دانلود مقاله راه حل های DNS و PKI مبتنی بر بلاک چین
چکیده
سیستم های نام دامنه و سیستم های اعتبار گواهی ممکن است در اجراهایشان دارای مشکلات امنیتی و اعتماد باشند. این مقاله به صورت خلاصه بررسی می کند که چگونه این سیستم ها کار می کنند و ممکن است مشکلات اجرا چه چیزی باشد. راه حل های غیرمتمرکز مبتنی بر بلاک چین وجود دارند که می توانند بر این مشکلات غلبه کنند. ما توضیح مختصری درباره این موضوع ارائه می کنیم که این سیستم های بلاک چین چگونه کار می کنند و نقاط قوت آنها را توضیح می دهیم. چالش های امنیتی DNS مشخص می شوند. راه حل های DNS مبتنی بر بلاک چین طبقه بندی می شوند و با توجه به خدمات آنها با جزئیات شرح داده می شوند. مزایا و امکان پذیر بودن این پیاده سازی ها موردبحث قرار می گیرند. در آخر اینکه، احتمال اینترنت غیرمتمرکز مورد بحث قرار می گیرد.
مقدمه
کاربران اینترنت بر سیستم نام دامنه (DNS) و زیرساخت کلیدی عمومی (PKI) برای اتصال به سرویس یک شبکه،عمدتاً وب، متکی هستند. این سیستم ها متمرکز هستند اما راه حلهای غیر متمرکز مبتنی بر بلاک چین نیز ممکن هستند.
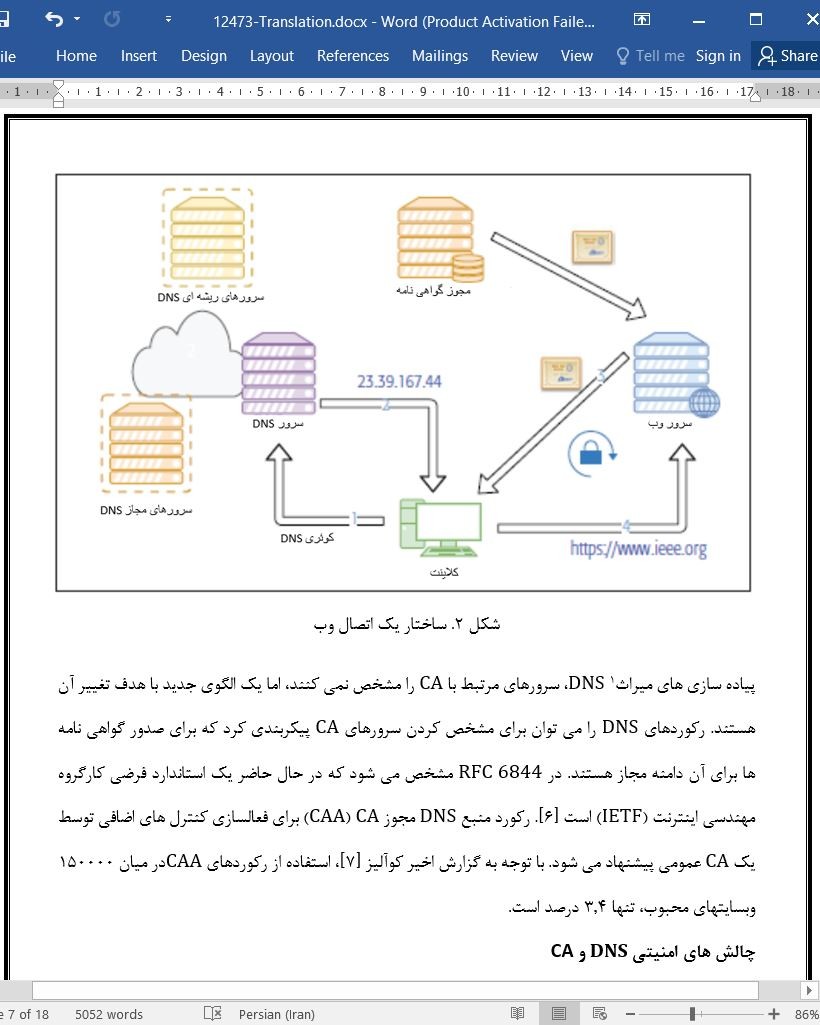
زیرساخت DNS در شکل ۱ خلاصه می شود. نسخه متمرکز در سمت چپ شکل نشان داده می شود.کاربر نام یک دامنه را با پرسیدن سرور تنظیم شده DNS (محلی) تعیین می کند. اگر در حال حاضر سرور محلی آدرس را بداند ( سرور معتبر یا ذخیره شده)، این سرور به صورت مستقیم به کاربر پاسخ خواهد داد. در غیر این صورت سرور از سرورهای ریشه DNS سوال خواهد کرد و سرور های دامنه سطح بالا (TLD)، سرور معتبر برای آن نام دامنه را پیدا می کنند. سپس سرور محلی DNS از آن سرور خواهد پرسید تا آدرس IP را یاد بگیرد و سپس به کاربر اطلاع دهد.
نتایج و نتیجه گیری ها
ما با مشکلات نقض بی طرفی، سانسور، و مشکلات حریم خصوصی مواجه هستیم که آزادی و قابلیت استفاده از اینترنت را تهدید می کند. انکار حملات سرویس باعث اختلال در بسیاری از سرویس های آنلاین می شود. استانداردها با سرعتی که باید داشته باشند، در حال تکامل نیستند. فناوری های غیرمتمرکز بلاک چین را می توان بعنوان یک راه حل توسعه داد.
همچنین، پیاده سازی های بلاک چین که سرویس نام و پسوندهای مخصوص میزبان مانند .bit و .eth را می دهند، می توانند توسط سرویس های دیگر مانند OpenNIC نظیر شوند. راه حل های ترکیبی به صورت کامل غیرمتمرکز نیستند، اما آنها هنوز مهم هستند و در خدمت هدفشان هستند. اهمیت چنین راه حلی این است که تنها یک نهاد واحد قادر به مدیریت فضای نام نخواهد بود، بلکه همچنین تعدادی گزینه دیگر نیز وجود خواهند داشت. همچنین این راه حل ها بعنوان یک زیرساخت کلیدی عمومی توزیع شده کار می کنند. وجود بسیاری از گره ها در شبکه P2P با بکارگیری فضای نام، در دسترس بودن را در طول حملات DDoS ارائه خواهد داد.
Abstract
Domain name systems and certificate authority systems may have security and trust problems in their implementation. This article summarizes how these systems work and what the implementation problems may be. There are blockchain-based decentralized solutions that claim to overcome those problems. We provide a brief explanation on how blockchain systems work, and their strengths are explained. DNS security challenges are given. Blockchain-based DNS solutions are classified and described in detail according to their services. The advantages and feasibility of these implementations are discussed. Last but not least, the possibility of the decentralized Internet is questioned.
Introduction
Internet users rely on the domain name system (DNS) and public key infrastructure (PKI) to connect to a network service, mainly the web. These systems are centralized, but blockchain-based decentralized solutions are also possible.
DNS infrastructure is summarized in Fig. 1. The centralized version is shown on the left side of the figure. The user resolves a domain name to an IP address by asking the configured (local) DNS server. If the local server already knows the address (authoritative server or cached), it will answer directly to the user. Otherwise, the server will ask the DNS root servers and top-level domain (TLD) servers to locate the authoritative server for that domain name. The local DNS server will then ask that server to learn the IP address and then inform the user.
Results and Conclusion
We are facing the violation of net neutrality, censorship, and privacy problems, which threaten the freedom and usability of the Internet. Denial of service attacks cause the disruption of many online services. The standards are not evolving as fast as they should. Decentralized blockchain technologies can be developed as a solution.
Blockchain implementations that give name service and host-specific extensions like .bit and .eth. can also be peered by other services like OpenNIC. The hybrid solutions are not fully decentralized, but they are still important and serve their purpose. The importance of such a solution is that there will not be only a single entity managing the namespace, but also some other alternatives as well. These solutions also work as a distributed public key infrastructure. The existence of many nodes on the P2P network serving the namespace will serve availability during DDoS attacks.
چکیده
مقدمه
استانداردهای DNS و PKI
چالش های امنیتی DNS و CA
DNS و DPKI مبتنی بر بلاک چین
تفکیک نام
مدیریت شناسه
ذخیره سازی توزیع یافته
برنامه های غیرمتمرکز
اینترنت غیرمتمرکز
تجربه عملی
نتایج و نتیجه گیری ها
منابع
Abstract
Introduction
DNS and PKI Standards
DNS and CA Security Challenges
Blockchain-Based DNS and DPKI
NaMe Resolution
Identity ManageMent
Distributed Storage
Decentralized Applications
Decentralized Internet
Practical Experience
Results and Conclusion
References
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه