufacturing systems [10] [12].
6. Conclusion
The IoT-based system is a smart, more comprehensive network of interconnected objects, which through unique address schemes (e.g., EPC-based address), can cooperate and interact with their neighbours to collect data, process data, and convert it to daily business-related decisions. The data obtained from the IoT applications along manufacturing business processes can make operational decision-making much more comfortable. However, standalone IoT application systems face different security problems ranging from attacks on IoT devices to attacks on transit data. Furthermore, the tight integration of the digital world with the physical world using automated information systems has further created IoT systems' vulnerabilities.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. دیجیتال سازی فرایند کسب و کار تولید
3. کارهای مرتبط با امنیت و حریم خصوصی IoT
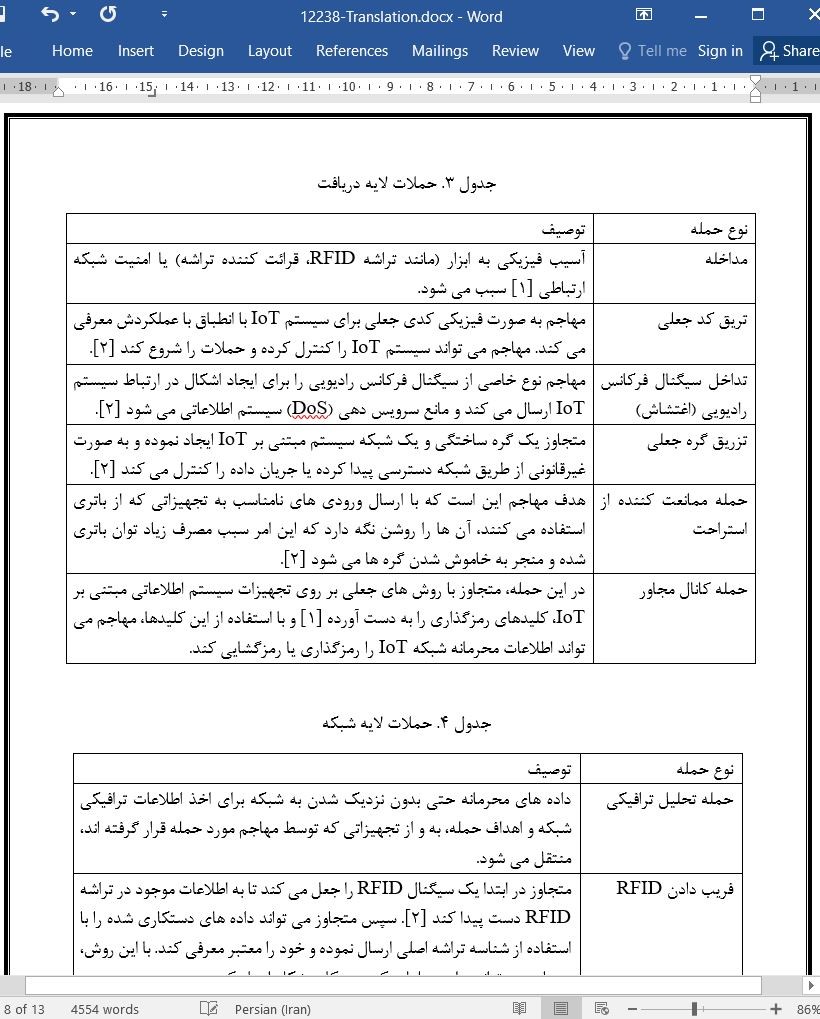
4. دسته بندی حملات امنیتی
4.1. حملات لایه کاربرد و راه حل ها
5. سرویس و سیاست (خط مشی) اطلاعاتی مبتنی بر IoT
6. نتیجه گیری
مراجع
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Digitization of manufacturing business process
3. Related work on IoT Security and Privacy
4. Categorization of security attacks
4. 1 Application Layer attacks and solutions
5. IoT based information service and policy
6. Conclusion
References
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه