حرکت به سوی شهرهای هوشمند
چکیده
یک شهر یک اکوسیستم انسانی بزرگ و دائمی است که خدمات و فرصتهای زیادی را به شهروندان خود ارائه میدهد. شهرسازی سریع و افزایش جمعیت، فشارهای زیادی را بر زیرساختهای شهری و خدمات رسانی وارد کرده است. شهرسازی کنونی برای مدرنیزه کردن زندگی شهری، به استراتژیهای قدرتمند و برنامه ریزی نوآورانهای نیاز دارد. بسیاری از شهرها کیفیت و عملکرد خدمات شهری را با دیجیتالی شدن، و هوشمندتر شدن ارتقا میبخشند. سیاستگذاران و مسئولین شهر در حال بررسی راه حلها هستند تا خدمات جدیدی را به روشی کارآمد، پاسخگو و پایدار برای جمعیت زیادی از مردم ارائه دهند. در این تحقیق، کلیه خدمات ممکن از جمله ابعاد مختلف شهر که میتوانند یک شهر را به یک شهر هوشمند تبدیل کنند، مورد بررسی قرار گرفته است. ایدههای مربوط به خدمات هوشمند از طریق اجرای یک پروسه خلاقانه جمع سپاری تحت نظر همنوعان در هند جمع آوری شدهاند. برای تجزیه و تحلیل ایدههای جمع آوری شده، از یک تحلیل عادی محتوای کیفی موجه استفاده شده است. ایدههای منحصر به فرد در 19 دسته مختلف از خدمات خوشه بندی شدهاند. این یافتهها طبقه بندی چندبعدی خدمات را همراه با توسعه زیرساختهای اساسی و مورد نیاز نشان میدهند. علاوه براین، چارچوب تحول شهر هوشمند (SCTF) برای کمک به سیاست گذاران، توسعه دهندگان شهری، مقامات دولتی و ارائه دهندگان خدمات از نظر درک و ترسیم بینشهای بیشتری از راهکارهای هوشمند پیشنهادی برای توسعه شهرهای هوشمند مطرح شدهاست. چهار حوزه کلیدی (برنامهریزی، زیرساخت فیزیکی، زیرساخت ICT و گسترش راهحلهای هوشمند) در چارچوب پیشنهادی برای نشان دادن تحولات شهر مورد بحث قرار گرفته است. چارچوب تحول شهر هوشمند (SCTF) پیشنهادی، توسط مقالات و نمونههایی که توسط شهرهای مختلف هوشمند در سراسر جهان برای نشان دادن اثربخشی آن پذیرفته شدهاند، پشتیبانی میشود. علاوه بر این، یک نقشه ذهنی برای نشان دادن روابط درونی میان ایدههای جمعآوریشده در یک تصور جذاب و روندی برای فرآیند تحول شهر طراحی شدهاست.
9. محدودیتها و تحقیقات آینده
توسعه خدمات هوشمند مستلزم تلفیق فن آوری پیشرفته در فعالیتهای شهری در سرسر حوزههای مختلف است. این مطالعه، راه حلهای مختلف هوشمند، چارچوبی برای تحول شهر و دیداری سازی نقشه ذهنی برای شهر هوشمند را ارائه میکند، اما در مورد شکل مناسب ادغام و ارتباط داخلی لایههای فیزیکی ، فن آوری اطلاعات و ارتباطات و زیرساختهای IoT توضیحی نمیدهد. طراحی خدمات، پیاده سازی و ارائه خدمات جدید به یک دوره زمانی نیاز دارد. این مطالعه هیچ چارچوب زمانی را برای درک چگونگی اجرا در زمان واقعی و تأثیر آن بر شهروندان برآورد نمیکند. چارچوب زمانی لازم برای اجرای مؤثر بطور معمول به عوامل مختلفی از جمله شکل کشور، ساختار دولت و ضرورت الزامات و غیره بستگی دارد. از این رو، ممکن است برای شهرها و همچنین کشورهای مختلف تفاوت داشته باشد.
Abstract
A city is a large and permanent human ecosystem which provides a lot of services and opportunities to its citizens. The rapid urbanization and increasing population have put a lot of strains on city infrastructures and service deliveries. The current urbanization requires strong strategies and innovative planning to modernize the urban life. Many cities are enhancing quality and performance of urban services by being digitalized, intelligent and smarter. The policymakers and city authorities are exploring solutions to deliver the new services in an efficient, responsive and sustainable manner for a large population. The study explores all the possible services among various city dimensions which can make a city smart. The ideas related to smart services are collected from the peer vetted creative crowdsourcing process performed online in India. A directed qualitative conventional content analysis is used to analyze the collected ideas. The unique ideas are clustered into 19 different service categories. The findings suggest multi-dimensional service classification along with required basic infrastructural development. Further, the Smart City Transformation Framework (SCTF) is proposed to help the policy makers, urban developers, government officials and service providers in terms of understanding and to draw more insights from the suggested smart solutions for development of smart cities. There are four key areas (Planning, Physical infrastructure, ICT infrastructure and Deploying Smart solutions) discussed in the proposed framework to illustrate the city transformation. The proposed SCTF is supported by literature and examples adopted by various smart cities across the world to illustrate its effectiveness. Moreover, a mind map is designed to illustrate the interrelationships among the collected ideas in an attractive and procedural visualization for city transformation process.
9. Limitations and future research
The development of smart services require incorporation of advanced technology into urban activities across different domains. The study suggests the various smart solutions, framework for city transformation and mind map visualization for smart city but it does not explain the proper layout for the integration and interconnection of physical layer, ICT and IoT infrastructure. The service design, implementation and delivery of new services require a period of time. The study does not estimate any time frame to understand the real-time implementation and impacts to the citizens. The required time frame for effective implementation usually depends on many factors such as country layout, government structure and urgency of the requirement etc. Hence, it may vary for different cities as well as countries.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
1.1. یک فشار عظیم بر روی زیرساختها و خدمات شهری
1.2 شهرهای هوشمند: جنبه جدیدی از شهری سازی
1.3 برنامه ریزی خدمات برای شهرهای هوشمند
2 بررسی مقالات
2.1 مروری بر نوع شناسی خدمات و مدلهای ارائه خدمات که قبلاً مطرح شدهاند
2.2 پذیرش فن آوری و مشارکت شهروندان در توسعه شهر هوشمند
2.3 پیشرفتهای فن آورانه برای طراحی و ارائه خدمات هوشمند
2.4 حفاظت از محیط زیست و کاهش بلایای طبیعی
3 روش شناسی
3.1 جمع سپاری
3.2 تحلیل محتوا
3.3 نگاشت ذهنی
4 نتایج
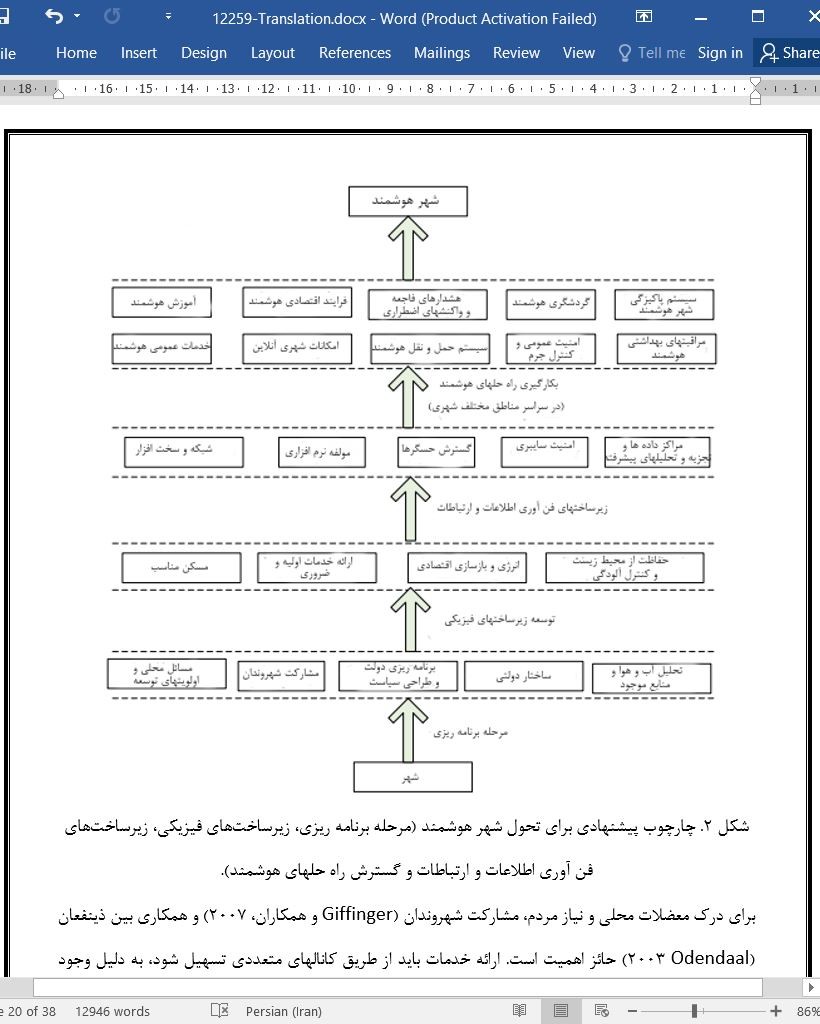
5 پیشنهاد ما: چارچوب تحول هوشمند شهر (SCTF)
5.1 مرحله برنامه ریزی
5.2 توسعه زیرساختهای فیزیکی
5.3 توسعه زیرساختهای فن آوری اطلاعات و ارتباطات (ICT)
5.4 بکارگیری راه حلهای هوشمند
6 دیداری سازی نقشه ذهنی برای تحول شهر هوشمند
7 مشارکت تحقیق و مفاهیم آن
8 نتیجه گیری
9 محدودیتها و تحقیقات آینده
منابع
ABSTRACT
1. Introduction
1.1. A huge strain on urban infrastructure and services
1.2. Smart cities: a new aspect of urbanization
1.3. Service planning for smart cities
2. Literature studies
2.1. An overview to previously proposed service typologies and service delivery models
2.2. Technological adoption and citizens' engagement in smart city development
2.3. Technological advancements for smart service design and delivery
2.4. Environment protection and mitigating natural calamities
3. Methodology
3.1. Crowdsourcing
3.2. Content analysis
3.3. Mind mapping
4. Results
5. Our proposal: Smart City Transformation Framework (SCTF)
5.1. Planning phase
5.2. Physical infrastructure development
5.3. ICT infrastructure development
5.4. Deploying smart solutions
6. A mind map visualization for smart city transformation
7. Research contributions and implications
8. Conclusions
9. Limitations and future research
References
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه