دانلود مقاله بازاریابی ویروسی در شبکه های اجتماعی: چشم اندازی اپیدمیولوژیک
چکیده
امروزه رسانههای اجتماعی آنلاین حاضر در همه جا دارای تاثیر فزاینده مدوامی روی کسب و کارها، سیاست و جامعه هستند. شناخت این مکانیسمهای جدیدتر انتشار اطلاعات، برای تصمیمگیری در مورد سیاستهای تبلیغاتی بسیار مهم است. با توجه به تعامل آزاد میان تعداد زیادی از اعضا، انتشار اطلاعات در رسانههای اجتماعی، دارای ویژگیهای مختلف مشابه با یک پدیده اپیدمی (همهگیر) است. در این مقاله، با در نظر گرفتن برخی تعاملات واقعبینانه در شبکههای اجتماعی، مدلی ریاضی را برای شناخت پدیدههای بازایابی دیجیتال با رویکردی اپیدمیولوژیک ارائه میدهیم. از رویکرد میدان-میانگین و همچنین تجزیه و تحلیل شبکه برای بررسی این پدیده برای هر دو مدل همگن و ناهمگن استفاده میکنیم و دینامیک انتشار و همچنین حالتهای توازن برای برای هر دو مورد را مطالعه مینماییم. فضای پارامتر و راهکارهای طراحی برای اجرای کمپینی تبلیغاتی با کارایی زیاد را مورد بررسی قرار میدهیم. علاوه بر این، پدیده دوپایایی را مشاهده میکنیم که تحت آن، شرایط لازم برای افزایش پایداری کمپین را تخمین زده و در عین حال از گسترش ویروسی آن مطمعن میشویم.
1. مقدمه
در این عصر اینترنت، اهمیت شبکههای اجتماعی در گسترش یک پیام، عقیده یا کمپین غیر قابل انکار است [۱، ۲، ۳]. طراحی راهکارهایی برای بهرهبرداری از شبکههای اجتماعی به منظور افزایش سرعت انتشارکمپین و همچنین پایداری آن، تبدیل به حوزه پژوهشی به طور فزاینده جالبی در میان مبارزان سیاسی و مدیران بازاریابی محصول شده است. با توجه به این ایدهها، بازاریابی ویروسی (VM)، به عنوان راهکار بازاریابی جدید و روشی برای ارتباط با مشتریان مورد استفاده قرار میگیرد که میتواند به طور بالقوه به سرعت به مخاطبان زیادی دست یابد [۴، ۵ ، ۶]. VM همچنین به عنوان بازاریابی دهان به دهان اینترنتی شناخته میشود، همچنان که افراد را تشویق به به اشتراکگذاری اطلاعات میکند [۷]. این تشویق گاهی اوقات با معرفی مزایایی (مانند امتیازات اعتباری، پول الکترونیکی، تخفیفهای اضافی، بازپرداختها، کدهای تبلیغاتی و غیره) برای مشتریان موجود، به عنوان پاداشی برای به اشتراکگذاری اطلاعات در شبکه همتای آنها انجام میشود.
5. نتیجهگیری
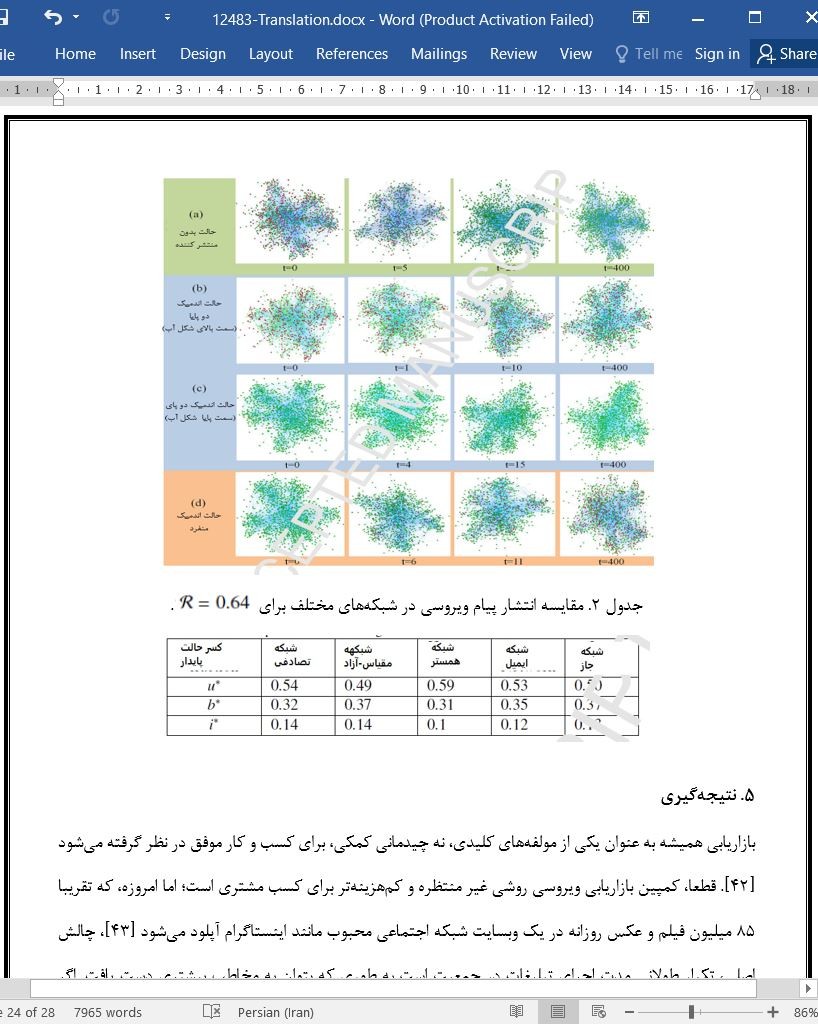
بازاریابی همیشه به عنوان یکی از مولفههای کلیدی، نه چیدمانی کمکی، برای کسب و کار موفق در نظر گرفته میشود [۴۲]. قطعا، کمپین بازاریابی ویروسی روشی غیر منتظره و کمهزینهتر برای کسب مشتری است؛ اما امروزه، که تقریبا ۸۵ میلیون فیلم و عکس روزانه در یک وبسایت شبکه اجتماعی محبوب مانند اینستاگرام آپلود میشود [۴۳]، چالش اصلی، تکرار طولانی مدت اجرای تبلیغات در جمعیت است به طوری که بتوان به مخاطب بیشتری دست یافت. اگر اینستاگرام را در نظر بگیریم که تقریبا ۵۰۰۰۰۰ تبلیغ کننده از این وبسایت محبوب برای مبارزه تبلیغاتی استفاده میکنند [۴۴]، اکثر آپلودها مانند یک سوزن در انباری پر از کاه هستند. مدلی که ما در این مقاله ارائه میدهیم اصل پایداری را برای مبارزات تبلیغاتی آنلاین به وسیله توسعه مدلی بر اساس دادههای نظرسنجی دقیق روانشناسی مصرف کننده ثابت میکند [۳۵]. تجزیه و تحلیل گسترده با معادلات میدان-میانگین و همچنین شبیهسازیهای شبکه نشان میدهد که ناحیه دوپایایی به عنوان مقدار α با افزایش نرخ دفع غیر خطی رشد میکند. دوپایایی به سیستم، فرصت حفظ حالت ویروسی خود را همچنین برای شرایط پارامتری ارائه میدهد. در حالی که مشاهده کردیم حالتهای پایدار انتشار در شبکه ها دارای ارتباط نزدیک با دینامیک سیستم میدان-میانگین هستند، به اهمیت ساختارهای شبکه در این مساله نیز پی بردیم. نه تنها در سیستم های مدل، بلکه همچنین در شبکه های اجتماعی واقعی نیز با در نظر گرفتن همه ناهمگنی موجود در جمعیت، نشان داه شده است که پایداری یک کمپین ویروسی در واقع وابسته به توجه افرادی است که علیرغم آگاهی از کمپین در آن شرکت نمیکنند. اگر درصد خاصی از این جمعیت خاموش شروع به انتشار در طرفداری از کمپین کند، حالت اندمیک آن در کل جمعیت حفظ میشود.
Abstract
Omnipresent online social media nowadays has a constantly growing influence on business, politics, and society. Understanding these newer mechanisms of information diffusion is very important for deciding campaign policies. Due to free interaction among a large number of members, information diffusion on social media has various characteristics similar to an epidemic. In this paper, we propose and analyze a mathematical model to understand the phenomena of digital marketing with an epidemiological approach considering some realistic interactions in a social network. We apply mean-field approach as well as network analysis to investigate the phenomenon for both homogeneous and heterogeneous models, and study the diffusion dynamics as well as equilibrium states for both the cases. We explore the parameter space and design strategies to run an advertisement campaign with substantial efficiency. Moreover, we observe the phenomena of bistability, following which we estimate the necessary conditions to make a campaign more sustainable while ensuring its viral spread.
1. Introduction
In this age of the Internet, the importance of social networks to spread a message, opinion or campaign is undeniable [1, 2, 3]. Devising strategies to exploit existing social networks to make a campaign fast spreading as well as sustainable is becoming an area of growing interest among political campaigners and product marketing managers. Based on this ideas, viral marketing (VM) is being adopted as a recent marketing strategy and a way of communication with customers, which can potentially reach a large audience very fast [4, 5, 6]. VM is also known as Internet Word-of-mouth marketing, as it encourages people to share information (product specifications, improvements, campaigns etc.) with their friends through email or other social media, and utilizes existing social networks [7]. This prompting is sometimes done by introduction of some benefits (like, credit points, e-cash, extra discounts, cashback, promo codes etc.) to the existing customers, as a reward for sharing information in their peer network.
5. Conclusion
Marketing is always considered as one of the key components, not an auxiliary arrangement, for a successful business [42]. Surely, a viral marketing campaign works as a less expensive and unexpected way to reach the customers; but nowadays, when almost 85 million videos and photos get uploaded every day in a popular social networking website like Instagram [43], the main challenge is making that advertisement execute long lasting iterations in the population, so that it can reach a bigger audience. If we consider just the case of Instagram, when almost 500,000 advertisers are using this popular website for campaigning [44], most of the uploads get tossed like a needle in a haystack. The model we propose in this paper establishes a principle of sustainability for online advertisement campaigns by developing a model relying on rigorous consumer psychology survey data [35]. Extensive analysis with mean-field equations as well as networks simulations shows that the region of bistability grows as the value of α, the nonlinear relapse rate increases. Bistability gives the system a chance to retain its viral state for adverse parametric conditions as well. While we have observed that the steady states of diffusion in networks are closely related to mean-field system dynamics, we also appreciated the importance of network structures in this issue. Not only on model systems, but in real social networks, with consideration of all heterogeneity that exists in a population, it has been shown that sustainability of a viral campaign is actually dependent on drawing the attention of those who are not participating in spite of being aware of the campaign. If a certain percentage of this inert population start broadcasting in favor of the campaign, it retains its endemic state in the entire population.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. مدل ارائه شده و تجزیه و تحلیل میدان-میانگین
2.1. فرمولبندی مدل
2.2. تجزیه و تحلیل توازن
2.2.1. پایداری
2.2.2. دوشاخگی
2.3. عدد تکثیر
2.4. شرایط برای دوپایایی
3. تجزیه و تحلیل گرافی-نظری
3.1. انتشار در حالت اولیه
3.2. تجزیه و تحلیل شبکه حالت پایدار
4. نتایج عددی
4.1. شبیهسازی مدل قطعی
4.2. شبیهسازی روی شبکههای مدل
4.3. شبیهسازی روی شبکههای واقعی
5. نتیجهگیری
منابع
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Proposed Model and Mean-Field Analysis
2.1. Model Formulation
2.2. Equilibrium Analysis
2.2.1. Stability
2.2.2. Bifurcation
2.3. Reproduction Number
2.4. Conditions for Bistability
3. Graph-theoretical Analysis
3.1. Propagation at Initial State
3.2. Steady State Network Analysis
4. Numerical Results
4.1. Simulation of the Deterministic Model
4.2. Simulation over Model Networks
4.3. Simulation over Real Networks
5. Conclusion
References
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه