دانلود مقاله یک رویکرد جدید برای زمان بندی پروژه با استفاده از ماتریس ساختار وابستگی فازی
چکیده
ماتریس ساختار وابستگی (DSM)، بعنوان یک راه حل جایگزین، یک ابزار مفید در زمان بندی پروژه هنگام نزدیک شدن به مباحث وابستگی اطلاعات بین فعالیت ها است. با این حال، رویکرد فعلی DSM با این معضل روبرو است که دقیقا نمی توان همپوشانی فعالیتها را در مرحله برنامه ریزی یک پروژه تخمین زد، و این راه حل را برای یک روش شناسی قوی برای مدیریت زمان بندی ها در شرایط نامطمئن وابستگی اطلاعات فراخوانی کرد. هدف تحقیق ما ارائه رویکردی است که از نظریه مجموعه فازی برای حل مسئله در یک محیط نامطمئن استفاده می کند. بعنوان تعمیمی از زمانبندی سنتی مبتنی بر DSM، همپوشانی و مدت زمان فعالیت ها را بعنوان اعداد فازی توصیف می کنیم و یک الگوریتم سیستماتیک برای محاسبه متغیرهای زمان فعالیتها و مدت زمان اجرای پروژه مطرح می کنیم. همچنین یک نمونه برای اثبات اثربخشی الگوریتم ارائه می کنیم.
1. مقدمه
روش سنتی مورد استفاده در مدیریت زمان پروژه، روش مسیر بحرانی (CPM)، برای برنامه ریزی و کنترل پروژه های پیچیده است. با این حال، روش مسیر بحرانی (CPM) سنتی که مبتنی بر توضیحات جریان های کاری با استفاده از نمادهای گرافیکی است، برای مدیریت دنباله مناسب و مخصوصا برای مدلسازی جریان اطلاعات (اپینگر، 2001؛ اپینگر و همکاران، 1994؛ یاسین و همکاران، 1999) مناسب نیست. بنابراین، ماتریس ساختار وابستگی، یا ماتریس ساختار طراحی (DSM)، یک روش جدید برای توصیف جریان اطلاعات است که بعنوان یک ابزار مفید برای مقابله مباحث طراحی سیستم های پیچیده استفاده شده است (استوارد، 1981). به دنبال این جریان، یک شاخه جداگانه ای از تحقیق براساس ماتریس ساختار طراحی (DSM) برای رفع مشکل جریان اطلاعاتی برای زمان بندی پروژه انجام شده است (کاروزکوزا و همکاران، 1998؛ چن و همکاران، 2003؛ ماهسواری و وارگسه، 2005). در زمان بندی مبتنی بر ماتریس ساختار طراحی (DSM)، لازم است تا "زمان موردنیاز ارتباطات" برای جمع آوری اطلاعات قبلی و در طول اجرای فعالیت ها ثبت شود (مشواری و وارگسه، 2005: 224). این زمان ارتباطات شامل زمانی برای جلسات، پردازش ایمیل ها، زمان انتظار برای تصمیمات، و فعالیتهای انجام شده برای جمع آوری اطلاعات هستند. علاوه بر این، همپوشانی فعالیتها مهم است و باید به منظور تخمین دقیق و برآوردن مدت زمان فشرده سازی پروژه مورد بررسی قرار گیرد.
6. نتیجه گیری و تحقیقات آینده
ما یک رویکرد فازی برای زمان بندی پروژه مبتنی بر ماتریس ساختار طراحی (DSM) داریم تا این مسئله را بررسی کنیم که همپوشانی ناشی از ابهام و عدم اطمینان وابستگی اطلاعات بین فعالیتها است. این الگوریتم را می توان بعنوان یک تعمیم از الگوریتم سنتی زمان بندی مبتنی بر DSM در نظر گرفت که توسط مشواری و وارگسه (2005) پیشنهاد شد، که به ویژه در ارتباط با مباحث فازی وابستگی اطلاعات مفید است. علاوه بر این، با توجه به مدیریت پروژه ها مانند توسعه جدید یک محصول یا طراحی مشارکتی، جریان اطلاعات یک عامل تعیین کننده مهم در زمان بندی است. بنابراین، با هدف ویژه آن مسئله روابط وابستگی متقابل فازی بین فعالیتها را حل می کند، که ناشی از جریان اطلاعات است بجای اینکه ناشی از جریان کلی کار باشد، همچنین این الگوریتم را می توان بعنوان شاخه دیگری از رویکردهای فازی برای زمان بندی پروژه در نظر گرفت، که از الگوریتم های سابق فازی مبتنی بر CPM&PERT پیشنهاد شده توسط چن و هوآنگ (2007)، چن و هسو (2008)، و لیبراتور (2008) متفاوت است. قدرت این الگوریتم فازی این است که می تواند به تحلیل درجه بحرانی فعالیتها، مسیرها، و تا حد بیشتری به مدت زمان اجرای یک پروژه در یک محیط نامطمئن وابستگی های اطلاعاتی بین فعالیتها اشاره کند.
Abstract
As an alternative solution, the Dependency Structure Matrix (DSM) is a useful tool in project scheduling when approaching information dependency issues between activities. However, the current DSM approach faces the dilemma that the overlap of activities cannot be precisely estimated in the planning stage of a project, and the solution calls for a robust methodology for managing schedules within uncertain conditions of information dependency. The aim of our research is to propose an approach that utilizes fuzzy set theory to solve the problem within an uncertain environment. As an extension of traditional DSM-based scheduling, we describe the overlap and duration of activities as fuzzy numbers and put forth a systematic algorithm to calculate the time variables of activities and project duration thereof. An example is also provided to demonstrate the effectiveness of the algorithm.
1. Introduction
The technique traditionally used in project time management is the Critical Path Method (CPM) for the planning and control of complicated projects. However, traditional CPM, which is based on the descriptions of task flows using graphic symbols, is not suitable for sequence management, especially for modeling information flow (Eppinger, 2001; Eppinger et al., 1994; Yassine et al., 1999). Therefore, the Dependency Structure Matrix, or Design Structure Matrix (DSM), a new technique for the description of information flow, has been employed as a useful tool for coping with design issues of complex systems (Steward, 1981). Following this stream, a separate branch of research based on DSM has been conducted to address the problem of information flow for project scheduling (Carrascosa et al., 1998; Chen et al., 2003; Maheswari and Varghese, 2005). In DSM-based scheduling, it is necessary to capture the “communication time” needed for collecting information before and during the execution of activities (Maheswari and Varghese, 2005: 224). This communication time includes time for meetings, processing emails, waiting time for decisions, and activities conducted to collect information. In addition, the overlap of activities is important and should be addressed in order to estimate correctly and meet the compressed project duration.
6. Conclusion and future research
We have proposed a fuzzy approach for DSM-based project scheduling to address the problem that the overlap caused by the vagueness and impreciseness of information dependency between activities. This algorithm can be regarded as an extension of the traditional algorithm of DSM-based scheduling proposed by Maheswari and Varghese (2005), which is particularly useful in dealing with fuzzy issues of information dependency. Moreover, with regard to the management of projects such as new product development or collaborative design, information flow is a very important determinant in scheduling. Therefore, with its special purpose to solve the problem of fuzzy interdependent relationships between activities caused by information flow rather than general work flow, this algorithm can also be regarded as another branch of fuzzy approaches for project scheduling, which is different from the former CPM&PERT-based fuzzy algorithms proposed by Chen and Huang (2007), Chen and Hsueh (2008), and Liberatore (2008).The strength of this fuzzy algorithm is that it can be referred to analyze the critical degree of activities, paths, and to a further degree, the duration of a project within an uncertain environment of information dependencies between activities.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. روش مسیر بحرانی (CPM) و PERT در مقابل ماتریس ساختار طراحی (DSM)
3. رویکرد فازی پیشنهادی زمان بندی پروژه مبتنی بر ماتریس ساختار طراحی (DSM)
3.1. الگوریتم سنتی زمان بندی مبتنی بر ماتریس ساختار طراحی (DSM)
3.2. رویکرد فازی پیشنهادی
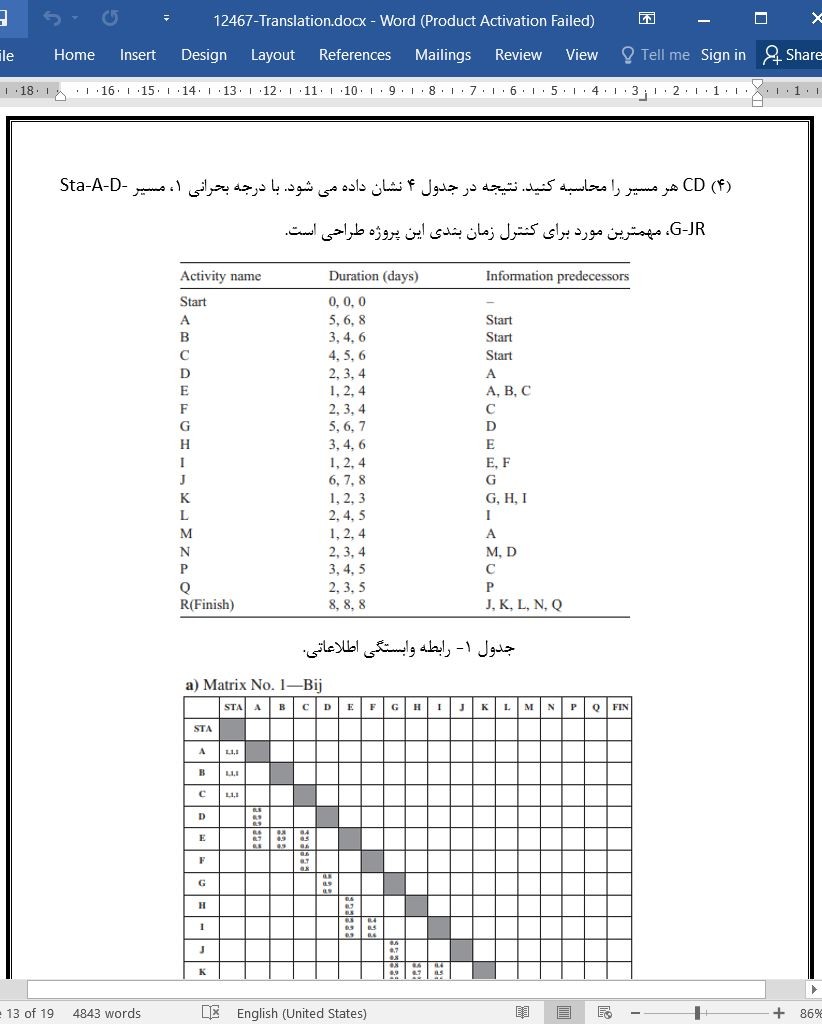
4. یک نمونه
5. مباحث بیشتر درباره الگوریتم فرضی
6. نتیجه گیری و تحقیقات آینده
منابع
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. CPM and PERT versus DSM
3. The proposed fuzzy approach of DSM-based project scheduling
3.1. Traditional algorithm of DSM-based scheduling
3.2. The proposed fuzzy approach
4. An example
5. Further discussion of the proposed algorithm
6. Conclusion and future research
References
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه