تاثیرات مدیریت منابع انسانی با مسئولیت اجتماعی بر مشروعیت سازمانی
چکیده
تقاضاهای اجتماعی برای مسئولیت اجتماعی شرکت(CSR)، در سال های اخیر افزایش یافته است. سازمان ها نیاز به پیگیری رفتاری از نظرِ اجتماعی مسئولانه، جهت جلب حمایت ذینفعان را درک می کنند. علاوه بر این، کاربرد اصول CSR در مدیریت منابع انسانی(HR) اهمیت زیادی یافته است و به تحقیقات تجربی بیشتری نیاز است. در واقع، اگر شرکت ها نه تنها از نظر خارجی، بلکه از نظر داخلی نیز شرکتی با مسئولیت اجتماعی تلقی شوند، می توان آنها را شرکتی مشروع دانست. تحت این سناریو، هدف اصلی این تحقیق، تحلیل رابطه بین پیاده سازی مدیریت منابع انسانی با مسئولیت اجتماعی و مشروعیت سازمانی است. علاوه براین، اهمیت و عملکرد سیاست های مختلف CSR از طریق پیاده سازی ماتریس اهمیت- عملکرد(IPMA) تحلیل خواهد شد. بدین منظور، ارزیابی های انجام شده توسط 157 خبره CSR بر تقریبا 30 شرکت چند ملیتی مدنظر قرار می گیرند. برای تحلیل داده ها از PLS-SEM استفاده شد و نشان دهنده رابطه قوی و مثبت بین شیوه های CSR است که بر کارکنان و مشروعیت سازمانی تمرکز دارد. نتایج، اطلاعات مهمی برای مدیران شرکت ارائه می دهند تا بهینه سازی منابع و مدیریت ذینفعان داخلی خود را از طریق ارائه سیاست های CSR صحیح و موثر، بهبود دهند.
1. مقدمه
در بازارهای امروزی، سازمان ها باید روابط خود را با ذینفعان خود مدیریت کنند تا ارزش و منافع طرفینی ایجاد کنند(هاریچ و همکاران، 2014؛ فرادنریچ و همکاران، 2020). فریمن(1984) مفهوم نظریه ذینفعان را معرفی نمود که منافع سازمانی مختلف را شناسایی کرده و نشان دهنده اهمیت نه تنها سودآور بودن است، بلکه بر اهمیتِ درکِ توجه به تاثیراتی دارد که فعالیتهای شرکت بر مخاطبان مختلف دارد.
گروه های ذینفع تحت تاثیر رفتار و اقدامات سازمان ها قرار می گیرند؛ با این وجود، درک این امر اهمیت دارد که این اقدامات بر ثبات سازمان ها نیز تاثیر دارند(سیلوا و همکاران، 2019). در واقع، بقای سازمان به شدت به توانایی سازمان در ارضای نیازهای ذینفعان و درک ادراک آنها بستگی دارد(آلمر و سلانو، 2000). بنابراین، اگر شرکت ها بخواهند در بلند و میان مدت موفق باشند، باید طیف کامل این نیازها را درک کنند و بتوانند روابط پایداری با پایگاه ذینفعان خود ایجاد کنند(دمیتریو و همکاران، 2021).
Abstract
Social demands for corporate social responsibility (CSR) have been increasing in recent years. Organizations understand the need to follow socially responsible behavior to receive stakeholder support. In addition, the application of CSR principles within human resources (HR) management has become more relevant, and more empirical research is needed. In fact, enterprises will be considered legitimate if they are viewed as socially embedded not only externally but also internally. Under this scenario, the main objective of this research is to analyze the relationship between the implementation of socially responsible HR management and organizational legitimacy. Furthermore, the relevance and performance of diverse CSR policies will be analyzed through the implementation of the importance-performance matrix (IPMA). For this purpose, the evaluations made by 157 CSR experts on approximately 30 multinational companies are considered. PLS-SEM is applied to the data and shows a strong and positive relationship between CSR practices focused on employees and organizational legitimacy. The results offer relevant information for company managers to improve their resource optimization and internal stakeholder management through the correct and efficient introduction of CSR policies.
1. Introduction
In today’s markets, organizations need to manage their relationships with stakeholders to create value and mutual benefits (Horisch et al., ¨ 2014; Freudenreich et al., 2020). Freeman (1984) introduced the stakeholder theory concept, which identifies diverse organizational interests and shows the importance of not only being profitable but also of understanding and caring about the impact that corporate activities have on different audiences.
Stakeholder groups are affected by organizations’ behavior and actions; however, it is important to understand that these actions also impact corporations’ stability (Silva et al., 2019). In fact, organizational viability strongly depends on the ability to satisfy stakeholders’ needs and understand their perceptions (Ulmer and Sellnow, 2000). Thus, if enterprises want to be successful in the medium-to-long term, they must identify the full range of these needs and be able to build lasting relationships with their stakeholder base (Dmytriyev et al., 2021).
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. چارچوب نظری
2.1. مسئولیت اجتماعی شرکت و کارکنان
2.2. مسئولیت اجتماعی شرکتی و مشروعیت
3. مواد و روش ها
3.1. نمونه و جمع آوری داده
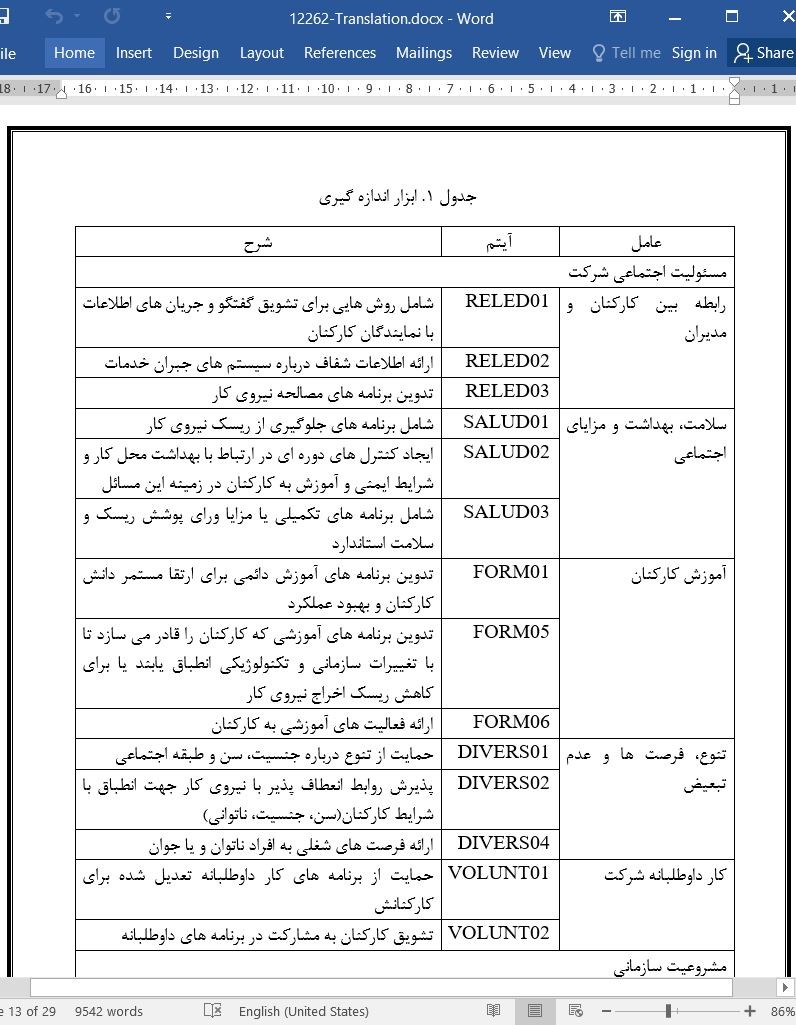
3.2. انداره گیری متغیر
3.3. تحلیل داده
4. نتایج
4.1. تحلیل توصیفی
4.2. مدل ساختاری
5. بحث و نتایج
منابع
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical framework
2.1. Corporate social responsibility and employees
2.2. Corporate social responsibility and legitimacy
3. Materials and methods
3.1. Sample and data collection
3.2. Variable measurement
3.3. Data analysis
4. Results
4.1. Descriptive analysis
4.2. Structural model
5. Discussion and conclusions
References
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه