تأثیرات روانشناختی، آموزشی درک شده و اثر مالی همه گیری کووید۱۹ بر رضایت از زندگی
چکیده
پیشینه: هدف از این مطالعه فراهم ساختن مکانیزم های عملیاتی برای درک تأثیر کووید ۱۹ بر رضایت از زندگی، با توجه به سلامت ذهنی عمومی دانشجویان است
روش ها: نمونه ای شامل ۱۶۵۳نفر از دانشجویان یونانی زبان دانشگاه (که ۷۲.۴٪ آن ها خانم ها و ۶۵.۳٪ آن ها کارشناسی با میانگین سنی ۲۶.۱ ٪) بودند که پرسشنامه آنلاین شامل معیارهایی برای تأثیرات روانشناختی، آکادمیک درک شده و اثر مالی همه گیری کووید ۱۹ بر سلامت ذهنی عمومی و رضایت از زندگی را تکمیل کردند.
نتایج: یک مدل میانجی برای آشکار ساختن این ارتباطات با در نظر گرفتن سلامت ذهنی عمومی دانشجویان به عنوان میانجی آزموده شد. یافته ها اثبات می کنند که تأثیرات قابل توجه مستقیم درک شده کووید ۱۹ بر وضعیت مالی شرکت کنندگان وجود دارد که بر رضایت از زندگی آن ها مؤثر بوده و تأثیرات غیر مستقیم درک شده کووید ۱۹ بر وضعیت مالی و عملکرد آکادمیک به ترتیب وجود دارد که بر رضایت از زندگی با توجه به سلامت روان عمومی مؤثر بوده است.
محدودیت ها: طرح مقطعی مطالعه، خودگزارش دهی داده و نمونه گیری گلوله برفی.
نتیجه گیری: یافته ها، بر درک ما از ارتباط بین تأثیر درک شده کووید ۱۹ بر رضایت از زندگی میان دانشجویان دانشگاه می افزاید و نقش حیاتی سلامت ذهنی عمومی را در میانجی گری روابط روشن می کنند. هدف گذاری عواملی که سلامت ذهنی عمومی را تحت تأثیر قرار می دهند، می تواند به کاهش مشکلات احتمالی کمک کند، هم چنین در یافتن راه هایی برای بهبود بهزیستی و سلامت ذهنی، تأثیر گذار باشد.
1. مقدمه
کشف بیماری عفونی جدید کرونا ویروس(کووید ۱۹) و آغاز همه گیری کرونا ویروس در سال ۲۰۱۹(سازمان بهداشت جهانی،۲۰۲۰)، تغییراتی بر زندگی عموم مردم تحمیل کرد که بسیاری از جنبه های زندگی آن ها اعم از سلامت روانی و تندرستی را مختل کرد. در نتیجه اعلان همه گیری کووید۱۹، چندین کشور اعمال سختگیرانه متنوعی به منظور جلوگیری از شیوع بیماری عفونی، شامل(فاصله گیری اجتماعی، قرنطینه، مقررات منع رفت و درآمد، قرنطینه های جزئی یا سراسری) را اجرا کردند که به طور چشم گیری مسیر زندگی مردم را تحت تأثیر قرار دادند و منجر به پیامدها و احساسات منفی روانی(به طور مثال: عصبانیت، گیجی، بیماری، تنهایی و افسردگی) شدند(Brooks et al.2020). بدین ترتیب به نظر می رسد که اثر سراسری همه گیری بر سلامت روانی و تندرستی عمومی آشکار است. روانپزشکی و روانپزشکاتجن، می توانند بخش حیاتی در این همه گیری و عواقب بلند مدت آن، داشته باشند، به ویژه، در ارتباط با سلامت روانی و روانشناختی پس از آن و قوی تر ساختن مکانیزم های خدمات سلامت در واکنش به کووید ۱۹.
Abstract
Background The purpose of this study was to provide an operating mechanism for understanding the effects of COVID-19′s on satisfaction with life, subject to students’ general mental health
Methods A sample of 1653 Greek speaking university students (72.4% females, 65.3% undergraduate, M age=26.1) completed an online survey including measures for perceived psychological, academic, and financial impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, general mental health and satisfaction with life.
Results A mediation model was tested to illuminate these relationships by considering students’ general mental health as a mediator. Findings demonstrated that there were significant direct effects of perceived COVID-19 impact on participants’ financial status on satisfaction with life and indirect effects of perceived COVID-19 impact on participants’ financial status and academic performance respectively on satisfaction with life through general mental health.
Limitations The study's cross-sectional design, self-report data and snowball sampling.
Conclusions The findings add to our understanding of the relationship between perceived COVID-19 impact and life satisfaction among university students, and they shed light on the critical role of general mental health in mediating the relationship. Targeting the factors that influence general mental health can help to mitigate potential problems while also finding ways to improve mental health and well-being.
1. Introduction
With the discovery of a new infectious coronavirus disease (COVID19) and the onset of the coronavirus pandemic in 2019 (World Health Organization, 2020), the changes imposed on the general population disrupted many aspects of their lives, including their mental health and well-being. The declaration of the COVID-19 pandemic resulted in several countries enforcing a variety of austerity measures to contain the spread of the infectious disease (i.e., social isolation, quarantines, curfews, and partial or nationwide complete lockdowns), significantly affecting people’s way of life and resulting in a number of negative psychological outcomes and feelings (e.g., anger, confusion, distress, loneliness, and depression) (Brooks et al., 2020). The quick rising of such feelings is serious considering their link with various incapacitating mental health illnesses and disorders (e.g., major depression and schizophrenia, obsessive compulsive, trauma-related, panic attacks) (Fiorillo and Gorwood, 2020). Additionally, the prolonged duration of the austerity measures has also increased stress and worrying concerning financial insecurity along with increased fear for supply shortages (Brooks et al., 2020). It seems therefore that the worldwide impact of the pandemic on public mental health and well-being is apparent. Psychiatry and psychiatrists can have a vital part to play in this pandemic and its long-term consequences, especially in dealing with the psychological and mental health aftermath and in solidifying health service mechanisms in reaction to COVID-19.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
1.1 تأثیر درک شده کووید۱۹ بر رضایت از زندگی دانشجویان دانشگاه
1.2. تعدادی از مطالعات، تأیید کرده اند که سلامت ذهنی عمومی
1.3. مطالعه حاضر
2.روش
2.1. روند
2.2. معیارها
3.2. تحلیل داده ها
3.نتایج
3.1. شرکت کنندگان
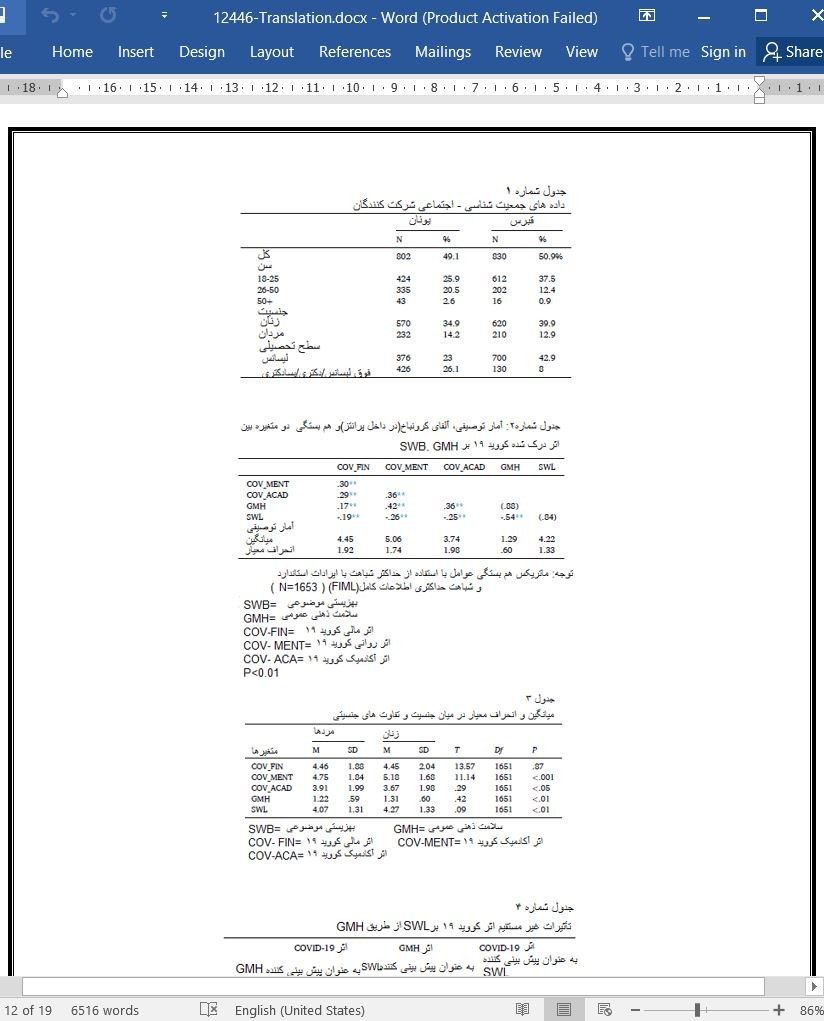
3.2. آمار توصیفی
3.3. اثر غیر مستقیم بر GMH
4.بحث
4.1. مفاهیم
4.2 محدودیت ها و نتیجه گیری
منابع
ABSTRACT
1. Introduction
1.1. The effects of the perceived COVID-19 impact on university students’ satisfaction with life
1.2. The indirect effects of general mental health
1.3. The present study
2. Method
2.1. Procedure
2.2. Measures
2.3. Data analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participants
3.2. Descriptive statistics
3.3. Indirect effects of GMH
4. Discussion
4.1. Implications
4.2. Limitations and conclusion
References
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه