دانلود مقاله رهبری خدمتگذار: توسعه و اعتبارسنجی یک مقیاس چند بعدی
چکیده
هدف- هدف از این مقاله، توسعه و اعتبارسنجی ابزاری است که برای ارزیابی رفتار رهبری خدمتگذار در صنعت مهمان نوازی چین در نظر گرفته شده است.
طراحی/ روش شناسی/ رویکرد- پس از بررسی مقالات، یک مقیاس با نه بعد و 18 آیتم ایجاد شد و سپس، با استفاده از نمونهای از 600 شرکت کننده از دانشکده پلی تکنیک و صنعت مهمان نوازی در معرض تحلیل عاملی اکتشافی (EFA) قرار گرفت و یک راه حل با 6 عامل و 33 آیتم را حاصل کرد. پس از آن، مقیاس به دست آمده با استفاده از نظریه پاسخ سؤال (IRT) به 24 آیتم خلاصه گردید. بر اساس دادههای 440 پاسخ دهنده در صنعت مهمان نوازی، متعاقباً این مقیاس 6 عاملی 24 آیتمی توسط تحلیل عاملی تاییدی (CFA) و آزمون اعتبار سازه، اعتبارسنجی شد.
یافتهها- بین عوامل موجود در این ابزار و مقیاسهای توسعه یافته غربی تفاوتهایی مشاهده شده است. این مطالعه با یک مقیاس 6 بعدی-24 آیتمی انجام شد. این ابعاد عبارت بودند از درستی، فداکاری، جامعه سازی، توانمندسازی مردم، بهبود عاطفی و چشم اندازسازی. نشان داده شد که این مقیاس رهبری خدمتگذار از قابلیت اطمینان و هماهنگی داخلی خوب و اعتبار ساختاری قدرتمندی برخوردار است.
اصالت/ارزش- این اولین مطالعهای است که از نظریه پاسخ سؤال (IRT) به عنوان یک ابزار آماری برای کوتاه کردن مقیاس رهبری خدمتگذار استفاده کرده است و همچنین از نظریه روانشناسی فرهنگی پشتیبانی بیشتری به عمل آورده است.
مقدمه
موفقیت در بیشتر سازمانها، به رهبری مؤثر و کارآمد بستگی دارد (Barrow، 1977). بی تردید رهبران تأثیر زیادی بر شرکتها، کارکنان ، مشتریان و سایر سهامداران خود دارند. با این حال، با رواج مشکلات مزمن اجتماعی در محل کار مانند سوءاستفاده از قدرت ، شیوههای غیر اخلاقی و نقض سلامت روانشناختی کارکنان و توازن بین کار و زندگی، بسیاری از سازمانها متحمل زیانهای اقتصادی و رسوایی اجتماعی فاحشی شدهاند (Sendjaya و همکاران، 2008). با توجه به جو پیچیده و چالش برانگیز امروزی، مردم به طور فزایندهای آگاه میشوند که حالتهای سنتی استبدادی رهبری، دیگر منافع بلند مدت مالی و اجتماعی را برای سازمانها تضمین نمیکنند. در نتیجه، مداوما گفته میشود که پارادایمهای رهبری قدیمی باید جایگزین شوند، و شیوه جدیدی از رهبری که اعتماد را افزایش میدهد، حیطه اخلاقی و مسئولیت اجتماعی قوی را برای تضمین موفقیت و سودآوری در سازمانهای امروزی ایجاد میکند باید مورد تاکید قرار گیرد (Van Dierendonck و Nuijten، 2011). این رویکرد جدید برای رهبری مستلزم آن است که افرادی که دارای سمتهای مدیریتی هستند زیردستان خود را در تصمیم گیری دخالت دهند ، کار گروهی و اجتماعی را تقویت کنند، رفتار اخلاقی و دلسوزانهای را به نمایش بگذارند و در نهایت رشد شخصی کارکنان را تقویت نمایند (Spears، 1995). این فلسفه رهبری نوظهور، رهبری خدمتگزار نامیده میشود.
محدودیتها و تحقیقات آینده
در بحث در مورد چالشهای روش شناختی، باید اذعان کرد که در واقع برخی دستورالعملها برای آگاهی از روشها و روند تحقیق وجود داشته است. به عنوان مثال، مشخص شد که هدف از این مطالعه، تدوین یک مقیاس معتبر و قابل اجرا از رهبری خدمتگزار در صنعت مهمان نوازی چین است. با این وجود، استفاده از آیتمهایی که هم اکنون در مقالات وجود دارند، ممکن است انتخاب روشها را در تولید آیتمها محدود کند. مطالعات مشابه در آینده ممکن است با استفاده از سایر تکنیکهای جمع آوری دادهها مانند گروههای کانونی، مطالعه اصولی و سایر روشهای کیفی، همانطور که توسط Brownو Bryant (2015) و Liden و همکاران (2014) بیان شده مزایای بیشتری را کسب کنند. محققان میتوانند از نمونه گیری تصادفی نیز استفاده کنند، زیرا این یک روش نمونه گیری بی طرفانه است. از سوی دیگر، میتوان از نظرسنجی آنلاین برای این منظور استفاده کرد اما مزایای سرعت، کارایی و هزینههای پایینتر را نیز در جمع آوری دادهها ارائه داد (Dillman و همکاران 2008). بی تردید، از آنجاییکه این مقیاس برای بخش مهمان نوازی و مستقر در چین توسعه یافته است، تعمیم پذیری این مقیاس، دومین محدودیت این مطالعه است. بنابراین، محقق باید نسبت به استفاده از آن در سایر فرهنگها یا صنایع دیگر محتاط باشد. سومین اشکال این مطالعه، فقط به توسعه و اعتبار سنجی مقیاس رهبری خدمتگزار مربوط میشود. برای بررسی دقیق سوابق و پیامدهای رهبری خدمتگزاران و همبستگی آنها، انجام تحقیقات ضروری است. محققان علاقه مند میتوانند با استفاده از این مقیاس، بررسی عمیقتری در این حوزه داشته باشند که این امر میتواند راههای جدیدی را برای چنین گفتگوهایی بگشاید.
Abstract
Purpose – The purpose of this paper is to develop and validate an instrument intended to measure servant leadership behavior in the Chinese hospitality industry.
Design/methodology/approach – After reviewing the literature, a scale of nine dimensions with 81 items was generated and then subjected to exploratory factor analysis (EFA) using a sample of 600 participants from a polytechnic college and hospitality industry, resulting in 6-factor-33-item solution. The derived measure was then shortened to 24 items by using item response theory (IRT). Drawing on the data from 440 respondents in the hospitality industry, this 6-factor-24 item measure was subsequently validated with confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) and the test of construct validity.
Findings – Difference in factors has been found between this instrument and western-developed scales. This study resulted in 6-dimension-24-items scale. These dimensions were named integrity, self-sacrifice, building community, empowering people, emotional healing and visioning. This servant leadership scale was demonstrated to have good internal consistency reliability and strong construct validity.
Originality/value – This is the first study that used IRT as a statistic tool to shorten a servant leadership scale and also this study provided additional support to cultural psychology theory.
Introduction
For most organizations, success depends on effective and efficient leadership (Barrow, 1977). Leaders undoubtedly have a profound impact on their companies, employees, customers and other shareholders. However, with a prevalence of social chronic problems in the work place, such as abuse of power, unethical practices and violation of employee’s psychological wellbeing and work-life balance, many organizations have suffered tremendous economic loss and social disgrace (Sendjaya et al., 2008). Given today’s challenging and complex climate, people are becoming increasingly aware that traditional autocratic modes of leadership no longer guarantee long term financial and social benefits for the organizations. Consequently, a call has been constantly made that the old leadership paradigms need to be replaced and emphasis should be shifted to a new mode of leadership which will enhance trust, encourage a strong moral compass, and social responsibility to secure success and profit in today’s organizations (Van Dierendonck and Nuijten, 2011). This new approach to leadership requires those in managerial positions to involve their subordinates in decision making, encourage teamwork and community, display ethical and caring behavior and ultimately enhance the personal growth of employees (Spears, 1995). This emerging leadership philosophy is called servant leadership.
Limitations and future research
In discussing methodological challenges, it should also be acknowledged there were indeed some guidelines that informed the research methods and procedures. For example, it was made clear the purpose of this study was to develop a valid and thus applicable servant leadership measure in the Chinese hospitality industry. However, the use of currently available items in the literature might constrain the choice of methods in generating items. Future studies of the same kind may gain more benefits by utilizing other data collecting techniques such as focus groups, grounded study and other qualitative methods as called for by Brown and Bryant (2015) and Liden et al. (2014). Researchers would also benefit from using random sampling as it is an unbiased sampling technique. Alternatively, online surveys could be used for the same purpose, but offer the advantages of speed, efficiency and lower costs in data collection (Dillman et al., 2008). Undoubtedly, generalizability of the scale is the second limitation of this study as this scale was developed for the hospitality sector and based in China. Thus, researcher should be cautious about applying it to other cultures or other industries. The third drawback is this study was only limited to the development and validation of a servant leadership scale. Research is needed to rigorously examine the antecedents and consequences of servant leadership and their interrelatedness. Interested researchers could delve deeper into this area using this scale, which might open the new ways to such conversations.
چکیده
مقدمه
بررسی مقالات
رهبری خدمتگذار
مقیاسهای رهبری خدمتگذار
مطالعات رهبری خدمتگزار انجام شده در چین
روش
ساخت آیتمها
نمونهها و روند کار
مقیاسها
تحلیل دادهها
نتایج
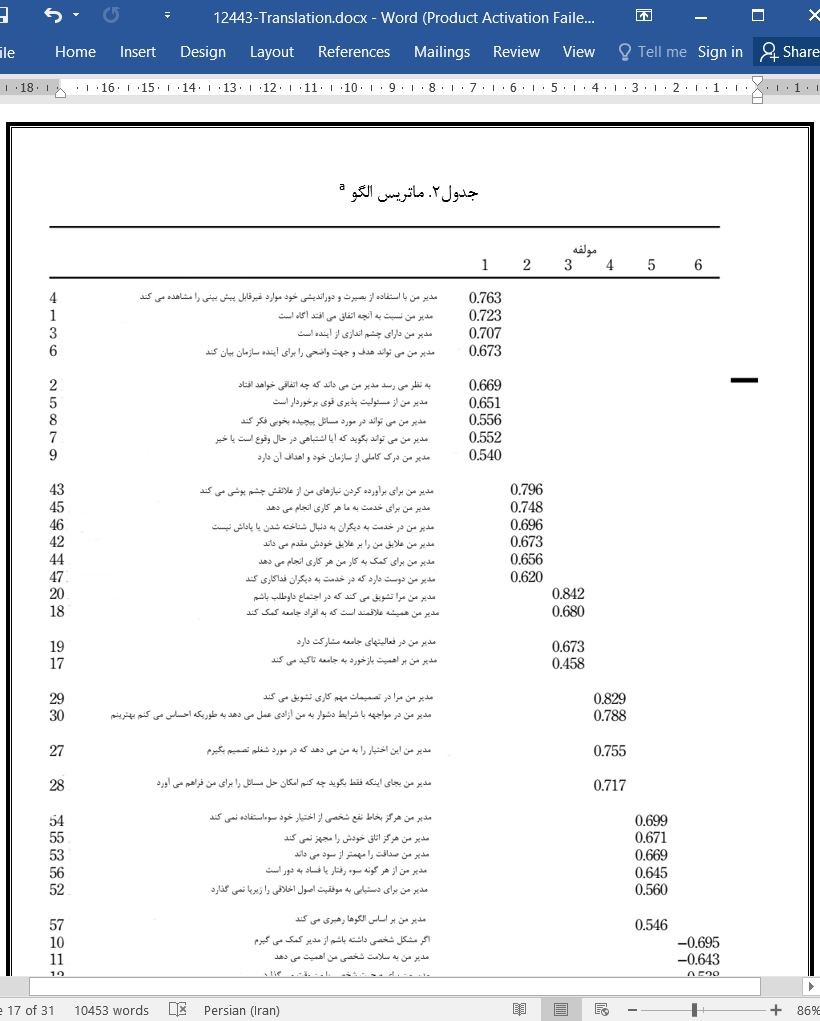
تحلیل عاملی اکتشافی
تحلیل عاملی تأییدی
پایایی، روایی همگرا، و روایی افتراقی
روایی وابسته به معیار
بحث
نتیجه گیریها و دلالتها
محدودیتها و تحقیقات آینده
منابع
Abstract
Introduction
Literature review
Servant leadership
Servant leadership measures
Servant leadership studies conducted in China
Method
Item construction
Samples and procedures
Measures
Data analysis
Results
Exploratory factor analysis
Confirmatory factor analysis
Reliability, convergent validity, and discriminant validity
Criterion-related validity
Discussion
Conclusions and implications
Limitations and future research
References
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه