سیستم های پشتیبانی از تصمیم برای تیم سازی
چکیده
مقاله حاضر به بحث درباره مساله عامل نرم در سیستم های پشتیبانی از تصمیم در تیمسازی می پردازد. مقاله حاضر از رویکرد جورسازی برای حل و فصل عوامل تشکیل تیم با ماهیت روان شناختی بهره می برد. موضوع مقاله حاضر شامل مفهوم نظری، روش تجربی و فناوری نرم افزاری برای بهینه سازی و اتوماسیون تصمیمات مربی درباره سازمان تیمی می باشد. رویکرد نویسنده درباره تکنیک جدید تشکیل گروه هدف، با توجه به اثربخشی و کارایی کار تیمی می باشد. تکنیک مزبور به پیاده سازی الگوریتم بهینه سازی بر اساس تجزیه و تحلیل ریاضی عوامل غیرافزایشی و پیچیده تعامل گروهی می پردازد. مدل های جورسازی برای ارزیابی و پیش بینی چنین اثراتی مانند تعریفگری و مشارکت پیشنهاد شدند. یک سیستم خبره به عنوان راه حلی مهندسی برای شبیه سازی عددی ارائه شده است. این نوع سیستم پشتیبانی از تصمیم موسوم به سیستم خبره آزمایش بوده و مبتنی بر تشخیص های حرفه ای و روان شناختی کار تیمی است.
4. نتیجه گیری
این تکنیک به کاربر اجاز می دهد تا در کوتاه ترین زمان به ایجاد ترکیب بهینه ای از گروه های هدف برای حل امور خاص، برای پیش بینی عملکرد کلی خود، نظارت بر پیشرفت در کیفیت کار تیمی، برای محاسبه نقشآفرینی فردی در کار تیمی و تعیین اثربخشی هزینه های فردی و گروهی برای رسیدن به هدف بپردازد.
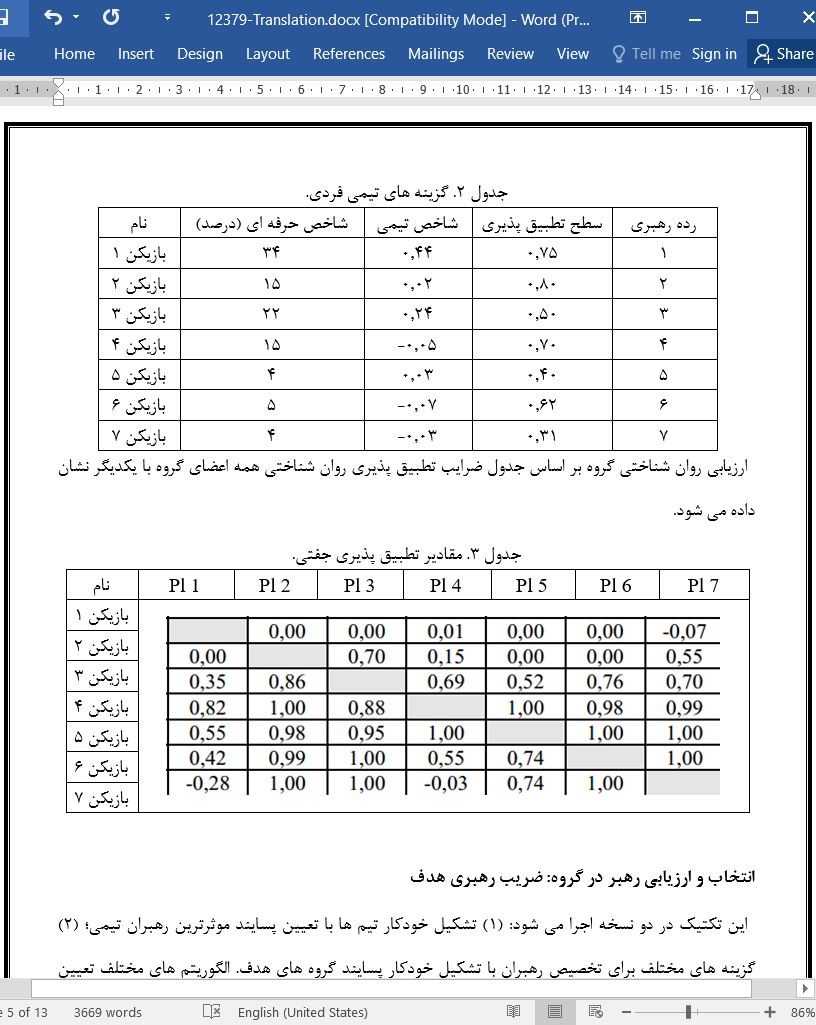
فناوری پیشرفته مبانی زیر را محقق می سازد: (1) ایجاد گروه های حرفه ای که به صورت بهینه برای حل امور مربوطه طراحی شدند؛ (2) انتخاب بهینه تیم موثر و رهبران کاری برای امور مربوطه؛ (۳) انتخاب بهینه نقش های تیمی و مناصب کاری اعضای گروه؛ (۴) تطبیق پذیری روان شناختی بهینه اعضای گروه؛ (۵) بهینه سازی کمّی گروه های هدف بر اساس معیار اثربخشی کار تیمی؛ (۶) نظارت بر پیشرفت کار تیمی کنونی گروه.
سیستم خبره کارکنان برای نمونه ای از تشکیل و ارزیابی کار تیمی تیم های پروژه، تشکیل و تدارک تیم های ورزشی، مطالعه کار تیمی در شرایط سخت (امدادگران، واحدهای آتش نشانی، خدمه قطار) و نیز برنامه ریزی طراحی سازمانی در ساختارهای تجاری و دولتی، مورد آزمایش و تطابق پذیری قرار گرفت.
Abstract
The article discusses the problem of soft factor in decision support systems for teambuilding. This paper initializes a match approach to solve the team formation factors with psychological nature. The subject of this article includes theoretical concept, experimental method and software technology for optimization and automation coacher decisions about team organization. Author’s approach concerns the new technique of target group formation, taking into account the effectiveness and efficiency of teamwork. The technique implements optimization algorithm based on mathematical analysis of non-additive and complex factors of group interaction. Match models for measuring and prediction to such effects as complimentarily and participation are proposed. As an engineering solution, an expert system for teambuilding simulation is demonstrated. This type of decision support system is called the test expert system and is based on the professional and psychological diagnostics of teamwork.
4. Conclusions
The technique allows the user in the shortest time to create optimal composition of target groups for the solution of specific tasks, to predict their total performance, to monitor progress in the quality of teamwork, to calculate the individual contributions to the teamwork and to determine the effectiveness of individual and group expenses to achieve the goal.
The developed technology satisfies the following principles: (1) creation of professional groups that are optimally designed to solve the corresponding task; (2) optimal choice of effective team and work leaders for the tasks; (3) optimal selection of team roles and work positions for group members; (4) optimal psychological compatibility of group members; (5) quantitative optimization of target groups on teamwork effectiveness criteria; (6) monitoring the progress of the current teamwork of the group.
The ‘Staff Expert System’ has been tested and adapted on the example of the formation and evaluation teamwork of project teams, formation and provision of sports teams, studying teamwork in extreme conditions (rescuers, fire brigades, train crews), as well as planning of organizational design in commercial and government structures.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. روش ها
2.1. تکنیک تشکیل
2.2. الگوریتم تشکیل
3. نتایج
3.1. رسمی سازی
3.2. پیاده سازی
4. نتیجه گیری
منابع
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Technique of formation
2.2. Formation algorithm
3. Results
3.1. Formalization
3.2. Implementation
4. Conclusions
References
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه