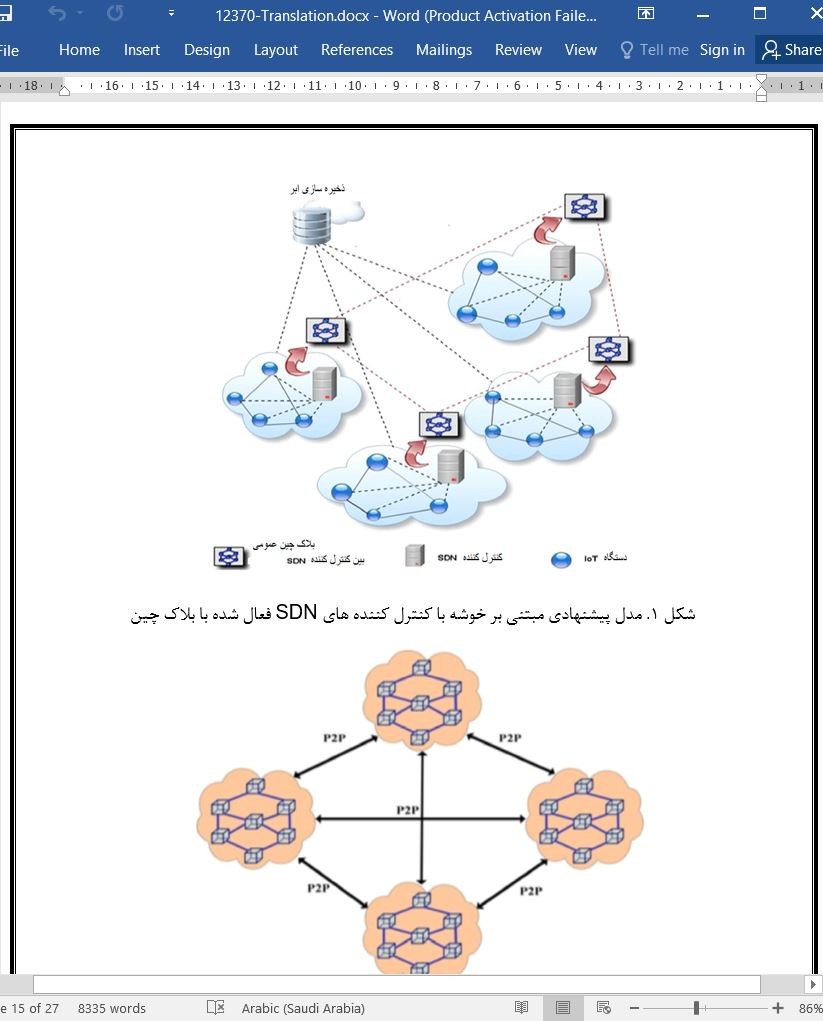
معماری امنیتی یکپارچه مبتنی بر AI، بلاک چین و SDN برای شبکه IOT
چکیده
اینترنت اشیا (IOT)، یکی از جدیدترین فناوری های امروزی است و یکی از توانمدسازهای کلیدی سیستم فیزیکی سایبری صنعتی (CPS) است. تقریباً در هر جنبه ای از زندگی اجتماعی ما از مبادلات مالی گرفته تا سیستم مراقبت های بهداشتی، ارتباطات و امنیت ملی، میدان جنگ تا خانه های هوشمند و غیره سهم دارد. با این حال، استقرار گسترده¬ی اینترنت اشیا با مشکلات خاصی مانند قابلیت همکاری، سازگاری، ناهمگونی، حجم زیاد داده، پردازش داده های ناهمگن و غیره نیز مواجه است. در این میان، بهره وری انرژی و امنیت مهمترین موضوعات هستند. منابع رایانش کمیاب دستگاههای اینترنت اشیا مانعی برای اشتراک اطلاعات در لبه یا شبکه اینترنت اشیا ایجاد می کنند. در واقع تداخل ناخواسته یا مخرب با داده های اینترنت اشیا ممکن است منجر به مشکلات شدیدی شود. در این تحقیق، محقق مزایای احتمالی یک سیستم بلاک چین را بیان می کند و آن را با شبکه نرم افزار محور (SDN) ادغام می کند، ضمن اینکه مباحث انرژی و امنیت را توجیه میکند. محقق با جزئیات بیشتر یک پروتکل مسیریابی جدید با ساختار خوشه ای برای شبکههای IOT با استفاده از معماری مبتنی بر بلاک چین برای کنترل کننده SDN پیشنهاد کرد. معماری پیشنهادی، گواهی اثبات کار (POW) با بلاک چین های عمومی و خصوصی را برای ارتباطات نظیر به نظیر (P2P) بین کنترل کننده های SDN و دستگاههای IOT رفع می کند. علاوه بر این، مکانیسم احراز هویت توسعه یافته مبتنی بر اعتماد، بلاک چین را برای دستگاه های اینترنت اشیا با منابع محدود بیشتر مورد پذیرش قرار میدهد. نتایج تجربی نشان میدهند که پروتکل مسیریابی مبتنی بر ساختار خوشه ای پیشنهادی از بردار فاصله بر حسب درخواست در شبکه ادهاک (AODV) پیشرفته، بردار فاصله توالی مقصد (DSDV)، شبکه حسگر موبایل امن (SMSN)، تشخیص خطای توزیع شده مبتنی بر خوشه با انرژی کارآمد (EESCFD)، و بردار فاصله چند مسیری بر حسب تقاضای ادهاک (AOMDV) از نظر مصرف انرژی، و توان عملیاتی شبکه، و تأخیر بسته عملکرد بهتری دارد. پروتکل پیشنهادی به غلبه بر مسائل به ویژه مدیریت انرژی و امنیت نسل بعدی سیستم های فیزیکی سایبری صنعتی کمک می کند.
1. مقدمه
خودکار سازی صنعتی بر اساس هوش مصنوعی (AI) و اینترنت اشیا (IOT) منجر به مفهوم کارخانه هوشمند می شود. مدیریت زنجیره تامین انطباقی، ادغام انسان و ربات، کیفیت تولید و نگهداری پیش بینی کننده، نمونه هایی از اتوماسیون صنعتی و سیستم های فیزیکی سایبری (CPS) هستند. تعداد زیادی از حسگرها در زمینه اتوماسیون صنعتی کارآمد و موثر مستقر می شوند و چنین استقرار گسترده ای منجر به مسائل مربوط به قابلیت همکاری، ناهمگونی بین دستگاهها، پردازش و داد و ستد کلان داده ها، ذخیره سازی سازی داده ها، مدیریت انرژی، ایمنی و امنیت میشود.
5. نتیجه گیری و تحقیقات آینده
نسل بعدی سیستم های فیزیکی سایبری صنعتی (CPS) نیازبه راه حل های مبتنی بر هوش مصنوعی (AI) دارند تا بر مشکلات ناهمگونی دستگاهها، تولید کلان دادهها توسط حسگرها، جریان داده ها، پردازش داده های ساخت نیافته ناهمگن و امنیت داده ها غلبه کنند. روند رو به افزایش خدمات هوشمند و باهوش با سقوط ناگهانی در شبکه SDN و خدمات مرتبط با آن ها راه اندازی می شود. برای ارائه خدمات امن و کارآمد نیاز فوری برای مدیریت مسئله کمبود انرژی و رایانش IOT وجود دارد. این تحقیق بر کاهش برخی از چالش های مرتبط با شبکه اینترنت اشیا تمرکز می کند. ما با استخراج قدرت هوش مصنوعی، معماری را برای شبکه های اینترنت اشیا پیشنهاد کردهایم تا امنیت را افزایش دهیم و بهرهوری انرژی را بهبود دهیم. ما دو فناوری در حال ظهور مبتنی بر هوش مصنوعی یعنی بلاک چین و SDN را یکپار چه کردیم و از مزایای احتمالی آنها از نظر تحلیل کارآمد دادهها، امنیت داده ها و مدیریت انرژی کارآمد استفاده کردیم. برای شبکه IOT با پشتیبانی از بلاک چین برای کنترل کننده SDN یک چارچوب مبتنی بر خوشه معرفی شد. در شبکه های عمومی و خصوصی بلاک چین استفاده می شود. مولفه تشنه به منبع POW حذف میشود تا بلاک چین را برای قابلیت اینترنت اشیا تنظیم کند. این روش باعث صرفه جویی زیادی در انرژی می شود، سرعت انتقال داده ها را افزایش میدهد و تأخیر را کاهش میدهد. آزمایش های گسترده نشان داده است که مدل پیشنهادی نسبت به رویکرد اصلی بلاکچین و پروتکل های مسیریابی فعلی بهتر عمل می کند. ما با این تحقیق در حوزه اینترنت اشیا امیدواریم که در آینده یک معماری P4 سطح بالا با پشتیبانی از بلاک چین را توسعه دهیم.
Abstract
Internet of things (IoT) is one of the most emerging technologies nowadays and it is one of the key enablers of industrial cyber physical system (CPSs). It has started to participate in almost every aspect of our social life, ranging from financial transactions to the healthcare system, communication to national security, battlefield to smart homes, and so on. However, the wide deployment of IoT suffers certain issues as well, such as interoperability, compatibility, heterogeneity, large amount of data, processing of heterogeneous data etc. Among others, energy efficiency and security are the utmost prominent issues. Scarce computing resources of IoT devices put hindrances on information sharing across edge or IoT network. Indeed, unintentional or malicious interference with IoT data may lead to severe concerns. In this study, the researcher exploits the potential benefits of a blockchain system and integrates it with software-defined networking (SDN) while justifying energy and security issues. More in detail, the researcher proposed a new routing protocol with the cluster structure for IoT networks using blockchain-based architecture for SDN controller. The proposed architecture obviates proof-of-work (PoW) with private and public blockchains for Peer-to-Peer (P2P) communication between SDN controllers and IoT devices. In addition to this, distributed trust-based authentication mechanism makes blockchain even more adoptive for IoT devices with limited resources. The experimental results show that the proposed cluster structure based routing protocol outperforms the state-of-the-art Ad-hoc On-demand Distance Vector (AODV), Destination-Sequenced Distance Vector (DSDV), Secure Mobile Sensor Network (SMSN), Energy efficient secured cluster based distributed fault diagnosis (EESCFD), and Ad-hoc On-demand Multipath Distance Vector (AOMDV), in terms of energy consumption, network throughput, and packet latency. Proposed protocol help overcome the issues especially, energy management and security of the next generation industrial cyber physical systems.
1. Introduction
Industrial automation leads to the concept of smart factory on the basis of artificial intelligence (AI) and internet of things (IoT). Adaptive supply chain management, human–robot integration, production quality and predictive maintenance are a few examples of the industrial automation and cyber physical systems (CPSs). A huge number of sensors are deployed in the field for effective and efficient industrial automation and such a vast deployment lead to the issues of interoperability, heterogeneity among devices, processing and dealing of big data, storage of data, energy management, safety and security.
5. Conclusion and future work
Next generation industrial cyber physical systems (CPSs) require artificial intelligence (AI) empowered solutions to overcome the issues of heterogeneity of devices, big data generation by the sensors, data streaming, processing of heterogeneous unstructured data and the data security. The increasing trend of smart and intelligent services triggers the avalanche in the IoT network and their related services. To provide secure and efficient services, there is an urgent need to manage the computing and energy scarcity problem of IoT. This study focuses on mitigating some of the challenges related to IoT’s network. By exploiting the power of AI, we have proposed architecture for IoT networks to enhance security and improve energy efficiency. We integrated the two emerging AI based technologies namely, blockchain and SDN, and leverage their potential benefits in terms of efficient data analysis, data security and efficient energy management. For the IoT network with blockchain support for the SDN controller, a cluster-based framework was introduced. On both public and private networks, the blockchain is used. The resource-hungry component of PoW is eliminated to tailor the blockchain for IoT capabilities. This method saves a large amount of energy, boosts data transfer rates, and reduces latency. Extensive testing has shown that the proposed model outperforms both the basic blockchain approach and current routing protocols. This study will In the IoT domain, we hope to develop a high-level P4 architecture with blockchain support in the future.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. بررسی ادبیات
3. مدل سیستم پیشنهادی
3.1. مکانیسم انتقال داده در دامنه SDN
3.2. سفارشی سازی بلاک چین ها برای بهبود امنیت و بهرهوری انرژی
4. آزمایش ها و نتایج
4.1. راه اندازی آزمایشی
4.2. ارزیابی عملکرد
4.2.1. توان عملیاتی
4.2.2. تاخیر پایان به پایان
4.2.3. مصرف انرژی
5. نتیجه گیری و تحقیقات آینده
منابع
ABSTRACT
1. Introduction
2. Literature review
3. Proposed system model
3.1. Data transfer mechanism in SDN domain
3.2. Customizing blockchains to improve security and energy efficiency
4. Experiments and results
4.1. Experimental setup
4.2. Performance evaluation
4.2.1. Throughput
4.2.2. End-to-end delay
4.2.3. Energy consumption
5. Conclusion and future work
References
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه