سبک های دلبستگی و پذیرش تبلیغات دهان به دهان الکترونیکی (e-WOM)
چکیده
برای بازاریابان بسیار مهم شده است که چرا افراد، تبلیغات دهان به دهان الکترونیکی (e-WOM) را در سایت های شبکه های اجتماعی می پذیرند. این مقاله قصد دارد پذیرش تبلیغات دهان به دهان الکترونیکی توسط کاربران سایت های شبکه های اجتماعی را بر اساس نظریه دلبستگی درک کند. برای درک اثر مستقیم پذیرش تبلیغات دهان به دهان الکترونیکی، اجتناب از دلبستگی، اضطراب وابستگی و اثرات متقابل آن ها را مورد بررسی قرار دادیم. علاوه بر این، اثر واسطه ایِ خود نظارتی و نظارت اجتماعی بین سبک های دلبستگی و پذیرش e-WOM نیز مورد ارزیابی قرار گرفته است. نتایج نشان داد که اجتناب از وابستگی اثر زیان آوری بر پذیرش e-WOM دارد؛ اضطراب وابستگی و اثر تعاملی تاثیر مثبتی بر پذیرش e-WOM دارند. خود نظارتی و نظارت اجتماعی یک اثر واسطه ای بین دو بعد دلبستگی (اجتناب و اضطراب) دارد و نظارت اجتماعی، واسطه ی پذیرش e-WOM و تعامل اضطراب و اجتناب است.
1- مقدمه
تبلیغات دهان به دهان الکترونیکی (e-WOM) به یک ابزار بازاریابی مهم در عصر رسانه های اجتماعی تبدیل می شود. مصرف کنندگان عادت دارند در سایت های شبکه های اجتماعی مانند فیسبوک و توییتر، اطلاعات را با دیگران به اشتراک بگذارند. تبلیغات دهان به دهان الکترونیکی (e-WOM) اینگونه تعریف می شود: "هر گونه بیان مثبت یا منفی توسط مشتریان بالقوه، مشتریان واقعی یا مشتریان سابق در مورد محصول یا شرکت که از طریق اینترنت برای بسیاری از مردم و موسسات در دسترس است" (هنیگ-تورائو، گووینر، والش و گرملر، 2004).
۵. بحث
در این مطالعه، تلاش کردیم تا پذیرش e-WOM افراد در سایت های شبکه های اجتماعی را از طریق سبک های دلبستگی درک کنیم و به دنبال این بودیم که چرا بررسی محصول/خدمات را در سایت های شبکه های اجتماعی می پذیرند. سبک های دلبستگی نشان داده اند که در این مطالعه تاثیر قابل توجهی بر پذیرش e-WOM در سایت های شبکه های اجتماعی دارند. نشانداده شده که خودنظارتی و نظارت اجتماعی دلیل بازدید کاربران از شبکه های اجتماعی است، به خصوص نظارت اجتماعی به عنوان عامل اصلی پذیرش e-WOM توسط کاربران نگران شناخته شده است.
Abstract
It becomes more and more important for marketers to understand why individuals adopt electronic word-of-mouth (e-WOM) on social networking sites. This paper aims to understand the social networking sites users e-WOM adoption based on the attachment theory. Attachment avoidance, attachment anxiety, and their interaction effects are tested to understand the direct effect on e-WOM adoption. Moreover, the mediating effect of self-surveillance and social surveillance between attachment styles and e-WOM adoption has also evaluated. The results indicated that attachment avoidance has an adverse effect on e-WOM adoption; attachment anxiety and the interactive effect have a positive effect on e-WOM adoption. Self-surveillance and social surveillance have a mediating effect between two attachment dimensions (avoidance and anxiety) and e-WOM adoption, and the interaction of anxiety and avoidance mediated by social surveillance.
1. Introduction
Electronic word-of-mouth (e-WOM) is becoming an important marketing tool in the social media era. Consumers are accustomed to sharing information with others on social networking sites (SNSs), such as Facebook or Twitter. e-WOM is defined as “any positive or negative statement made by potential, actual, or former customers about a product or company, which is made available to a multitude of people and institutions via the Internet” (Hennig-Thurau, Gwinner, Walsh, & Gremler, 2004, 39).
5. Discussion
In this study, we tried to understand personal e-WOM adoption in social networking sites through attachment styles and sought to know why they adopt the product/service reviews in social networking sites. Attachment styles have demonstrated that have a significant effect on eWOM adoption on social networking sites in this study. Self-surveillance and social surveillance have been shown as the reasons why users adopt reviews in the social networking sites, especially, social surveillance as the main cause for fearful users to adopt e-WOM actively.
چکیده
1- مقدمه
2. پیشینه نظری و فرضیات
2.1. پذیرش e-WOM و دلبستگی
2.2. تئوری دلبستگی
2.1.1. تعامل اضطراب و اجتناب
2.3. اثر واسطه ای خود نظارتی و نظارت اجتماعی
3. روش شناسی
3.1. چارچوب مفهومی
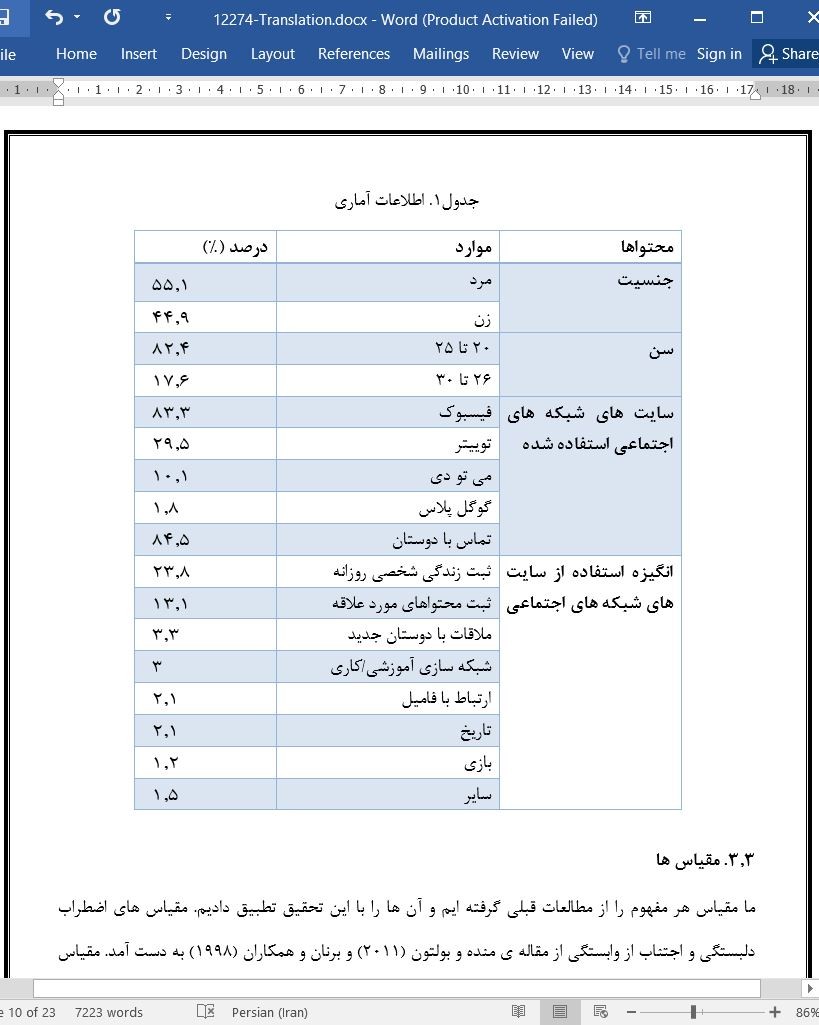
3.2. جمع آوری داده ها و نمونه
3.3. مقیاس ها
4. تجزیه و تحلیل داده و نتایج
4.1تجزیه و تحلیل مدل اندازه گیری
4.2. نتایج بررسی فرضیه
5. بحث
منابع
ABSTRACT
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical background and hypotheses
2.1. e-WOM adoption and attachment
2.2. Attachment theory
2.2.1. Interaction of anxiety and avoidance
2.3. The mediating effect of self-surveillance and social surveillance
3. Methodology
3.1. Conceptual framework
3.2. Sample and data collection
3.3. Measures
4. Data analysis and results
4.1Measurement model analysis
4.2. Results of hypotheses testing
5. Discussion
References
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه