روش نوسانگر جایگزین ارتقا یافته برای تحلیل واکنش خاک و سازه با در نظر گرفتن خاک های نرم
چکیده
هدف این تحقیق ارتقای کارایی روش نوسانگر جایگزین برای تحلیل واکنش خاک و سازه (SSI) در ساختمان های دارای پایه انعطاف پذیر روی رسوب خاک های نرم است. روش نوسانگر جایگزین یک ساختمان دارای پایه انعطاف پذیر درجه آزادی منفرد (SDOF) را به ساختمان نوسانگر دارای پایه ثابت معادل (EFSDOF) تبدیل می کند تا طیف واکنش برای سازه های دارای پایه ثابت بصورت مستقیم برای سیستم های SSI مورد استفاده قرار بگیرد. مدل SSI نوسانی به عنوان مبنای ارزیابی عملکرد نوسانگر EFSDOF مورد استفاده قرار می گیرد. هم طیف واکنش انعطاف پذیر و هم چکش خواری ثابت در کمتر از 20 گزارش تکان افقی زمین در خاک های نرم مورد بررسی قرار گرفتند. تاثیرات محتوای فرکانس تکان های زمین و میرائی اولیه سیستم های SSI بررسی شده اند. نتیجه گیری شده است که طیف افزایش مطلق بجای طیف نیمه شتابی باید برای نوسانگرهای EFSDOF در سیستم های SSI نیرو محور استفاده شوند. همچنین، نشان داده شده است که استفاده از نوسانگر EFSDOF برای پیش بینی طیف چکش خواری ثابت در شرایط وجود نسبت میرائی اولیه سیستم SSI بیش از 10 درصد می تواند مناسب باشد.بر اساس نتایج بدست آمده از این تحقیق، فاکتور اصلاح برای ارتقای دقت روش نوسانگر جایگزین برای خاک های نرم پیشنهاد می شود.
1. مقدمه
طراحی اولیه یک ساختمان معمولی در آئین نامه های کنونی طراحی لرزه ای عمدتا بر اساس تحلیل طیف انعطاف پذیری می باشد، به طوری که مقاومت غیر ارتجاعی و میزان جابجایی با استفاده از فاکتورهای اصلاحی مثل کاهش مقدار ثابت مقاومت چکش خواری Rμ(کاهش مقاومت حاصل از رفتار نوسانی غیر خطی) و نسبت جابجایی غیر ارتجاعی Cμ ارزیابی می شود (1-3). شکل های طیف واکنش انعطاف پذیری و فاکتورهای اصلاحی در بسیاری از آئین نامه های طراحی (مثل 3و4) با توجه به میانگین نتایج تحلیل واکنش – تاریخ انجام شده در نوسانگرهای جایگزین یک ساختمان دارای پایه انعطاف پذیر درجه آزادی منفرد (SDOF) با استفاده از چندین تکان زمین (7-5) بدست می آیند. در فعالیت های مهندسی، محتوای فرکانس تکان های شتابدار زمین در یک منطقه دارای خاک نرم با استفاده از از یک دوره از پیش تعیین شده (8) به عنوان یک پارامتر تاثیر گذار برای ارزیابی واکنش لرزه ای ساختمان ها توصیف می شود.
Abstract
This paper aims to improve the effectiveness of the replacement oscillator approach for soil-structure interaction (SSI) analysis of flexible-base structures on soft soil deposits. The replacement oscillator approach transforms a flexible-base single-degree-of-freedom (SDOF) structure into an equivalent fixed-base SDOF (EFSDOF) oscillator so that response spectra for fixed-base structures can be used directly for SSI systems. A sway-rocking SSI model is used as a baseline for assessment of the performance of EFSDOF oscillators. Both elastic and constant-ductility response spectra are studied under 20 horizontal ground motion records on soft soil profiles. The effects of frequency content of the ground motions and initial damping of the SSI systems are investigated. It is concluded that absolute acceleration spectra, instead of pseudo-acceleration spectra, should be used for EFSDOF oscillators in force-based design of SSI systems. It is also shown that using an EFSDOF oscillator is not appropriate for predicting the constant-ductility spectra when the initial damping ratio of the SSI system exceeds 10%. Based on the results of this study, a correction factor is suggested to improve the accuracy of the replacement oscillator approach for soft soil conditions.
1. Introduction
The preliminary design of typical building structures in current seismic design codes and provisions is mainly based on elastic spectrum analysis, where the inelastic strength and displacement demands are estimated by using modification factors, such as the constant-ductility strength reduction factor Rμ (i.e. reduction in strength demand due to nonlinear hysteretic behaviour) and inelastic displacement ratio Cμ [1–3]. The spectral shapes of elastic response spectra and modification factors in most seismic design codes and provisions (e.g. [3,4]) are derived by averaging the results of response-history analyses performed on single-degree-of-freedom (SDOF) oscillators using a number of earthquake ground motions [5–7]. In engineering practice, the frequency content of a ground acceleration motion at a soft soil site is often characterized by a predominant period [8] as an influential parameter for estimating the seismic response of buildings.
چکیده
1.مقدمه
2.مدل واکنش خاک – ساختمان
3.پارامترهای مدلسازی
4.نوسانگر EFSDOF
5.پارامترهای واکنش
6.طیف واکنش شتاب ارتجاعی
7.فاکتور کاهش مقاومت چکش خواری ثابت و نسبت جابجایی غیر ارتجاعی
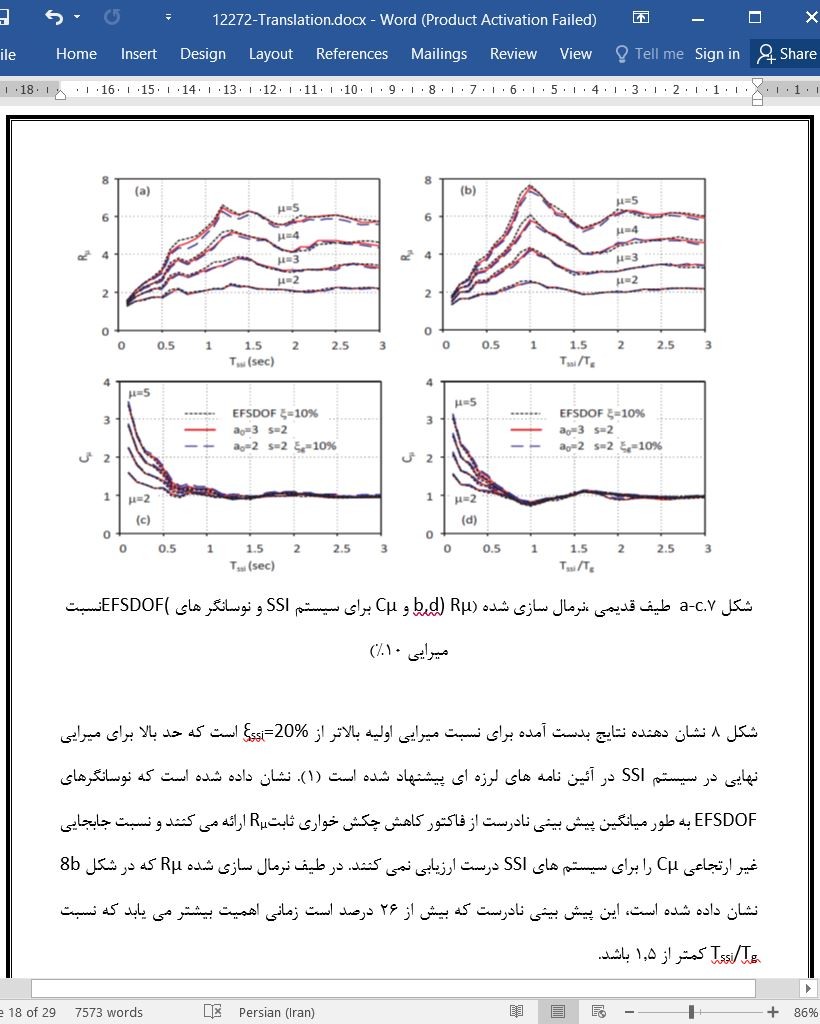
8.نسبت چکش خواری سازه ای و سراسری
9. بحث
10. نتیجه گیری ها
منابع
ABSTRACT
1. Introduction
2. Soil-structure interaction model
3. Modelling parameters
4. EFSDOF oscillator
5. Response parameters
6. Elastic acceleration response spectrum
7. Constant-ductility strength reduction factor and inelastic displacement ratio
8. Structural and global ductility ratios
9. Discussion
10. Conclusions
References
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه