دانلود مقاله رابطه میان فرهنگ و کارآفرینی: از ابعاد فرهنگی تا پروژه GLOBE
چکیده
این مقاله تئوری و مفهومی است و هدف آن شناسایی مطالعات پیشین است که رابطه میان ابعاد فرهنگی پروژه GLOBE و کارآفرینی را برآورد کردهاند. یکی از مهمترین نظریههای فعلی که سعی بر توضیح رابطه میان فرهنگ و فعالیت کارآفرینی دارند، نظریه اقتصاد نهادگرایی نورث است. از سوی دیگر، GLOBE 9 ابعاد فرهنگی برای شناسایی اقدامات فرهنگی و ارزشهای فرهنگی جامعه مشخص کرده است. از این عوامل فرهنگی، نویسندگان مطالعاتی انجام دادهاند که ابعاد مربوط به فعالیت تجاری را مشخص میکند.
1. مقدمه
ماهیت کارآفرینی آغاز تغییر از طریق آفرینش یا نوآوری است (موریسون و همکاران ، 1999). بازارها، مشتریان و مشاغل جدید از طریق نوآوری و نوسازی سازمانی که بر سیستمهای اجتماعی و اقتصادی بخشهای صنعتی، منطقهای و ملل تاثیر میگذارد، به وجود میآیند (موریسون و همکاران، 1999). کارآفرینی یک پدیده سیستماتیک در نظر گرفته میشود که نیاز دارد تا افراد ریسک کنند و شرکت جدیدی به وجود بیاورند، و محیطی برای بهبود این ابتکار فردی خلق کنند. در این زمینه مطالعاتی وجود دارد که بر شناسایی عوامل تشویق کننده کارآفرینی و همچنین موانعی که باعث محدودیت آن میشوند، تمرکز دارد؛ در میان جدیدترین و مهمترین نظریات، نظریه اقتصاد نهادگرایی وجود دارد که نشان میدهد که عوامل رسمی و غیر رسمی بر فعالیت کارآفرینی تاثیر میگذارد و فرهنگ که بخشی از عوامل غیر رسمی است، از عناصر کلیدی کسب و کار به شمار میرود.
2. نتیجهگیری
کارآفرینی یک پدیده سیستماتیک است که به افرادی نیاز دارد که مایل به ریسک کردن و قبول چالش ایجاد و توسعه سرمایهگذاری جدید هستند. در این زمینه، مطالعاتی وجود دارد که بر شناسایی عواملی که باعث ترویج یا مهار کارآفرینی میشوند، تمرکز کرده است؛ در میان تاثیرگذارترین جریانها نظریه اقتصاد نهادگرایانه وجود دارد که عقیده دارد عوامل رسمی و غیر رسمی وجود دارد که بر فعالیت کارآفرینی تاثیر میگذارد و فرهنگ عوامل به اصطلاح غیر رسمی و یکی از ابعاد اصلی در توسعه فعالیت کارآفرینی است.
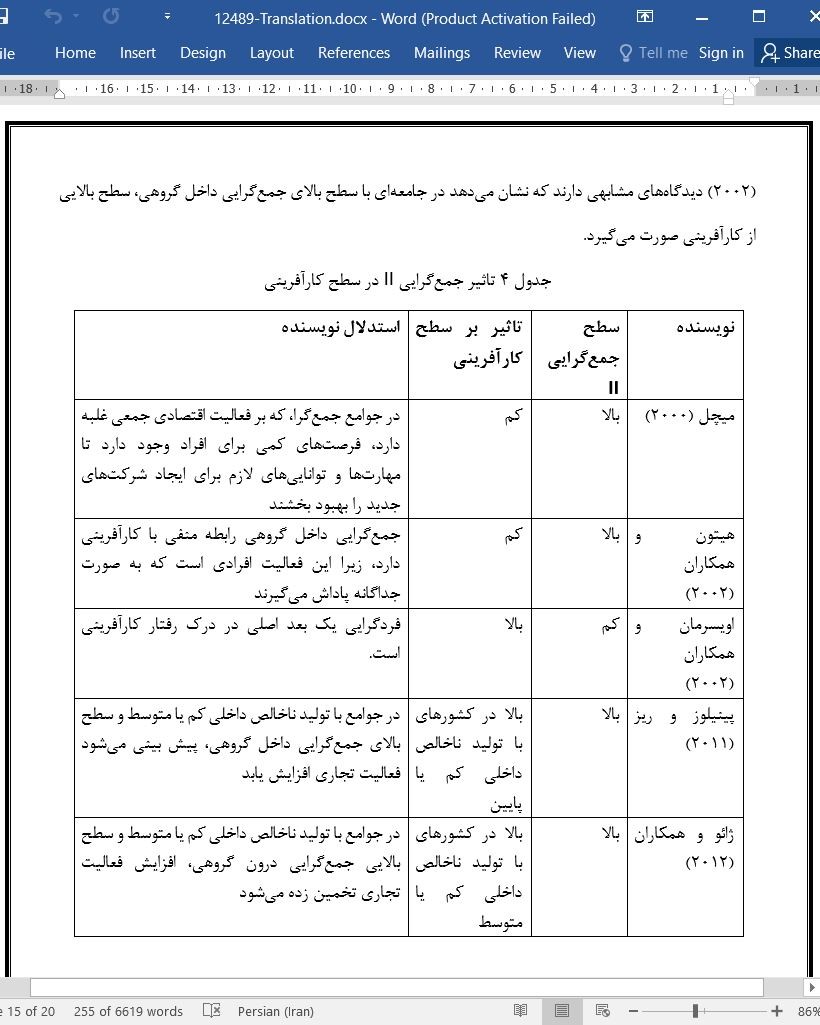
در میان مدلهای یافت شده در ادبیات برای شناسایی ابعاد فرهنگی جامعه در مطالعات در زمینه سازمانی، مطالعه انجام شده توسط GLOBE برجستهتر است (هاوس و همکاران، 2002؛ هاوس و جاویدان، 2004)، در این مطالعه رابطه میان فرهنگ و رهبری بررسی میشود، اما رابطه فرهنگ با فعالیت کارآفرینی مورد آنالیز قرار نمیگیرد. GLOBE 9 بعد فرهنگی برای شناسایی اقدامات فرهنگی و ارزشهای فرهنگی جامعه مشخص میکند. از این عوامل فرهنگی، نوینسدگان مطالعاتی انجام دادهاند که ابعاد مربوط به فعالیت تجاری عبارتند از: فاصله قدرتی (میچل و همکاران، 2000؛ اردیچویلی و گاسپاریشویلی، 2003؛ ژائو و همکاران، 2012)، اجتناب از عدم قطعیت (بوسنیتز و لاو، 1996؛ پینیلوز و ریز، 2011؛ مولر و توماس، 2001؛ اوتیو و همکاران، 2013؛ هیتون و همکاران، 2002)، جمعگرایی I (میچل و همکاران، 2002؛ لیم و همکاران، 2010؛ اوزگن، 2012؛ گریلو و توریک، 2005؛ کلاپر و همکاران، 2006)، جمعگرایی (میچل و همکاران، 2000؛ هیتون و همکاران، 2002؛ پینیلوز و ریز، 2011؛ ژائو و همکاران، 2012)، قاطعیت (اوزگن، 2012) و جهتگیری انسانی (ژائو و همکارن، 2012).
ABSTRACT
This article is theoretical and conceptual, and aims to identify previous studies that have estimated the relationship between the cultural dimensions of the GLOBE project and entrepreneurship. Among the most important current theories that attempt to explain the relationship between culture and entrepreneurial activity is the Institutional Economic Theory of North. On the other hand, GLOBE raises nine cultural dimensions to identify cultural practices and cultural values of a society. From these cultural factors authors have developed studies that conclude that the dimensions that are related to business activity.
1. Introduction
The essence of entrepreneurship is the initiation of change through creation or innovation (Morrison et al., 1999). New markets, customers and jobs are created through innovation and organizational renewal, which create an impact on both the social and economic systems of industrial sectors, regions and nations (Morrison et al., 1999). Entrepreneurship is considered a systemic phenomenon, which requires individuals to take the risk and the challenge of creating a new company, and to necessitate an environment to promote this individual initiative. In this sense, there are some studies that have focused on identifying the factors that encourage entrepreneurship as well as potential obstacles that limit it; among the most current and important theories is the Institutional Economic Theory, which states that there are both formal and informal factors influencing entrepreneurial activity, and where culture, which is part of the informal factors, is one of the key elements for business.
2. Conclusions
Entrepreneurship is a systemic phenomenon that requires individuals who are willing to take the risk and the challenge of creating and developing a venture. In this sense, there are some studies that have focused on identifying the factors that promote or inhibit entrepreneurship; among the most influential currents is the Institutional Economic Theory, which suggests that there are formal and informal factors influencing entrepreneurial activity, being the culture of the so-called informal factors and one of the key aspects for the development of entrepreneurial activity.
Among the models found in the literature to identify the cultural dimensions of society in studies of organizational field, the one conducted by GLOBE stands out (House et al., 2002; House and Javidan, 2004), in which the relationship between culture and leadership is studied, but the relationship of culture with entrepreneurial activity were not analyzed. GLOBE raises nine cultural dimensions to identify cultural practices (society "is") and cultural values (society "should be") of a society. From these cultural factors authors have developed studies that conclude that the dimensions that are related to business activity are: Power Distance (Mitchell et al., 2000; Ardichvili and Gasparishvili, 2003; Zhao et al., 2012), Uncertainty Avoidance (Busenitz and Lau, 1996; Pinillos and Reyes, 2011; Mueller and Thomas, 2001; Autio et al., 2013; Hayton et al., 2002), Collectivism I (Mitchell et al., 2002; Lim et al., 2010; Ozgen, 2012; Grilo and Thurik, 2005; Klapper et al., 2006), Collectivism (Mitchell et al., 2000; Hayton et al., 2002; Pinillos and Reyes, 2011; Zhao et al., 2012), Assertiveness (Ozgen, 2012) and Humane Orientation (Zhao et al., 2012).
چکیده
1. مقدمه
1.1 کارآفرینی: مفهوم و سهم اقتصادی
1.2. نظریه اقتصاد نهادگرا و ایجاد کسب و کار
1.3. فرهنگ
1.4. فرهنگ و کارآفرینی
2. نتیجهگیری
منابع
ABSTRACT
1. Introdução
1.1. Entrepreneurship: Concept and economic contribution
1.2. Institutional economic theory and business creation
1.3. Culture
1.4. Culture and Entrepreneurship
2. Conclusions
Bibliographic references
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه