دانلود مقاله تقویت فروش B2B با تجزیه و تحلیل داده های کلان مشتری
چکیده
تمرکز این مقاله بر روی استفاده از تجزیه و تحلیل داده های کلان در مدیریت ارتباط B2B با مشتری بوده و تاثیرات تجزیه و تحلیل داده های کلان بر ارتباط با مشتری و رشد فروش با استفاده از مجموعه داده های چند صنعتی از 417 موسسه B2B را بررسی می کند. این مقاله همچنین بررسی می کند که آیا فرهنگ تحلیلی درون شرکتی این تاثیرات را متعادل می سازد. در این مقاله پی می بریم که استفاده از داده های کلان مشتری بطور قابل ملاحظه ای رشد فروش را تقویت کرده (یعنی نتایج عملکردی پولی) و ارتباط را با مشتری بهبود می دهد (نتایج عملکردی غیر پولی). هرچند در موسسه هایی که از تجزیه و تحلیل بازاریابی حمایت می شود مورد دوم بیشتر مشاهده می شود، در حالی که مورد اول هیچ گونه تاثیری را از فرهنگ تحلیلی بر نمی دارد. این مقاله بصورت تجربی ثابت می کند که تجزیه و تحلیل داده های کلان مشتری ارتباط را با مشتری بهتر کرده و باعث رشد فروش در موسسه های B2B می شود.
1. مقدمه
یک نظر سنجی در ایالات متحده و دنیا حاکی از آن است که 84% موسسه های پیشرو صنعتی شروع به تجزیه و تحلیل داده های کلان کرده اند تا بتوانند با دقت بیشتری تصمیم گیری کنند (استاتیستا ، 2018). تجزیه و تحلیل داده های کلان، یعنی بکارگیری داده های کلان و روش های تحلیلی مرتبط، با کاهش هزینه ها و ایجاد زمینه های جدید تر برای نوآوری و جلوگیری، بیشترین منافع را برای موسسه ها به ارمغان می آورد (شرکای نیو ونتیج، 2017). تجزیه و تحلیل داده های کلان موسسه ها را قادر می سازد که ارتباط تجاری خود را تقویت کنند، برای مثال در مدیریت زنجیره تامین (گوناسکاران و همکاران، 2017) و مدیریت ارتباط با مشتری (نام، لی، و لی؛ 2019، فیلیپس-رن و هوسکینسون؛ 2015، زربینو، آلوئینی، دولمین، و مینینو، 2018). در مدیریت ارتباط با مشتری، تجزیه و تحلیل داده های کلان باعث ایجاد موج جدیدی از استراتژی ها جهت پشتیبانی از شخصی سازی و سفارشی سازی فروش و خدمات به مشتری (انشاری، آلموناوار، لیم، و المودیمیق، 2018)، و ایجاد ارتباط قوی تر و شخصی تر با مشتریان می شود ( دی لیما فرانسیسکو، مورا، سابینو، سنتوس، و اسکواریکو، 2016). همچنین، داده های کلان در شناسایی انتظارات مشتریان از شرکت ها و پیش بینی خواسته های آتی آنان (پررا، دیلینی، کولاوانسا، 2018) در استفاده از فن آوری ها و ابزارهای (امتیاس و کیوانپور، 2011) داده های کلان نقشی اساسی دارد.
5.3. محدودیت ها و تحقیقات آتی
مقیاس این مقاله به بررسی استفاده از داده های کلان مشتری در مدیریت مشتری های B2B و مدل برداری تاثیر تجزیه و تحلیل داده های کلان بر عملکرد مشتری با فرهنگ تحلیلی به عنوان متعادل گر محدود بوده است. این مقاله با استفاده از داده های جمع آوری شده از چندین بخش صنعتی انجام شده است، و مطالعات آتی می تواند یافته های ما را عمیق تر کرده و بررسی کند که آیا این یافته ها قابل تعمیم به بخش های خاص صنعتی مانند تولید و خرده فروشی می باشند. مطالعات آتی می تواند این مدل را با استفاده از ساختار های اضافی مانند مدیریت و طرفداری از تیم گسترش دهد، و با گرایش IT و انعطاف پذیری IT شرایط متعادل گری که تحت آن تجزیه و تحلیل داده های کلان می تواند برتری رقابتی را برای شرکت به همراه داشته باشد را بهتر بشناسد. این مقاله از معیار های ذهنی و نسبی عملکرد ارتباط با مشتری و رشد فروش استفاده کرده است، که می تواند در آینده به منظور ارائه تصویری فراگیر تر از تاثیر تجزیه و تحلیل داده های کلان بر عملکرد شرکت، با معیار های عینی تعویض شود. بعلاوه، داده های مقاله پیش رو از مدیران ارشد جمع آوری شده است، در حالی که، مقالات پیشین در مورد رابطه میان عملکرد موسسه و تجزیه و تحلیل داده های کلان این موضوع را فقط در میان تحلیل گران تجاری و متخصصین IT (آکتر و همکاران، 2016؛ وامبا و همکاران، 2017) انجام داده اند. اگرچه مدیران ارشد بهترین شناخت را از اهداف استراتژیک شرکت و معیارهای عملکردی آن دارند، ولی احتمال دارد آنها تصویر محدودی را از تجزیه و تحلیل داده های کلان در سطح عملی شرکت داشته باشند. از این رو، یک مقاله چند سطحی که متشکل از رویکرد های مدیران ارشد و تحلیلگران تجاری است، می تواند بینش فراتری را ارائه دهد.
Abstract
This study focuses on the use of big data analytics in managing B2B customer relationships and examines the effects of big data analytics on customer relationship performance and sales growth using a multi-industry dataset from 417 B2B firms. The study also examines whether analytics culture within a firm moderates these effects. The study finds that the use of customer big data significantly fosters sales growth (i.e. monetary performance outcomes) and enhances the customer relationship performance (non-monetary performance outcomes). However, the latter effect is stronger for firms which have an analytics culture which supports marketing analytics, whereas the former effect remains unchanged regardless of the analytics culture. The study empirically confirms that customer big data analytics improves customer relationship performance and sales growth in B2B firms.
1. Introduction
A survey in the United States and worldwide reports that 84% of industry‑leading firms have started big data analytics initiatives to bring greater accuracy to their decision-making (Statista, 2018). Big data analytics, i.e. the utilization of big data and related analytics methods, is reported to deliver the most value to firms by reducing expenses and creating new avenues for innovation and disruption (NewVantage Partners, 2017). Big data analytics enables firms to strengthen their business operations, for example, in supply chain management (Gunasekaran et al., 2017) and customer relationship management (Nam, Lee, & Lee, 2019; Phillips-Wren & Hoskisson, 2015; Zerbino, Aloini, Dulmin, & Mininno, 2018). In customer relationship management, the emergence of big data analytics will enable a new wave of strategies to support the personalization and customization of sales and customer services (Anshari, Almunawar, Lim, & Al-Mudimigh, 2018), and to build stronger and more personal relationships with customers (De Lima Francisco, Moura, Sabino, Santos, & Esquarcio, 2016). Also, big data is useful to identify what customers actually expect from companies and to predict their future demands (Perera, Dilini, & Kulawansa, 2018) utilizing big data technologies and tools (Emtiyas & Keyvanpour, 2011).
5.3. Limitations and future research
The scope of this study was limited to exploring the use of customer big data in managing B2B customer relationships and modelling the impact of big data analytics on company performance with an analytics culture as a moderator. The study was conducted using data collected from several industry sectors, and future studies could deepen our findings and examine whether these results are generalizable to specific industry sectors, such as manufacturing or retailing. Future studies could extend the model by including additional constructs, such as management and team advocacy, an IT orientation and IT flexibility to better understand the moderating conditions under which big data analytics can provide competitive advantages for companies. The study adopted subjective and relative measures of customer relationship performance and sales growth, which could be replaced by objective measures in future studies to present a more pervasive picture of the impact of big data analytics on company performance. Additionally, the data for the present study was collected from senior managers, while previous studies on the relation between firm performance and big data analytics have been conducted mainly among business analysts and IT professionals (Akter et al., 2016; Wamba et al., 2017). Although senior managers have the best understanding of the company's strategic objectives and performance metrics, they may have a limited picture of the exploitation of big data analytics at the operational level of the company. Thus, a multilevel study combining the views of the senior management and business analysts, could potentially provide further insights.
H1. Big data analytics has a positive effect on a B2B firm's customer relationship performance.
H2. Customer relationship performance has a positive effect on a B2B firm's sales growth.
H3. Big data analytics has a positive effect on a B2B firm's sales growth.
H4a. An analytics culture positively moderates the relationship between big data analytics and customer relationship performance in B2B firms.
H4b. An analytics culture positively moderates the relationship between big data analytics and sales growth in B2B firms.
H1: تجزیه و تحلیل داده های کلان تاثیر مثبتی بر عملکرد ارتباط با مشتریان موسسه های B2B دارد.
H2: عملکرد در ارتباط با مشتری تاثیر مثبتی بر روی رشد فروش موسسه B2B دارد.
H3: تجزیه و تحلیل داده های کلان اثر مثبتی بر روی رشد فروش دارد.
H4a: فرهنگ تحلیلی به صورت مثبتی رابطه میان تجزیه و تحلیل داده های کلان و عملکرد ارتباط با مشتری را در موسسه های B2B متعادل می کند.
H4b: فرهنگ تحلیلی به صورت مثبتی رابطه میان تجزیه و تحلیل داده های کلان و رشد فروش را در موسسه های B2B متعادل می کند.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. پس زمینه نظری و ایجاد فرضیه
2.1. ارتباط B2B در عصر داده های کلان
2.2. تجزیه و تحلیل داده های کلان مشتری در مدیریت B2B ارتباط با مشتری
2.3. تجزیه و تحلیل داده های کلان و عملکرد موسسه
2.4. تاثیر متعادل کننده فرهنگ تحلیلی در یک موسسه
3. داده ها و روش
3.1. مقیاس های اندازه گیری
3.2. جمع آوری داده ها و نمونه
4. نتایج
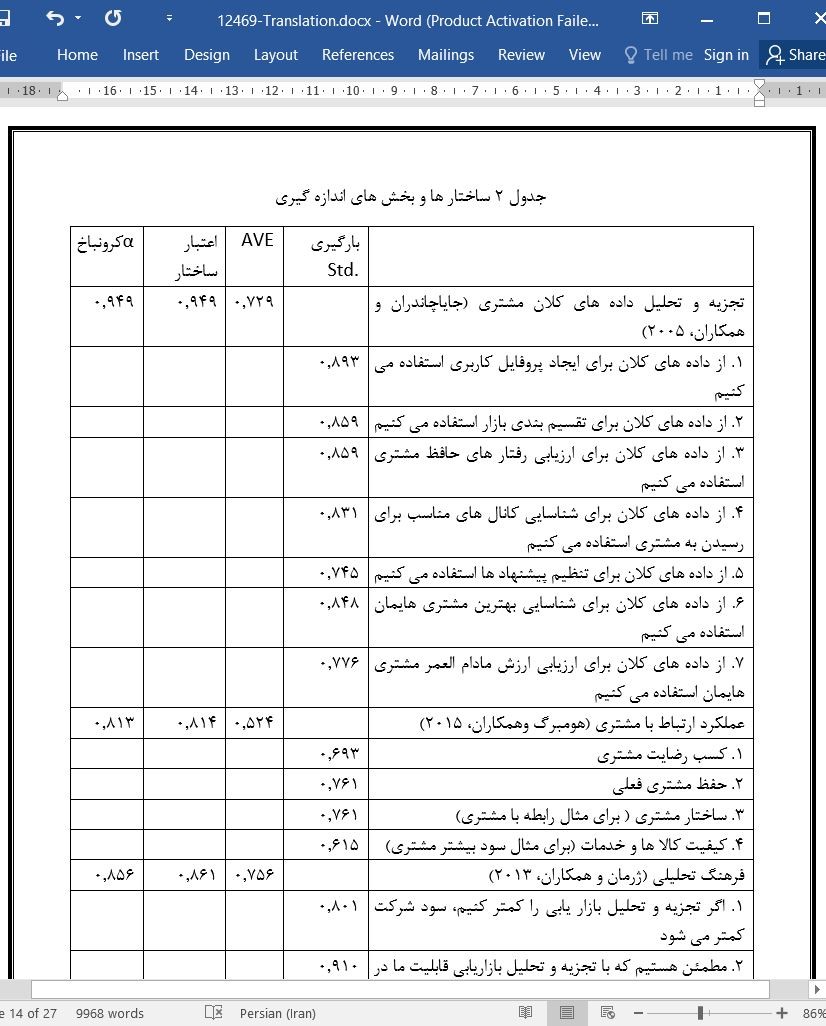
4.1. مدل اندازه گیری
4.2. مدل ساختاری
5. بحث و نتیجه گیری
5.1. هم بخشی نظری
5.2. هم بخشی عملی
5.3. محدودیت ها و تحقیقات آتی
منابع
ABSTRACT
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical background and hypotheses development
2.1. B2B relationships in the era of big data
2.2. Customer big data analytics in B2B customer relationship management
2.3. Customer big data analytics and firm performance
2.4. Moderating effect of a firm's analytics culture
3. Data and method
3.1. Measurement scales
3.2. Data collection and sample
4. Results
4.1. Measurement model
4.2. Structural model
5. Discussion and conclusion
5.1. Theoretical contribution
5.2. Practical contribution
5.3. Limitations and future research
References
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه