دانلود مقاله روش طراحی ژنراتورهای ورنیر آهنربای ثابت برای سیستم توربین های بادی
چکیده
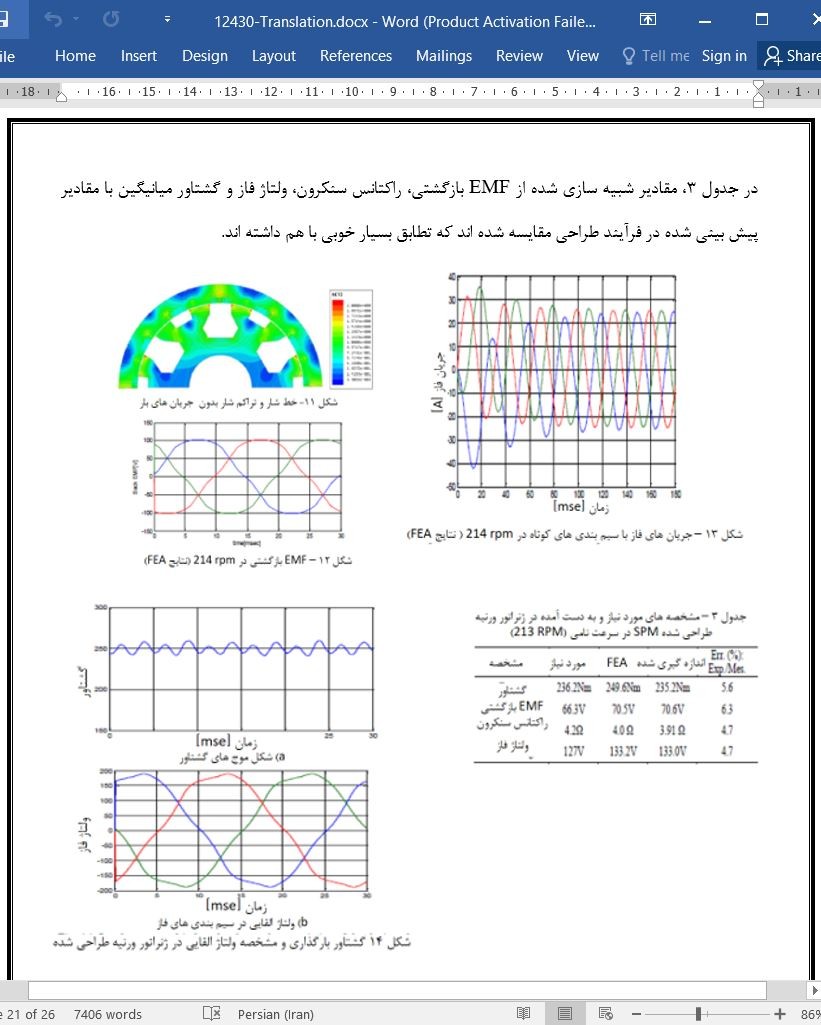
در این مطالعه، یک روش طراحی جدید برای ژنراتور های ورنیر مغناطیس ثابت با هدایت مستقیم (DDPMVG) برای سیستم های توربین بادی سبک با توان بالا و بدون جعبه دنده ارائه شده است. زمانی که الزام توان حداکثری در نظر گرفته شود، سرعت های مبنا و ماکسیموم برای ژنراتور، اول از مشخصه های ایرودینامیک تیغه های توربین بادی به دست می آید. سپس پارامتر های الکتریکی ضروری برای ژنراتور ها با در نظر داشتن طرح کنترل بیشترین پارامتر گشتاور (MTPA) در ژنراتور های PM محاسبه می شود. برای مشخص کردن حالت هندسی مناسب برای پارامتر های به دست آمده، همبستگی های بین پارامتر ها و حالت های هندسی PMVG با در نظر داشتن سیم بندی های متمرکز، به دست می آیند. با استفاده از همبستگی های به دست آمده و پارامتر های ایجاد شده، یک فرایند طراحی سیستمی از PMVG ارائه می شود. برای یک مورد پژوهی، یک 5kW DD-PMVG با روتور خارجی با استفاده از روش پیشنهاد شده، طراحی می شود. مشخصه های عملکردی ژنراتورهای طراحی شده نیز با شبیه سازی های المان محدود (FE) تحلیل شده و سپس با نتایج پیش بینی شده با تحلیل ها، مقایسه می شود. در نهایت، نتایج آزمایش ها ارائه می شوند.
1. مقدمه
اخیرا، نسبت به انرژی های تجدید پذیر علاقه گسترده ای ایجاد شده و تحقیق و توسعه در رابطه با آن ها نیز نسبت به قبل بیشتر شده است. در میان این روش ها، ژنراتورهای بادی در انواع سایزها،، از توربین های کوچک برای شارژ کردن باتری در نواحی مسکونی دور افتاده گرفته تا مزارع بادی گسترده برای ارائه برق به سیستم های انتقال برق ملی را شامل می شوند. به صورت خاص، تولید انرژی از باد حالا از زمین به دریا منتقل شده است و در عین حال، ظرفیت تولید آن ها نیز به گیگاوات رسیده است. این گرایش ها باعث شکل گیری چالش های زیر می شوند؛ زمانی که بخش مکانیکی مانند جعبه دنده در توربین های بادی روی دریا با مشکل رو به رو شود، تعمیرات آن باعث شکل گیری فرایند بسیار پیچیده و گران می شود. ازین رو، می توان از ژنراتور های هدایت مستقیم (DD) بدون جعبه دنده استفاده کرد، اما در این حالت، وزن ژنراتور بسیار زیاد می شود [4-1]. ازین رو، برای حل کردن این دو مشکل به صورت همزمان، پیشنهاد شده از ژنراتورهای DD استفاده شود که تراکم توان بسیار بیشتری دارند.
تا کنون، ماشین های بسیار منحصر به فرد زیادی برای کاربردهایی با سرعت کم و گشتاور بالا ارائه شده است مانند جعبه دنده های مغناطیسی، ماشین های ورنیر، ماشین های معکوس سازی شار و ماشین های سوییچ شار و غیره [25-4]، و سپس ثابت شده که تمام این ماشین ها در دسته ماشین آلات شار مدولاسیون قرار می گیرند که از تاثیرات جعبه دنده مغناطیسی استفاده می کنند که گاهی با نام تاثیرات مدولاسیون شار نیز شناخته می شوند [5].به صورت خاص، اثبات شده که موتور های ورنیر با مغناطیس ثابت (PM)، که یک ساختار تزویج مغناطیسی از جعبه دنده مغناطیسی و موتور PM می باشد، از نظر تئوری تراکم توان خروجی بالاتری دارد زیرا از شارPM اصلی به صورت همزمان با شار مدولاسیون استفاده می کند [6و 7].
6. جمع بندی
برای بهبود مشکلات محاسبه عملکرد تکراری و عدم صحت ناشی از آن در روش طراحی مرسوم ماشینهای برقی با سرعت متغیر ، این مقاله یک روش طراحی جدید را ارائه می دهد که از نظر ریاضیات واضح و شفاف بوده و در نتیجه مستقیم و دقیق است. به عنوان یک مورد مطالعاتی ، یک ژنراتور 5 کیلو وات مستقیم ، با روتور بیرونی PM ورنیر برای سیستم توربین بادی با استفاده از روش پیشنهادی، طراحی شده است. روش پیشنهاد شده نشان می دهد که طراحی مستقیم با انتخاب سرعت های عملیاتی برای روتور مانند سرعت های مبنا و سرعت قطع، برای تعیین کردن حالت هندسی ژنراتور به صورت دقیق مفید می باشد.
می توان نتایج این تحقیق را به شرح زیر خلاصه کرد. ما در این تحقیق نشان دادیم وقتی ژنراتور PM توسط یک مدار معادل الکتریکی عادی نشان داده شود ، ترکیبات مختلفی از ثابت های مدار وجود دارد که عملکرد گشتاور مورد نیاز یک توربین بادی را برآورده می کند. به عبارت دیگر ، ممکن ژنراتور هایی با ساختارهای مختلف وجود داشته باشد. معادله ثابت های مدار که از نظر ساختار های هندسی از سیم بندی های متمرکز در ژنراتور ورنیر PM ارائه شده است، با در نظر داشتن تاثیر دنده مغناطیسی به دست آمده است. ما با تعیین برخی محدودیت ها و فرضیات معقول از قبیل نسبت چگالی جریان سطحی ، نسبت فاصله هوایی به ضخامت آهنربا ، یک طرح معکوس را برای تعیین شکل هندسی با استفاده از ثابت های مدار انجام داده ایم. سپس، طراحی معکوس برای مشخص کردن حالت هندسی ژنراتور های ورنیر از ثابت های مدار به صورت موفق با تخصیص بعضی از محدودیت ها و فرضیات معقول مانند نسبت تراکم جریان سطحی و نسبت فضای خالی به ضخامت آهنربا، به دست آمد.
Abstract
In this study, a novel method for design of a direct drive(DD) PM vernier generator (PMVG) is proposed for a gearless, high power and lightweight wind turbine system. In the proposed design method, the base and maximum speeds of the generator are firstly obtained from the nature of aerodynamic power, and then the electrical circuit parameters of the generator are scoped with consideration of the control strategy of PM machines. To determine the generator geometries using the scoped parameters, the relational equations between the parameters and geometries of a PMVG with concentrated windings are derived. A systematic method for design using the derived equations and the parameters is developed, and the 5kW PMVG with outer rotor is designed through the proposed method. The performance characteristics of the designed generator are analyzed with FE simulations and compared with analytically predicted results.
I. INTRODUCTION
Recently, the interest in renewable energies is very high, and the research and the development on them are more active than ever. Among them, wind-powered generators operate in every size range, from small turbines for battery charging at isolated residences to large wind farms that provide electricity to national electric transmission systems. In particular, wind power generation is being transferred from the ground to the sea, and at the same time, the capacity of generation is growing to the level of gigawatts. These tendencies cause the following compromise; when a mechanical component such as a gear box in an offshore wind turbine breaks down, the maintenance procedure is very complicated and expensive. Therefore, it is beneficial to adopt a direct-drive (DD) generator with no gears, but in this case, the weight of the generator becomes excessively large [1-4]. Hence, to solve these two problems at once, it is necessary to use a DDgenerator having much higher power density.
Thus far, various unique machines for the low speed-high torque applications have been presented such as magnetic gears, vernier machines, flux reversal machines and flux switching machines etc. [4-25], and then it is proven that all these machines are classified into the modulation flux machinery which utilizes the magnetic gear effects,alternatively called the flux modulation effects [5]. Especially, it was proven that the permanent magnet (PM) vernier motor, which is a magnetically coupled structure of the magnetic gear and the PM motor, has theoretically much higher output power density because it uses the main PM flux at the same time as the modulation flux [6, 7].
VI. CONCLUSION
To improve the problems of the repetitive performance calculation and the resulting inaccuracy in the conventional design procedure of variable-speed electrical machines, this paper proposes a novel design method which is mathematically clear and thus direct and accurate. As a case study, a 5kW direct-drive, outer-rotor PM vernier generator for wind turbine system was designed using the proposed method. The proposed method shows the direct design procedure from choosing the operational speeds of the rotor such as the base and the cut-off speeds to determining the geometries of the generator in details.
The results of this study can be summarized as follows. It has been shown that there are various combinations of circuit constants that satisfy the torque performance required for a wind turbine when a PM generator is represented by a regular electric equivalent circuit. In other words, there may be generators of various different structures. The circuit constant equations expressed in terms of the geometrical structure of the concentrated winding PM vernier generator were derived in consideration of the magnetic gear effects. We have successfully performed a reverse design to determine the shape from the circuit constants by assigning some constraints and reasonable assumptions such as the ratio of the surface current density, the ratio of the gap to the magnet thickness. Then, the reverse design to determine the geometries of a PM vernier generator from the circuit constants has been successfully performed by assigning some constraints and reasonable assumptions such as the ratio of the surface current density, the ratio of the gap to the magnet thickness.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. ملاحظات طراحی برای ژنراتور های بادی هدایت مستقیم
3. همبستگی های بین ثابت های مدار و حالت های هندسی ژنراتورهای ورنیر PM با سیم کشی متمرکز
4. تعیین حالت های هندسی PMVG
5. شبیه سازی و نتایج آزمایش
6. جمع بندی
منابع
Abstract
1. INTRODUCTION
2. DESIGN CONSIDERATION FOR A DIRECT-DRIVE WIND POWER GENERATOR
3. CORRELATIONS BETWEEN CIRCUIT CONSTANTS AND GEOMETRIES OF A PM VERNIER GENERATOR WITH CONCENTRATED WINDINGS
4. DETERMINATION OF GEOMETRIES OF A PMVG
5. SIMULATION AND EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
6. CONCLUSION
REFERENCES
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه