دانلود مقاله مدل سازی استفاده از انرژی تجدیدپذیر به وسیله نقشه شناختی فازی نامطمئن
چکیده
منابع انرژی تجدید پذیر (خورشیدی ، بادی ، جزر و مدی و غیره) که منابع نامحدودی هستند و از توزیع منصفانهای در جهان برخوردارند، جایگزینی برای سوختهای فسیلی پایانپذیر (کویل، نفت، گاز طبیعی و غیره) هستند. لازم است فنآوریها و روشهای صحیح برای استفاده بهتر از منابع انرژی تجدید پذیر از جمله عدم اطمینان و بینظمی در ایجاد منابع مشخص شوند. در این مطالعه، عوامل زیستمحیطی پویا که بر تولید انرژی خورشیدی و بادی مؤثرند تعریف میشوند و روابط بین آنها بهطور زبانی توسط کارشناسان بیان میشود. این روابط زبانی در بین عوامل دیگر و حالات اولیه آنها توسط روش جدید نقشه شناختی زبانی نامطمئن که تعمیمی از مجموعههای فازی نامطمئن و نقشه شناختی فازی است ارزیابی میشوند. ایجاد وابستگی بین عوامل، با شبیهسازی مدل با توجه به شرایط اولیه عوامل مشاهده شد. بنابراین، این مدل در تصمیمات مربوط به سرمایهگذاری در انرژی خورشیدی و بادی به سرمایهگذاران و دولتها کمک میکند.
مقدمه
انرژی به دست آمده از منابع طبیعی نامحدود مانند نیروی باد، نیروی برقابی، انرژی خورشیدی، انرژی زمینگرمایی، زیستتوده، نیروی جزر و مدی و انرژی موج انرژی تجدید پذیر نامیده میشوند. بین سالهای 1990 تا 2014 مجموع تولید برق تجدید پذیر 191٪ افزایش یافته است (1). 28٪ از کل تولید برق اروپا در سال 2014 از انرژی تجدید پذیر به دست آمده است (1). اگرچه نیروگاههای برقابی بالاترین ظرفیت تولید انرژی تجدید پذیر را دارا هستند، اما ظرفیت تولید انرژی بادی و خورشیدی در سالهای اخیر بهطور قابلتوجهی در حال افزایش است. شکل 1 سهم انرژی از منابع تجدید پذیر را در مصرف ناخالص نهایی انرژی در سال 2011 نشان میدهد.
در بین منابع انرژی تجدید پذیر، انرژی خورشیدی بالاترین ظرفیت افزایش را دارا است. در سال 2014 ، ظرفیت تولید انرژی خورشیدی در مقایسه با سال 2013 با 14.1 درصد افزایش یافته است (1). اگرچه، افزایش قابلتوجهی در ظرفیت نصب شده منابع انرژی خورشیدی وجود دارد، اما درصد انرژی خورشیدی در کل ظرفیت نصب شده هنوز هم محدود است. درک ظرفیت انرژی خورشیدی و مدلسازی آن میتواند باعث افزایش تولید انرژی خورشیدی شود. عوامل و روابط بین تولید انرژی خورشیدی، نامشخص، پیچیده و مبهم است. نقشههای شناختی فازی ابزارهایی عالی برای رفع پیچیدگی و ابهام ذاتی موجود در مشکلات مدلسازی هستند (2). مجموعههای فازی نامطمئن، تعمیمی از مجموعههای فازی هستند که در آن میتوان میزان بیش از یک عضویت از یک عنصر را تعریف کرد (3،4). مجموعههای فازی نامطمئن و مجموعه اصطلاحات زبانی نامطمئن، امکان بیان بهتر ارزیابیهای کارشناسان را فراهم میآورند (4-6). در این مطالعه، از نقشههای شناختی فازی نامطمئن برای مدلسازی ظرفیت تولید انرژی خورشیدی استفاده شده است.
نتیجهگیری
انرژی تجدید پذیر جایگزین مهمی برای انرژی متعارف است که منابع آن محدود است و بالاخره گران میشود. تمایل به انرژی تجدید پذیر، بر اهمیت تعیین یک فنآوری مناسب برای تولید انرژی در یک محیط پویا میافزاید. برای مقابله با این نوع مسائل پیچیده در بخش انرژی، ما از مدل جدید HFCM استفاده کردهایم که تعمیمی از مجموعههای فازی نامطمئن و نقشه شناختی فازی است.
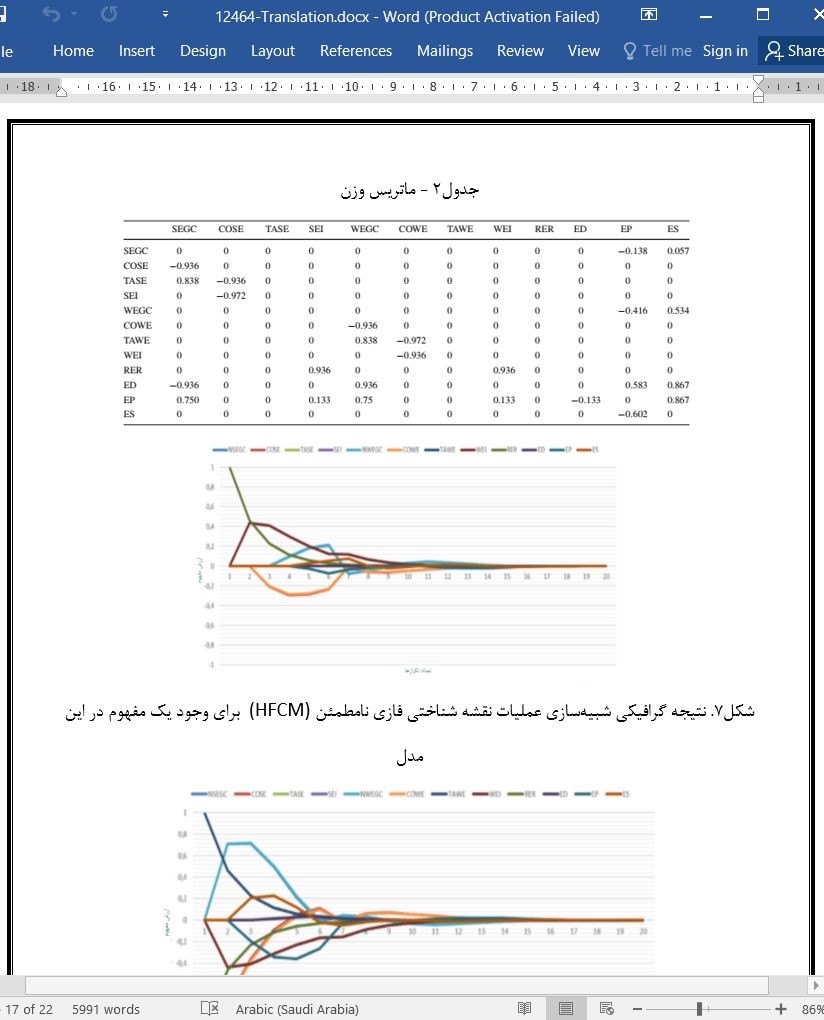
در این مطالعه، روابط علّی بین مفاهیم در تولید انرژی خورشیدی و بادی توسط مجموعه اصطلاحات زبانی توصیف شده است که به کارشناسان کمک میکند تا ارزیابیهای خود را با زبان طبیعی بیان کنند. این اصطلاحات زبانی با استفاده از عملیات HFLTS و OWA به توابع عضویت فازی ذوزنقهای تبدیل میشوند. توابع عضویت فازی ذوزنقهای با روش میانگین موزون فازی زدایی میشوند و مانند یک ماتریس وزن به بازه (-1، 1) تبدیل میشوند. ماتریس وزن و حالت اولیه عوامل در فرایند تکرار در تابع آستانهای تانژانت هذلولی در معادله (3) شامل میشوند تا به همگرایی برسند. مقادیر همگرا، حالت پایدار عوامل موجود در مدل را نشان میدهند.
Abstract
Renewable energy sources (solar, wind, tidal, etc.), which are unlimited and have a fair distribution in the world, are an alternative to the depleting fossil fuels (coil, petroleum, natural gas, etc.). It is necessary to identify the right technologies and methods to make more effective use of renewable energy sources including uncertainty and irregularity in resource creation. In this study, dynamic environmental factors affecting the production of solar and wind energy are defined and the relations among them are linguistically expressed by the experts. These linguistic relationships among factors and their initial states are assessed by new developed hesitant linguistic cognitive map method that is an extension of hesitant fuzzy sets and fuzzy cognitive map. Relational development between factors was observed by simulating the model according to the initial condition of the factors. Thus, the model helps investors and governments to direct their solar and wind energy investment decisions.
Introduction
The energy obtained from infinite natural sources such as wind power, hydropower, solar energy, geothermal energy, biomass, tidal power and wave power are called renewable energy. In the last two decades, renewable energy has become a serious energy source. Between the years 1990 and 2014, total renewable electricity generation enlarged by 191% [1]. Europe’s 28% of overall electricity generation is obtained from renewable energy in 2014 [1]. Although hydropower plants have the highest renewable energy generation capacity, wind and solar power generation capacities are significantly increasing in the recent years. Figure 1 shows the share of energy from renewable sources in gross final consumption of energy in 2011.
Among the renewable energy sources, solar power has the highest increase capacity. In 2014, solar power generation capacity increased by 14.1% compared with 2013 [1]. Although there is a significant increase in the installed capacity of solar energy sources, the percentage of solar energy in the total installed capacity is still limited. Understanding and modeling the solar energy capacity can enhance the solar energy production. The factors and the relations among the solar energy generation are uncertain, complex and vague. Fuzzy cognitive maps are excellent tools for dealing with complexity and ambiguity inherent in modeling problems [2]. Hesitant fuzzy sets are the extensions of fuzzy sets where more than one membership value of an element can be defined [3,4]. Hesitant fuzzy sets and hesitant linguistic term sets enable better expressing the experts’ evaluations [4–6]. In this study, hesitant fuzzy cognitive maps are used for modeling solar energy generation capacity.
Conclusion
Renewable energy is an important alternative to conventional energy whose sources are finite and becoming expensive in time. The tendency to the renewable energy increases the importance of the determining right energy generation technology in a dynamic environment. To deal with this kind of complex problems in the energy sector, we applied the new HFCMs model that is an extension of hesitant fuzzy sets and fuzzy cognitive map.
In this study, the causal relationships among concepts in solar and wind energy generation are described by linguistic term sets that help expert to express their evaluations with natural language. These linguistic terms are transformed into trapezoidal fuzzy membership functions using HFLTS and OWA operations. Trapezoidal fuzzy membership functions are defuzzified with the weighted average method and transformed to [−1, 1] interval as a weight matrix. Weight matrix and the initial state of the factors are included the iteration process within hyperbolic tangent threshold function in Eq. (3) until convergence. Converge values represent the steady state of the factors in the model.
چکیده
مقدمه
نقشه شناختی فازی
نقشه شناختی فازی نامطمئن (HFCM)
مدلسازی مصرف انرژی تجدید پذیر بر اساس HFCMها
نتیجهگیری
منابع
Abstract
Introduction
Fuzzy cognitive map
Hesitant fuzzy cognitive map (HFCM)
Modeling renewable energy usage based on HFCMs
Conclusion
References
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه