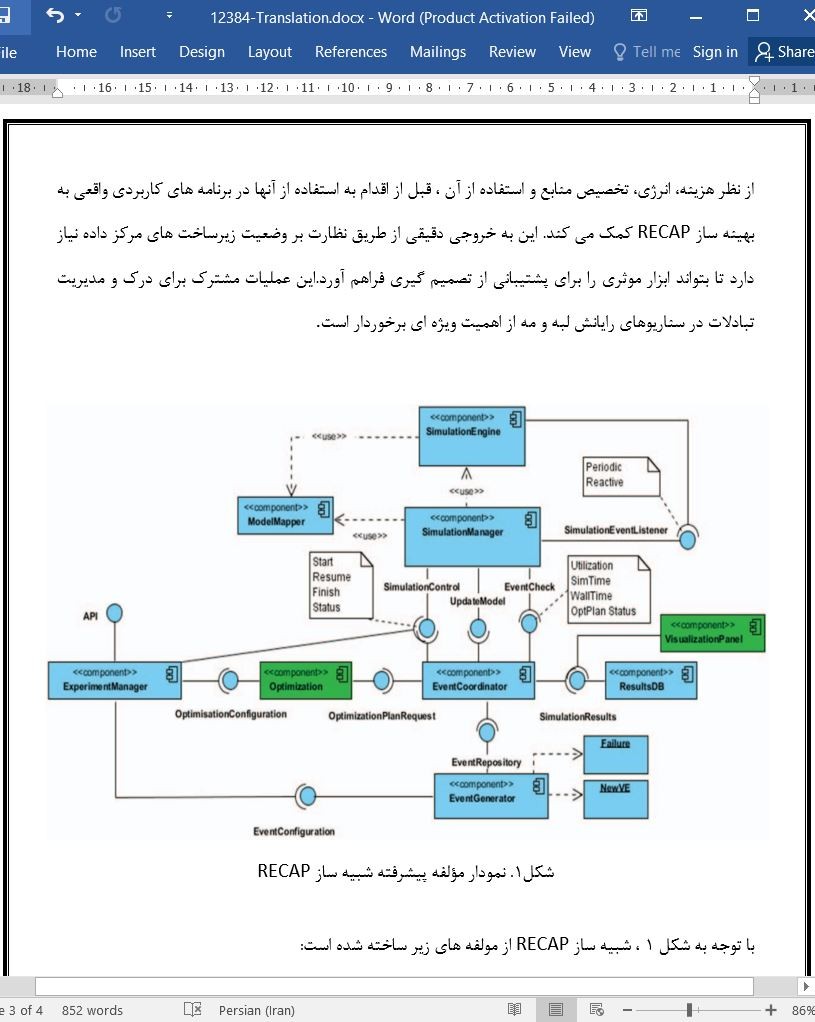
شبیه ساز RECAP: شبیه سازی سناریوهای رایانش ابری / لبه / مه
چکیده
با توجه به روند فزاینده ای که نسبت به رایانش لبه و مه وجود دارد، هدف شبیه ساز REACAP این است که سناریوهای مقیاس بزرگ را در فضای رایانش ابری، مه و لبه شبیه سازی کند تا پشتیبانی از تصمیم گیری و کنترل را برای مدیریت نرم افزار و منبع مرکزی داده ها فراهم آورد. این امر از طریق شبیه سازی نرم افزار و زیر سیستم های نرم افزار، شبیه سازی منابع زیرساختی و سیستمهای مدیریت منابع و آزمایش و اعتبارسنجی نتایج شبیه سازی محقق خواهد شد. شبیه ساز RECAP و مدلهای مرتبط از درک تأثیرگذاری بر منابع، معیارهای بار کاری و میزان خدمات (QoS) و همچنین تبادلات به منظور بهره وری انرژی و هزینه در سناریوهای رایانش ابری ، لبه و مه پشتیبانی کرده و آنها را پیش بینی می کند، ضمن اینکه توافقات سطح سرویس (SLAs) کاربران را حفظ می نماید.
1. مقدمه
امروزه سیستمهای محاسباتی در مقیاس بزرگ به صورت سیستمهای توزیع شده ساخته می شوند، درجاییکه مؤلفه ها و خدمات به دلایل مقیاس، ناهمگونی، هزینه و بهره وری انرژی از طریق کلاینتها و دستگاه ها از راه دور توزیع می شوند و قابل دسترس هستند. مولفه های برخی سیستم ها، بخصوص سیستمهای حساس به تاخیر یا سیستمهای بسیار قابل دسترس، نیز به منظور افزایش قابلیت اطمینان و کاهش تأخیر در جای نزدیکتری به کاربران نهایی قرار دارند، که به این سبک محاسبه اغلب رایانش لبه یا مه می گویند. با این وجود، در حالیکه سالهای اخیر شاهد پیشرفتهای چشمگیری در تجهیزات سیستم و همچنین اتوماسیون و بهره وری انرژی مرکز داده ها بوده است، منابع محاسباتی و ظرفیت شبکه اغلب با استفاده از مدلهای سرویس best-effort و مکانیسمهای QoS درشت دانه حتی در مراکز داده پیشرفته تامین می شوند. این محدودیتها به عنوان یک مانع بزرگ پیش روی تکامل آتی اینترنت اشیاء (IoT) و جامعه شبکه مند دیده می شوند که پیش بینی می شود به میزان قابل توجهی بار شبکه ها و مراکز داده را افزایش دهند (Ostberg و همکاران، 2017).
Abstract
With the increasing trend towards edge and fog computing, the aim of the RECAP simulator is to simulate large scale scenarios in the cloud, fog and edge computing space in order to provide decision and control support for application and data center resource administration. This will be accomplished through the simulation of applications and application subsystems, simulation of infrastructure resources and resource management systems, and experimentation and validation of simulation results. The RECAP simulator and associated models will provide support for understanding and predicting impact on resources, workloads and quality of service (QoS) metrics as well as trade-offs for energy efficiency and cost within cloud, edge and fog computing scenarios, while maintaining the service level agreements (SLAs) of users.
1 INTRODUCTION
Large-scale computing systems are today built as distributed systems, where components and services are distributed and accessed remotely through clients and devices for reasons of scale, heterogeneity, cost and energy efficiency. In some systems, in particular latency-sensitive or high availability systems, compo- nents are also placed closer to end-users in order to increase reliability and reduce latency, a style of com- puting often referred to as edge or fog computing. However, while recent years have seen significant ad- vances in system instrumentation as well as data center energy efficiency and automation, computational resources and network capacity are often provisioned using best-effort models and coarse-grained QoS mechanisms, even in state-of-the-art data centers. These limitations are seen as a major hindrance in the face of the coming evolution of the Internet of Things (IoT) and the networked society, which are project- ed to significantly increase the load on networks and data centers (Ostberg et. al, 2017).
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. شبیه ساز RECAP
منابع
ABSTRACT
1. INTRODUCTION
2. THE RECAP SIMULATOR
REFERENCES
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه