چهارچوبی برای پیاده سازی سیستم های برنامه ریزی منابع سازمان، در سازمان های کوچک و متوسط
چکیده
امروزه، سازمان های کوچک و متوسط(SMEs)، با چالش های جهانی و تغییرات مداوم در تقاضای مشتری، اخیراَ هم با کووید۱۹ و انتظار یک بیماری حاد تنفسی همه گیر(SARS) در آینده که چالش های بیشتری را ایجاد می کنند، روبرو هستند، بنابراین، سازمان های کوچک و متوسط(SMEs)، نیاز به اتوماسیون منعطف به منظور پاسخگویی سریع تر نسبت به این تغییرات دارند. با انتقال به اقتصاد دیجیتال، استفاده از فناوری های هوش مصنوعی(AI)، ادغام فرایندهای کسب و کار و داشتن اطلاعات به روز که مدیریت سطح بالای سازمان را قادر به اخذ تصمیمات بهتر، سریع ترو آگاهانه می کند، می توان به این هدف دست یافت. برنامه ریزی منابع سازمان(ERP) یکی از راه حل ها برای SMEs به منظور غلبه بر این چالش ها و دست یافتن به مزیت رقابتی است. Subanidja, and Broto, 2019 در مطالعه شان بیان می کنند که سیستم های ERP آن طور که در کسب و کارهای بزرگ معرفی شده اند، هنوز در سازمان های کوچک و متوسط(SMEs)، به کار گرفته نشده اند. اگرچه، SMEs شهرت قابل توجیهی در فعال بودن، تمایل و پذیرا بودن نسبت به تطبیق با فناوری های جدید، مفاهیم و بهبودها دارند. هم چنین، SMEs در چندین خصوصیت ذاتی که احتمالاَ بر پیاده سازی سیستم برنامه ریزی منابع (ERP) تأثیر گذار است، متفاوت هستند، بدین ترتیب، به نظر نمی رسد که استفاده از چهارچوب یکسان که برای شرکت های بزرگ، ایجاد شده اند، برای پیاده سازی سیستم ERP در SMEs کار درستی باشد. یکی از ریسک های اصلی در تطبیق ERPدر SMEs این مورد است که SMEs ها منابع محدودی دارند، بنابراین، آن ها نمی توانند در پیاده سازی سیستم ERP شکست بخورند. بدین ترتیب، هدف از این مطالعه، کشف فرایند پیاده سازی ERP در محیط SMEs است. چهار چوب ایجاد شده به منظور پیاده سازی سیستم ERPدر SMEs مورد استفاده قرار گرفته است. در هنگام پیاده سازی سیستم ERP در SMEs ، موضوعاتی نظیر حدود روند پیداه سازی که به وضوح تعریف شده، برنامه ریزی پروژه مناسب و حداقل سفارشی سازی سیستم منتخب برای پیاده سازی، نیاز به شناسایی دارند. این مطالعه هم در تحقیق و هم در عمل اجرا شده است و یافته های تحقیق می تواند به متخصصان وسازمان های SMEs کمک کند وزمانیکه پروژه های ERP آغاز شده اند، به عنوان راه های تحقیقاتی آینده پیشنهاد شود.
6. نتیجه گیری
اهمیت سیستم ERP به منظور حمایت از SMEs تا حد زیادی شناخته شده است. بدین ترتیب، هدف اصلی از این مطالعه ایجاد چهارچوبی به منظور کمک به SMEs در پیاده سازی سیستم ERP و مشخص کردن موضوعات مورد نیاز در طول پیاده سازی سیستم ERP است. چهارچوب ایجاد شده در این مقاله شامل ۹ فاز است که هر فاز دارای ورودی، پردازش ها و خروجی می باشد.کاربرد این چهارچوب از طریق مطالعه موردی شرکتی که در پیاده سازی سیستم ERP، چهارچوب این فازها را به کار گرفته است، توضیح داده شده است. این مطالعه به تحقیقات در حال انجام در مورد پیاده سازی سیستم ERP در SMEs کمک می کند. SMEs با در نظر داشتن پیاده سازی سیستم ERP در آینده، می توانند از چهارچوب ایجاد شده توسط این مطالعه و با پیروی از گام ها و فازهای مناسب که هم چنین در این مطالعه نشان داده شدند، استفاده کنند. تغییرات ایجاد شده توسط covid-19 در کسب و کارها به طرز چشمگیری متناوباَ روابط بین افراد و کسب و کار را درباره استخدام، مشتری، خرده فروشان، عرضه کنندگان وارائه دهندگان خدمات تغییر داده، سازمان بهداشت جهانی(WHO) تأکید کرده که احتمال همه گیری (SARS) است. این چهارچوب، روش شناسی برای SMEs فراهم می کند که «برنده بازی » باشند.
Abstract
Today Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) face global challenges and continuous change in consumer demands, most recently COVID-19 and the prospect of a future Serious Acute Respiratory (SARS) pandemic generating further challenges, thus SMEs require to be more flexible to respond quickly to these changes. This can be achieved by transformation into the digital economy, use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) techniques, integrating business processes and to have real-time information which will enable senior management to make better, quicker informed decisions. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is one of the solutions for the SMEs to overcome these challenges and to obtain a competitive advantage. Subanidja, and Broto, 2019 stated that ERP systems are still not widely implemented by SMEs compared to their introduction in large businesses. However, the SME have a justifiable reputation for being proactive, open, willing and receptive to the adoption of new technologies, concepts and improvements. Also, SMEs differ in several inherent characteristics which are likely to impact on the ERP system implementations, hence it does not make sense to use the same frameworks that have been developed for large companies to implement ERP system within SMEs. One of the main risks of adopting ERP in SMEs is that SMEs have limited resources, so they cannot afford to fail to implement ERP system. Therefore, the purpose of this study is to explore ERP implementation process in SME context. The developed framework has been used to implement an ERP system in a SME. It highlighted the issues that need to be addressed while implementing ERP system in SMEs such as clearly defined scope of implementation procedure, suitable project planning and minimal customisation of the system selected for implementation. This study contributed to both research and practice and the research findings could aid practitioners and SMEs when embarking on ERP projects, as well as, to suggest future research avenues.
6. Conclusion
The importance of ERP system for supporting SMEs has been widely recognised. Therefore, the main objective of this study was to develop a framework to assist SMEs to implement ERP system and to highlight issues that need to be addressed during implementing the ERP system in the SMEs. The developed framework in this paper consist of nine phases where each phase has input, processes, and output. The applicability of the framework was explained through a case study of a company that employed a phases of implementation of the framework. This study contributes to the on-going research on implementation of ERP systems in SMEs. SMEs considering the implementation of ERP systems in future, can use the developed framework in this study by following the appropriate steps and phases which have also been demonstrated in the case study. The business changes generated by COVID-19 dramatically alternate the individual and business relationship regarding employment, customer, retailer, supplies, and service provided, the World Health Organization (WHO) has indicated the probability of further SARS pandemic. This framework provides a methodology for SMEs to be ‘ahead of the game’
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. روش شناسی
3. پیشینه شرکت
4. چهارچوب ایجاد شده
1.4.فاز۱: تحلیل فرایند
2.4. فاز۲: ساختن محدوده کار(SOW)
3.4. فاز۳: ایجاد طرح پروژه
4.4. فاز۴: ساخت سیستم
5.4. فاز۵: آماده سازی رویه های عملیاتی استاندارد(SOP)
6.4. فاز۶: ایجاد طرح انتقال داده
7.4. فاز۷: آزمون های پذیرش کاربر
8.4. فاز۸: آموزش کاربران
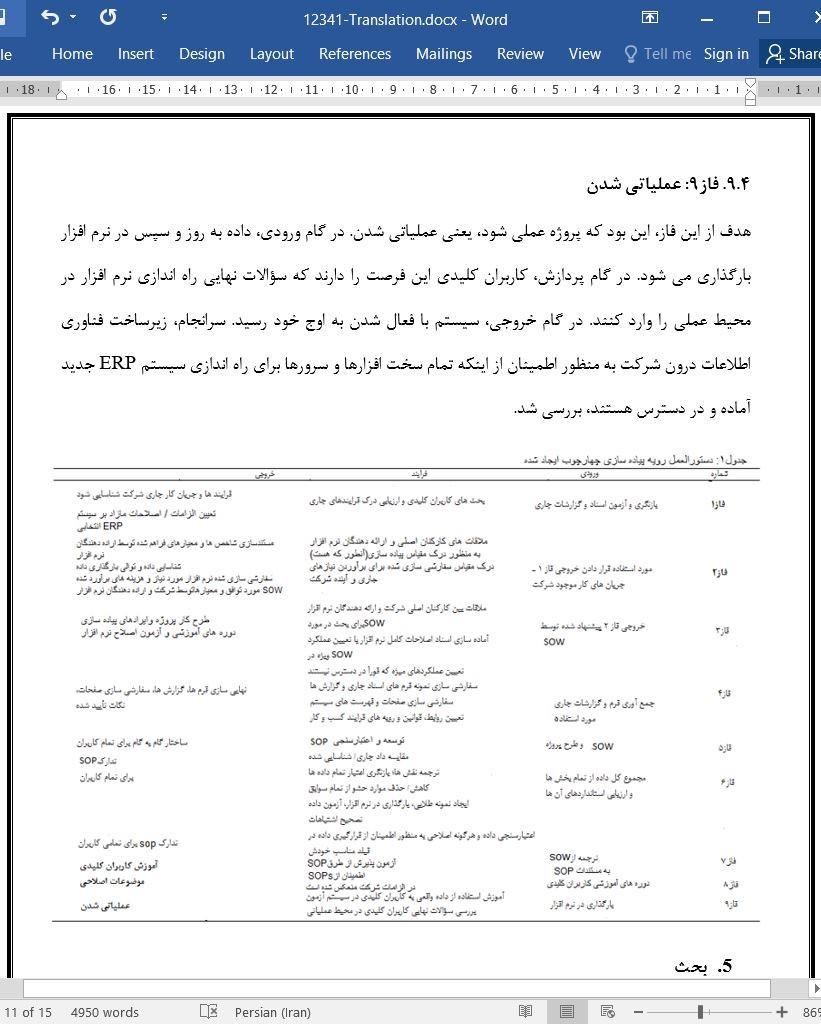
9.4. فاز۹: عملیاتی شدن
5. بحث
6. نتیجه گیری
7. محدودیت ها
8. مسئولیت نویسندگان
9. منابع
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
3. Company Background
4. Developed Framework
4.1. Phase 1: Process Analysis
4.2. Phase 2: Preparing the Scope of Work (SOW)
4.3. Phase 3: Creating a Project Plan
4.4. Phase 4: Build the System
4.5. Phase 5: Preparing the Standard Operating Procedures (SOP)
4.6. Phase 6: Creating a Data Migration Plan
4.7. Phase 7: User Acceptance Tests
4.8. Phase 8: User Training
4.9. Phase 9: Go – Live
5. Discussion
6. Conclusion
7. Limitation
8. CRediT authors statement
9. Reference
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه