تنوع بخشی پرتفوی وام، ساختار بازار و ثبات بانک
چکیده
این مقاله بررسی می کند که آیا تنوع بخشی وام بانکی و تمرکز بازار با ثبات مالی بانک درارتباط هست یا خیر. این مطالعه همچنین بررسی می کند که تاثیر تنوع بخشی وام بر ثبات بانک بسته به سطح رقابت یا تمرکز بازار بانکداری چگونه تغییر می کند. ما فهمیدیم که افزایش تنوع سازی وام تاثیر مثبتی بر قدرت مالی بانک دارد. ما نشان می دهیم که تمرکز بازار با ریسک ورشکستگی بانک رابطه منفی دارد، که با دیدگاه "ثبات و تمرکز" سازگار می باشد. نتایج با استفاده از روابط متقابل بین تنوع سازی پرتفوی بانک و تمرکز بازار نشان می دهند که متنوع سازی بانکهایی که در بازارهای بسیار متمرکز فعالیت می کنند، در مقایسه با آنهایی که در بازارهای غیر متمرکز هستند، از نظر اقتصادی باثبات تر می باشند.
1- معرفی
تعداد تعطیلی های بانک در جدیدترین بحران مالی ایالات متحده به شدت بالا رفته است. شرکت بیمه سپرده فدرال (FDIC) گزارش می دهد که 465 بانک تجاری بیمه شده ایالات متحده بین ژانویه 2008 تا دسامبر 2012 شکست خوردند، درحالیکه فقط 27 بانک از اکتبر 2000 تا دسامبر 2007 تعطیل شدند. سیاستمداران و قانونگذاران ادعا می کنند که عدم رقابت در صنعت بانکداری ممکن است نقش مهمی در دوران بحران مالی داشته باشد (به عنوان مثال، Akins et al., 2016). Cole and White (2012) و دفتر حسابداری دولتی (2013) گزارش می دهند که تمرکز بر وامهای املاک و مستغلات تجاری از جمله عوامل کمک کننده ای هستند که منجر به افزایش احتمال تعطیلی های اخیر بانک در تمام دولتها شده است. آخرین گزارشهای مربوط به عدم موفقیت بانک و فروپاشی موسسات بزرگ مالی (مانند برادران لمن، شرکت هلدینگ بانک آمریکایی (Washington Mutua) و بانک سرمایه گذاری جهانی نیویورک (Bear Stearns)) طی بحران مالی سوالات زیر را مطرح می کنند: آیا بانکها با تنوع پرتفوی های وام آسیب پذیری مالی را افزایش می دهند یا کاهش؟ آیا بانکها در بازارهای بسیار متمرکز، در مقایسه با آنهایی که در بازارهای غیر متمرکز قرار دارند، از نظر اقتصادی باثبات تر هستند یا برعکس؟ آیا ماهیت رقابتی بازاری که بانک در آن فعالیت می کند بر رابطه بین تنوع بخشی فعالیتها و آسیب پذیری بانک تاثیر می گذارد؟ ویژگی های مهم بانکی و اقتصادی که بر ثبات مالی بانک به طور قابل توجهی تاثیر می گذارند، چیست؟ در این مقاله، ما با انجام دادن یک تحقیق تجربی، با استفاده از نمونه بانکهای تجاری ایالات متحده طی دوره 2002:Q1 تا 2013:Q3 به این سوالات بدون پاسخ می پردازیم.
Abstract
This paper examines whether the choice of bank loan diversification and market concentration are associated with a bank's financial stability. This study also investigates how the effect of loan diversification on bank stability varies depending on the level of the concentration or the competitiveness of the banking market. We find that increased loan diversification has a positive impact on the bank's financial strength. We show that market concentration is negatively associated with bank insolvency risk, consistent with the “concentration-stability” view. The results using interaction terms between loan portfolio diversification and market concentration indicate that diversifying banks operating in highly concentrated markets are more financially stable compared to those in less concentrated markets.
1. Introduction
The number of bank closures has sharply risen particularly during the most recent financial crisis in the United States. The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) reports that 465 insured U.S. commercial banks failed between January 2008 and December 2012, while only 27 banks closed from October 2000 to December 2007. Politicians and regulators claim that the lack of competition in the banking industry may have played a significant role in the financial crisis period (e.g., Akins et al., 2016). Cole and White (2012) and Government Accountability Office (2013) report that the concentration on commercial real estate loans is among the contributing factors that led to an increased likelihood of recent bank closures across all states. The latest banking failure reports and collapse of large financial institutions (such as Lehman Brothers, Washington Mutual and Bear Stearns) during the financial crisis raise the following questions: Do banks reduce or increase financial fragility from diversification of their loan portfolios? Are banks in highly concentrated markets more financially stable than those in less concentrated markets or vice versa? Does the competitive nature of the market where the bank operates influence the relationship between diversification of activities and bank fragility? What are the important bank and economic characteristics that significantly influence a bank’s financial stability? In this paper, we address these unanswered questions by undertak ing an empirical investigation using the samples of U.S. commercial banks over the period 2002:Q1–2013:Q3.
چکیده
1- معرفی
2- ادبیات مربوطه و توسعه فرضیه ها
1-2- تنوع بخشی پرتفوی وام و ثبات بانک
2-2 تمرکز بازار و ثبات بانک
3-2 اثر متقابل تنوع بخشی وام و تمرکز بازار بر ثبات بانک
3 - روش شناسی و ساخت متغیر
1-3 چارچوب تجربی
2-3 تعریف متغیرها
1-2-3 ثبات مالی بانک
2-2-3 تنوع بخشی پرتفوی وام
3-2-3 تمرکز بازار
4-2-3 اندازه شرکت
5-2-3 سهم بدون سود
6-2-3 نقدینگی
7-2-3 سپرده های کارگزاری
8-2-3 سپرده های اصلی
9-2-3 عضو شرکت هلدینگ بانکی
10-2-3 بانکهای نوظهور
11-2-3 انتخاب نظارتی و سرپرستی
12-2-3 نرخ بیکاری و نرخ رشد تولید ناخالص داخلی (GDP)
4 - داده ها و نتایج تجربی
1-4 نمونه
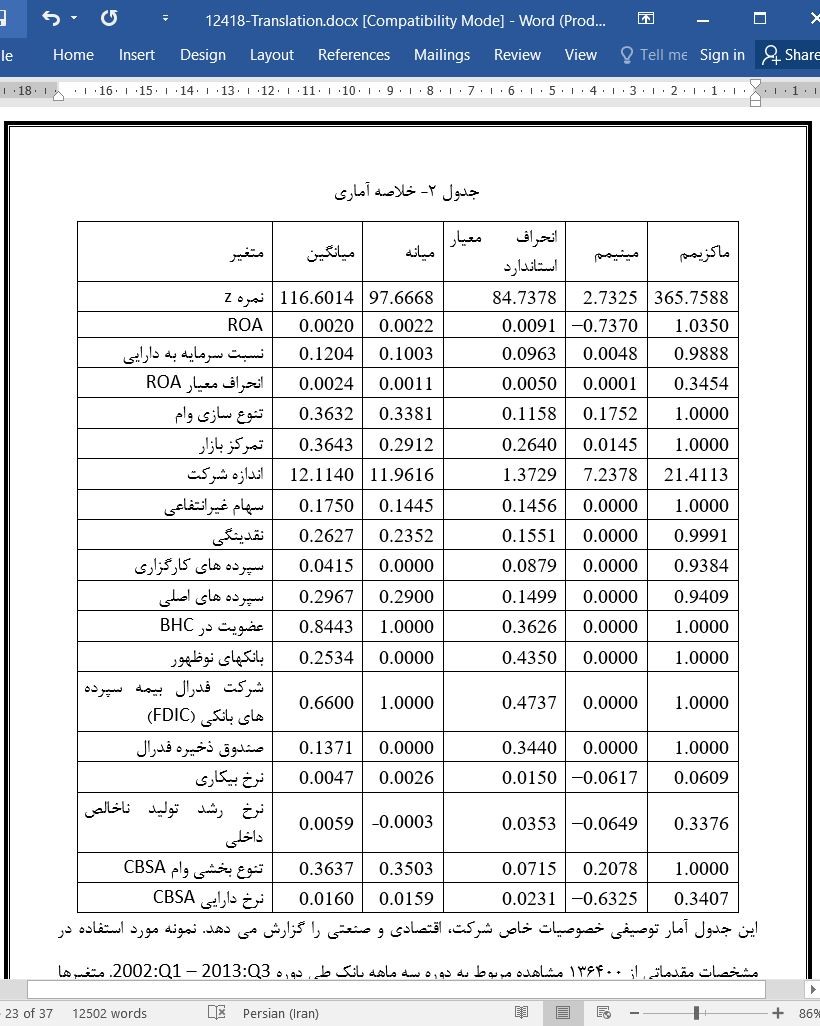
2-4 نتایج برای مشخصات اولیه
3-4 تست های استواری (پایداری)
1-3-4 کنترل ادغام ها و مالکیت ها
2-3-4 آنالیز برای دوره های قبل از بحران، بحران و بعد از بحران
3-3-4 روش گشتاورهای تعمیم یافته متغیرهای ابزاری (IV-GMM)
-5نتیجه گیری
منابع
ABSTRACT
1. Introduction
2. Related literature and hypotheses development
2.1. Loan portfolio diversification and bank stability
2.2. Market concentration and bank stability
2.3. Interaction effect of loan diversification and market concentration on bank stability
3. Methodology and variable construction
3.1. Empirical framework
3.2. Definition of variables
3.2.1. A bank’s financial stability
3.2.2. Loan portfolio diversification
3.2.3. Market concentration
3.2.4. Firm size
3.2.5. Non-interest share
3.2.6. Liquidity
3.2.7. Brokered deposits
3.2.8. Core deposits
3.2.9. Member of bank holding company
3.2.10. De novo banks
3.2.11. Supervisory choice
3.2.12. Unemployment rate and GDP growth rate
4. Data and empirical results
4.1. The sample
4.2. Results for primary specification
4.3. Robustness tests
4.3.1. Controlling for mergers and acquisitions
4.3.2. The analysis for the pre-crisis, the crisis, and the post-crisis periods
4.3.3. Instrumental variables-generalized method of moments (IV-GMM)
5. Conclusion
References
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه