دانلود مقاله تحلیل ارتعاش تصادفی ساختمان چند طبقه با مدل پارامتر توزیع شده
چکیده
هدف مقاله حاضر این است که یک مدل پارامتر توزیع شده دقیق را برای تحلیل ارتعاش تصادفی ساختمان های چند طبقه فراهم سازد. ما برایاستخراج معادلات حاکم بر رفتار پویای سیستم و همچنین جنبش شناسی مربوطه و شرایط حدی طبیعی از اصل هامیلتون استفاده نمودیم. ما سپس فرکانس طبیعی و اَشکال حالت مدل توسعه داده شده را بصورت تحلیلی استخراج می کنیم و اعتبار آنرا با استفاده از شبیه سازی های عناصر متناهی تأیید می کنیم. ما همچنین مشاهده کردیم که پیش بینی های مدل پیشنهاد شده برای فرکانس های طبیعی سیستم، دقیق تر از پیش بینی های مدل ناپیوسته موجود در مقالات است. ما با استفاده از یک تقریب حالت منفرد در معادله لاگرانژ، معادلات دیفرانسیل جزئی حرکت را به یک معادله دیفرانسیل معمولی کاهش می دهیم (ساده می کنیم). با فرض یک نوفه سفيد با باند محدود برای تسریع پشتیبانی، خصوصیات واکنش تصادفی (بعنوان مثال مقدار مورد انتظار، خودهمبستگی، چگالی طیفی و میانگین مجذورها) سیستم را با استفاده از نظریه ارتعاش تصادفی محاسبه می کنیم. ما ماهیت کیفی و کمی مشخصه واکنش را نیز مورد تحلیل قرار دادیم تا اثرات پارامترهای مختلف طراحی بر روی واکنش سیستم را آشکار سازیم. رویکرد مدلسازی پیشنهاد شده در این مقاله را میتوان برای پیش بینی رفتار پویای ساختارهای پیچیده تر برای انواع مختلفی از تحریکات جبری یا تصادفی مورد استفاده قرار داد. روش تحلیلی ارائه شده برای محاسبه واکنش تصادفی سیستم را هم میتوان برای اتخاذ تصمیمات آگاهانه تر در فرآیند طراحی مورد استفاده قرار داد.
1. مقدمه
محافظت از سازه های مهندسی در مقابل ارتعاشات ناخواسته همیشه یکی از چالش های مهندسین عمران و مکانیک بوده است. در ساختمان سازی زلزله میتواند ارتعاشات ناخواسته شدیدی را بر سیستم وارد سازد و تنش های آنقدر بزرگی را ایجاد کند که در نهایت منجر به فروپاشی فاجعه آمیز سازه شوند. بنابراین محققان تلاش کرده اند تا تکنیک های جدیدی را ابداع کنند تا پدیده های ارتعاشی در این سازه ها را مطالعه کنند و همچنین تکنیک های خنثی سازی ارتعاش جدیدی را توسعه دهند تا سطح ارتعاش را به حداقل برسانند.
در تعدادی از مطالعات زلزله بصورت یک حرکت تکیه گاهی هماهنگ مدلسازی شده است. بعنوان مثال فرشیدیان فر و سهیلی [1] پارامترهای بهینه میراگرهای جرمی تنظیم شده برای سازه های بلند را مورد مطالعه قرار داده اند و اثرات متقابل ساختمان خاک تحت تحریکات بستر هماهنگ (هارمونیک) را بررسی کرده اند. پاریک و رید [2] عملکرد میراگرهای جرمی تنظیم شده – که بصورت یکنواخت و خطی توزیع شده اند – را در خنثی کردن ارتعاشات ناشی از تحریکات هماهنگ و زلزله، بررسی کرده اند.
5. نتیجه گیری
بررسی واکنش پویای ساختمان های تحت بارهای زلزله، گام مهمی در طراحی این ساختمان ها است. چنین مطالعه ای میتواند از چندین لحاظ پیچیده باشد. اول اینکه ماهیت تحریکات زلزله تصادفی است که این منجر به پیچیده شدن شبیه سازی ها می گردد. همچنین ساختمان ها سیستم های چند بخشی متشکل از توده های صلب (معرف کف ها) هستند که بصورت متقابل به تعدادی تیرهای انعطاف پذیر (معرف دیوارها) متصل شده اند. تا جاییکه ما اطلاع داریم محققان هنوز یک مدل پارامتر توزیع شده چند بخشی دقیق برای رفتار ارتعاشی این سازه ها فراهم نساخته اند بلکه معمولاً یک مدل پارامتر متمرکز ساده را برای این سیستم در نظر گرفته اند. بنابراین هدف مقاله حاضر این بود که مدل دقیق تر و جامع تری را برای تحلیل پویای ساختمان های تحت اثر بارهای تصادفی، فراهم سازد. معادلات حرکت و شرایط حدی متناظر را بر مبنای اصل هامیلتون استخراج کردیم. ما مشکل مقدار ویژه دقیق را حل کردیم و عبارات تحلیلی را برای اَشکال مود سیستم – که اعتبار از طریق FEA تأیید شده بود – استخراج کردیم. سپس با استفاده از یک فرضیه مود منفرد، واکنش ساختمان به حرکت تصادفی تکیه گاه را نیز بر مبنای نظریه ارتعاش تصادفی شبیه سازی کردیم و عبارات شکل بسته را برای پارامترهای آماری مختلف واکنش بر حسب پارامترهای تحریک، فراهم ساختیم. ما خصوصاً میانگین، خودهمبستگی، چگالی طیفی و میانگین مجذورهای خمش نسبی طبقات را بدست آوردیم، و پارامترهای مختلف طراحی در واکنش تصادفی سازه را مورد بحث قرار دادیم.
مطالعه حاضر چارچوب جدیدی را برای بهبود مدلهای پویای سازه های پیچیده در واکنش به تحریکات تصادفی زلزله فراهم ساخته است. این چارچوب جدید – که توزیع توده و صلابت سیستم را هم مد نظر قرار میدهد – را هنوز هم میتوان به چندین طریق بهبود داد. بعنوان مثال در این مقاله، برای تحلیل از یک نظریه الاستیسیته خطی استفاده کرده ایم. با اینحال زمانیکه یک سازه زلزله را تجربه میکند سیستم ممکن است به رژیم غیرخطی تبدیل شود و ممکن است یک مدلسازی ساختمانی پارامتر توزیع شده غیرخطی بعد از یک تحلیل ارتعاش تصادفی غیرخطی، ضروری به نظر برسد. بعلاوه بررسی اثرات سنگ بستر و عدم سکون ممکن ورودی ها، میتواند این تحقیق را بهتر نیز سازد. علیرغم تمام این مسائل، مدل پیوسته چند بخشی توسعه یافته و تحلیل کیفی و کمی فراهم شده برای شبیه سازی تصادفی ساختمان در مقاله حاضر را می توان برای برآورده سازی بهتر الزامات طراحی این ساختمان ها به یک شیوه دقیق تر مورد استفاده قرار داد.
Abstract
The objective of the current paper is to provide an accurate distributed parameter model for random vibration analysis of multi-floor buildings. The Hamilton's principle is employed to derive the equations governing the dynamic behavior of the system as well as the related kinematic and natural boundary conditions. The natural frequency and mode shapes of the developed model are then extracted analytically and validated using finite element simulations. It is also observed that the predictions of the proposed model for the natural frequencies of the system is far more accurate than those of that of the discrete model available in the literature. Using a single mode approximation in the Lagrange equation, the partial differential equations of the motion are reduced to a single ordinary differential equation. Assuming a band limited white noise for the acceleration of the support, the random response specifications (such as expected value, autocorrelation, spectral density and mean square) of the system is calculated by making use of the random vibration theory. The qualitative and quantitative nature of the response characteristic are also analyzed to reveal the effects of different design parameters on the system's response. The suggested modeling approach in this paper may be employed for prediction of the dynamic behavior of more complex structures to different types of deterministic or random excitations. Also the provided analytical method for the random response calculation of the system can be utilized to make more informed decisions in the design process.
1. Introduction
Protection of engineering structures against un-wanted vibrations have always been a challenge for civil and mechanical engineers. In building constructions, an earthquake can bring about severe unwelcomed vibrations of the system and produce large stresses which ultimately can lead to catastrophic collapse of the structure. So researchers have been trying to innovate new techniques to study the vibrational phenomena in such structures and also to develop new vibration suppression techniques to minimize their vibration level.
In some studies, the earthquakes have been modeled as harmonic support motion. For example Farshidianfar and Soheili [1] investigated the optimized parameters of tuned mass dampers for high rise structures considering soil structure interaction effects under harmonic base excitations. Park and Reed [2] examined the performance of uniformly and linearly distributed multiple mass dampers in suppressing the vibrations resulted from harmonic and earthquake excitations.
5. Conclusion
Investigation of the dynamic response of the buildings under earthquake loads is an important step in the design of these constructions. Such a study can be complicated in different ways. First, the nature of the earthquake excitations is random which intricates the simulations. Also, buildings are multi-body systems consisting of rigid masses (representing the floors) interconnected to some flexible beams (representing the walls). As far as the authors knew, the researchers had not yet provided an accurate multi-body distributed parameter model for the vibratory behavior of such structures, but they usually considered a simple lumped parameter model for the system. So, the objective of the current paper was to provide a more comprehensive and accurate model for dynamic analysis of buildings under the effect of random loads. The equations of motion and the corresponding boundary conditions were derived based on Hamilton's principle. The exact eigen value problem were solved and analytical expressions were derived for mode shapes of the system which were validated via FEA. Then utilizing a single mode assumption, the response of the building to stochastic motion of the support were also simulated based on the random vibration theory and closed-form expressions were provided for different statistical parameters of the response in terms of those of the excitation. Specifically, the mean, autocorrelation, spectral density and the mean square of the relative deflection of the floors were obtained and the effect of different design parameters on the random response of the structure were discussed.
The current study provided a new frame work for improving the dynamic models of complex structures in response to random earthquake excitations. This new frame work which takes the distribution of mass and stiffness of the system into account can still be improved in several ways. For example, in this paper, a linear elasticity theory was exploited for the analysis. However, when a structure experience earthquake, the system may go to the nonlinear regime and a nonlinear distributed parameter structural modeling followed by a subsequent nonlinear random vibration analysis seems to be necessary. Moreover, considering the rock-bed effects and possible non-stationarity of the inputs may ameliorate this research. Despite all these, the developed multi-body continuous model and the qualitative and quantitative analysis provided for the stochastic simulation of the building in this paper can be employed to better address the design requirements of these constructions in a more accurate way.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. مدلسازی ریاضی
3. تحلیل مقدار ویژه
4. مدلسازی ارتعاش تصادفی
5. نتیجه گیری
منابع
ABSTRACT
1. Introduction
2. Mathematical modeling
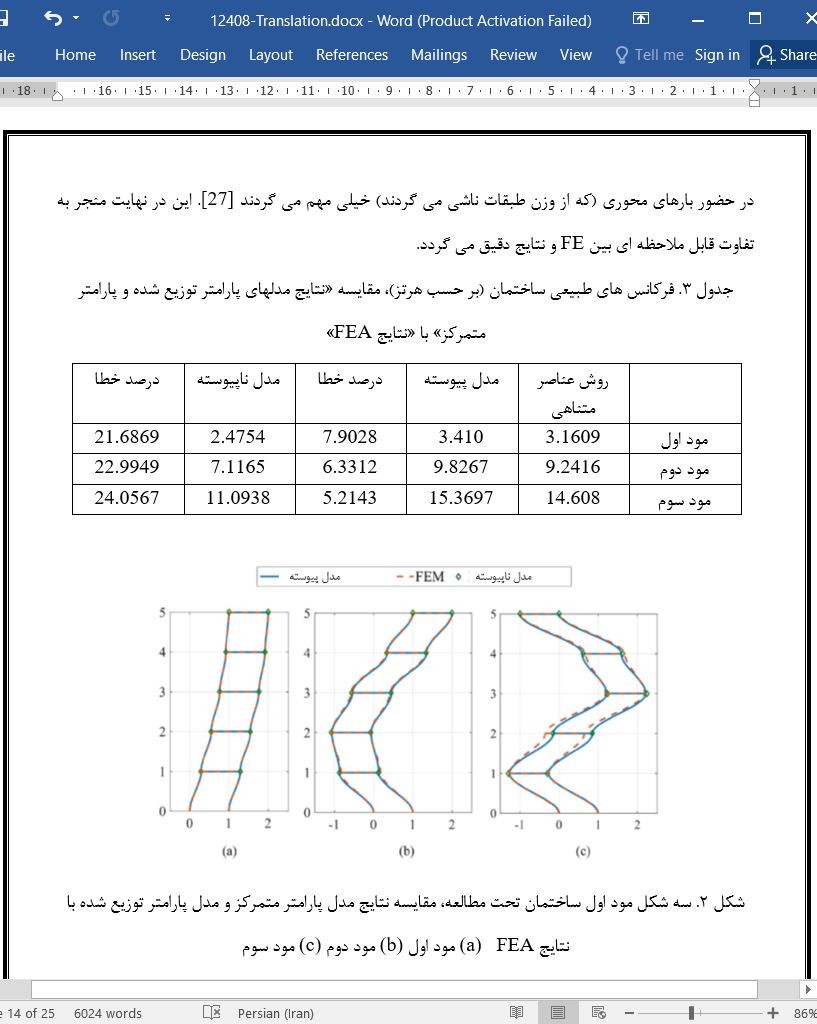
3. Eigen value analysis
4. Random vibration modeling
5. Conclusion
References
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه