یکپارچه سازی فرایند مسیریابی مبتنی بر اینترنت اشیاء برای مدیریت زنجیره تامین غذا
چکیده
رشد شتابان جمعیت در محدوده های کلانشهری فشار فزاینده ای به مناطق شهری وارد کرده است. راهبرد محوری در قبال شهرهای هوشمند باید شامل راه حلی برای زندگی کلانشهری و محیط بوم شناختی باشد. یکی از حوزه های کاربردی مهم اینترنت اشیاء در شهرهای هوشمند، صنعت غذا است. سامانه های اینترنت اشیاء به پایش، تحلیل، و مدیریت صنعت غذای بلادرنگ در شهرهای هوشمند کمک می کنند. در این پژوهش، ما یک زنجیره ی تأمین غذای پویای مبتنی بر اینترنت اشیاء برای شهرهای هوشمند پیشنهاد می کنیم که نه تنها کیفیت غذا را تضمین می کند بلکه مسیریابی وسایل نقلیه ی هوشمند و نیز رهگیری منشأ آلودگی در مواد غذایی را فراهم می آورد. افزون بر این، یک راهبرد گردآوری داده های حسگرهای هوشمند بر مبنای اینترنت اشیاء مورد استفاده قرار می گیرد که کارایی و صحت شبکه ی زنجیره ی تأمین را با حداقل ابعاد مجموعه داده بهبود می بخشد و با ارائه ی یک الگوریتم مسیریابی وسایل نقلیه، منشأ آلودگی مواد غذایی آلوده در بازارها رهگیری می شود. مدل پیشنهادی ما با یک ارزیابی جامع و فراگیر مورد ارزشیابی قرار می گیرد و در این راستا از مقیاس ها عملکردی گوناگونی همچون پیگیری صحت، تأخیر، زمان اجرا، و زمان پیمایش استفاده می شود. نتایج نشان می دهد که سامانه ی پیشنهادی در مقایسه با رویکردهای موجود عملکرد بهتری دارد.
5- نتیجه گیری
در این مقاله، ما شبکه ی زنجیره ی تأمین غذای مبتنی بر اینترنت اشیاء را ارائه می کنیم که به طور کارامدی محصول غذایی آلوده در درون شبکه ی زنجیره ی تأمین را ردیابی و رهگیری می کند و نیز منشأ محصول غذایی آلوده را تعیین می کند. افزون بر این، ما همچنین مسیریابی وسایل نقلیه ی پویا با استفاده از الگوریتم مستعمره ی زنبور عسل را ارائه می کنیم تا زمان پیمایش و اجرای طی حمل و نقل را به حداقل برساند. در اثر پیشنهادی، ما نخست سامانه ی DPSTT را پیش نهادیم که محصول غذایی آلوده و منشأ اصلی را با استفاده از رویکرد نمونه گیری و تقسیم بندی پویای مبتنی بر برآورد بیز ردیابی و رهگیری می کند و سپس گراف جهت دار غیرمدور (DAG) و طرح پیمایش جست وجوی اول عمق (DFS) محصول غذایی را ردیابی و پیگیری می کند. بر اساس تحلیل نتایج، چنین برمی آید که الگوریتم ردیابی و پیگیری DPSTT ما به صحت ردیابی 3/95 درصدی تحت نرخ نمونه گیری کمینه ی 6/7 درصدی در مقایسه با رویکرد سنتیِ نمونه گیری کلی دست می یابد. افزون بر عملکرد بهتر در زمینه ی صحت ردیابی و پیگیری، ما تحلیل مقایسه ای مدل های مسیریابی پویای پیشنهاد با الگوریتم های موجود ازجمله الگوریتم حریصانه و تخصیص تصادفی بر مبنای پارامترهای مقایسه ای شامل زمان اجرا، زمان پیمایش، و تأخیر را نشان می دهیم. تحلیل ارزیابی عملکرد نشان می دهد که مدل پیشنهادی بهترین مسیر بهینه را پیشنهاد می کند که کم ترین زمان پیمایش، کم ترین تأخیر، و کم ترین زمان اجرا را فراهم می آورد. در این مقاله، ما پیشنهاد کردیم که همه ی اطلاعات منابع مواد غذایی با یک انبار مرکزی مقایسه شود و این منابع فراداده به شکل یکنواخت و یکدستی نظام مند شوند. در آینده، این مقاله را می تواند به نحو زیر گسترش و تعمیم داد: 1) انجام وظایف رایانش ابری در خود لبه ی شبکه برای بهینه سازی بیش تر تأخیر و مصرف کم تر انرژی. 2) کاربرد عملی و واقعی زنجیره ی تأمین غذا در یک جامعه به عنوان بستر آزمایش برای یک مدیریت کلانشهری.
Abstract
The rapid growth of population in metropolitan areas has put incremental pressure on urban cities. The centric strategy towards smart cities are expected to cover solution for metropolitan life and ecological environment. One of the significant application areas of IoT in smart cities is the food industry. IoT systems help to monitor, analyze, and manage the real-time food industry in smart cities. In this research, we proposed an IoT based Dynamic Food Supply Chain for Smart Cities which not only ensures the food quality but also provides intelligent vehicle routing as well as tracing sources of contamination in FCM. Furthermore, a smart sensor data collection strategy based on IoT is utilized which would improve the efficiency and accuracy of the supply chain network with the minimized size of dataset and vehicle routing algorithm is introduced and tracing the contamination sources of infected food in the markets. Our proposed model is evaluated with the comprehensive evaluation and used various performance metrics such as tracing accuracy, delay, execution time, and traveling time. The results show that the proposed system outperforms when compared with existing approach.
5. Conclusion
In this paper, we present IoT based Food Supply chain network that efficient trace and track the contaminate food product within supply chain network and also determine the source of contaminated food product. Moreover, we also present dynamic vehicle routing using Bee Colony algorithm to minimize the traveling and execution time during transportation. In the proposed work first, we proposed DPSTT system that trace and track the contaminated food product and root source using Bayesian estimation based dynamic sampling and portioning approach and later trace and track the food product DAG graph and DFS traversal scheme. From result analysis, it is indicated that our DPSTT tracing and tracking algorithm achieve tracing accuracy of 95.3% under minimum sampling rate of 7.6% in comparison to traditional global sampling approach. In addition to outperforming tracing accuracy, we demonstrate comparison analysis of proposed dynamic routing models with existing algorithms including greedy and random allocation based on comparison parameters including execution time, traveling time, and delay. The performance evaluation analysis illustrates that the proposed model suggests the best optimal path that provides minimum traveling time, minimum delay and minimum execution time. In this work, we supposed that all source information of foodstuff is compared by a central repository and these metadata sources are systematized in a uniform way. In future, this work can be extended by (1) performing cloud computation tasks at the network edge itself for more delay optimization and less energy consumption. (2) Real-world application of the provenance of the food supply chain in a community as our testing bed for megacity management.
چکیده
1- مقدمه
2- آثار مرتبط
3- روش شناسی
3-1 شبکه ی زنجیره ی تأمین غذای مبتنی بر اینترنت اشیاء
3-1-1 تولیدکننده ی غذا
3-1-2 مرکز انبار کارخانه ی تولیدی
3-1-3 صنعت پردازش و بسته بندی غذا
3-1-4 انبار تأمین غذا و مرکز توزیع
3-1-5 فروشگاه
3-1-6 مصرف کننده
3-1-7 رایانش ابری
3-1-8 پیمانه ی ردیابی و پیگیری آلودگی غذا
3-1-9 پیمانه ی مولد مسیر وسایل نقلیه (VRG)
3-2 مدل مسیریابی وسایل نقلیه بر مبنای مستعمره ی مورچگان
3-2-1 شبکه ی جاده و وسایل نقلیه
3-2-2 مسیریابی وسایل نقلیه ی پویا با بهینه سازی مسیر مستعمره ی مورچگان
3-2-3 اعلان هشدار
4- نتایج و بحث
4-1 گردآوری داده ها
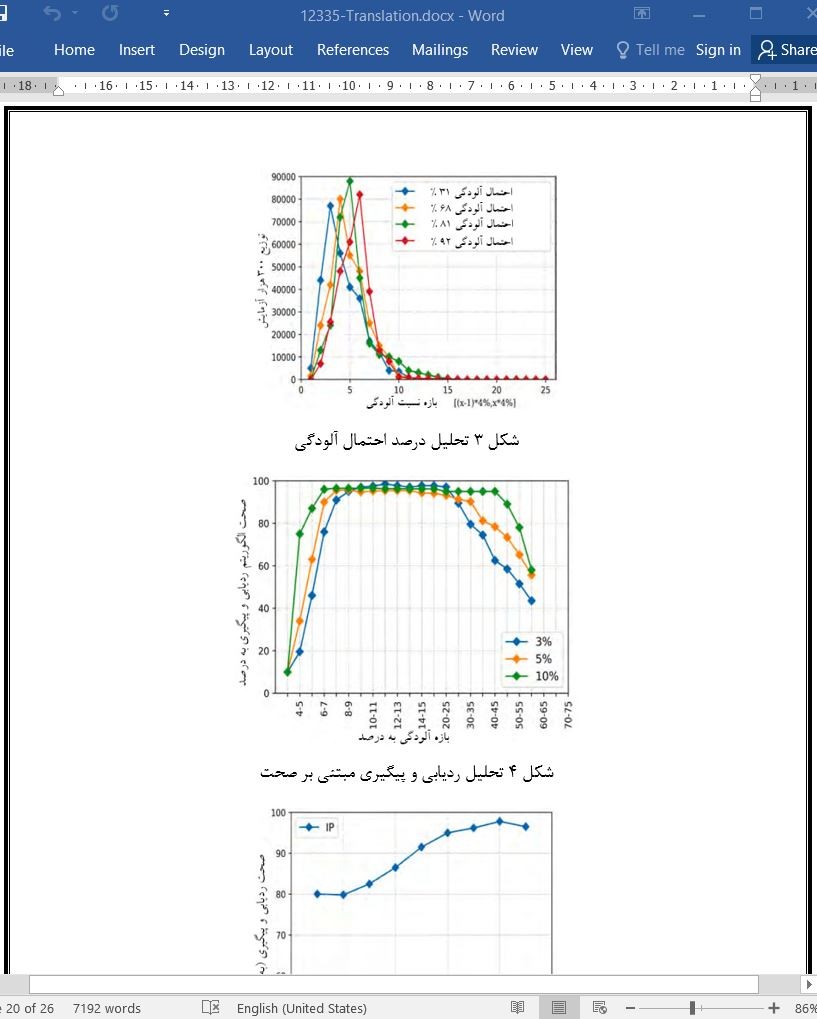
4-2 تحلیل صحت سامانه ی DPSTT
4-2-1 سناریوی 1
4-3 سناریوی 2
4-4 تحلیل مقایسه ای میان DVRACRO پیشنهادی و الگوریتم موجود بر مبنای زمان پیمایش
4-5 تحلیل مقایسه ای میان DVRACRO پیشنهادی و الگوریتم موجود بر مبنای زمان اجرا
5- نتیجه گیری
منابع
ABSTRACT
1. Introduction
2. Related works
3. Methodology
3.1. IoT based Food Supply Chain Network
3.1.1. Food producer (FP) At this stage we deployed various IoT sensors at farm land to gather
3.1.2. Manufacturing Warehouse Centre (MWC)
3.1.3. Food processing and packaging industry
3.1.4. Food supply warehouse and distribution center (FSWDC)
3.1.5. Supermarket
3.1.6. Consumer
3.1.7. Cloud computation
3.1.8. Contaminate food tracing and tracking (CFT) module
3.1.9. Vehicle route generator (VRG) module
3.2. Ant colony based vehicle routing model
3.2.1. Road and vehicle network
3.2.2. Dynamic vehicle routing with ant colony route optimization
3.2.3. Alert notification
4. Result and discussion
4.1. Data collection
4.2. Accuracy analysis of DPSTT system
4.2.1. Scenario 1
4.3. Scenario 2
4.4. Comparative analysis between proposed DVRACRO and existing algorithm based on traveling time
4.5. Comparative analysis between proposed DVRACRO and existing algorithm based on execution time
5. Conclusion
References
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه