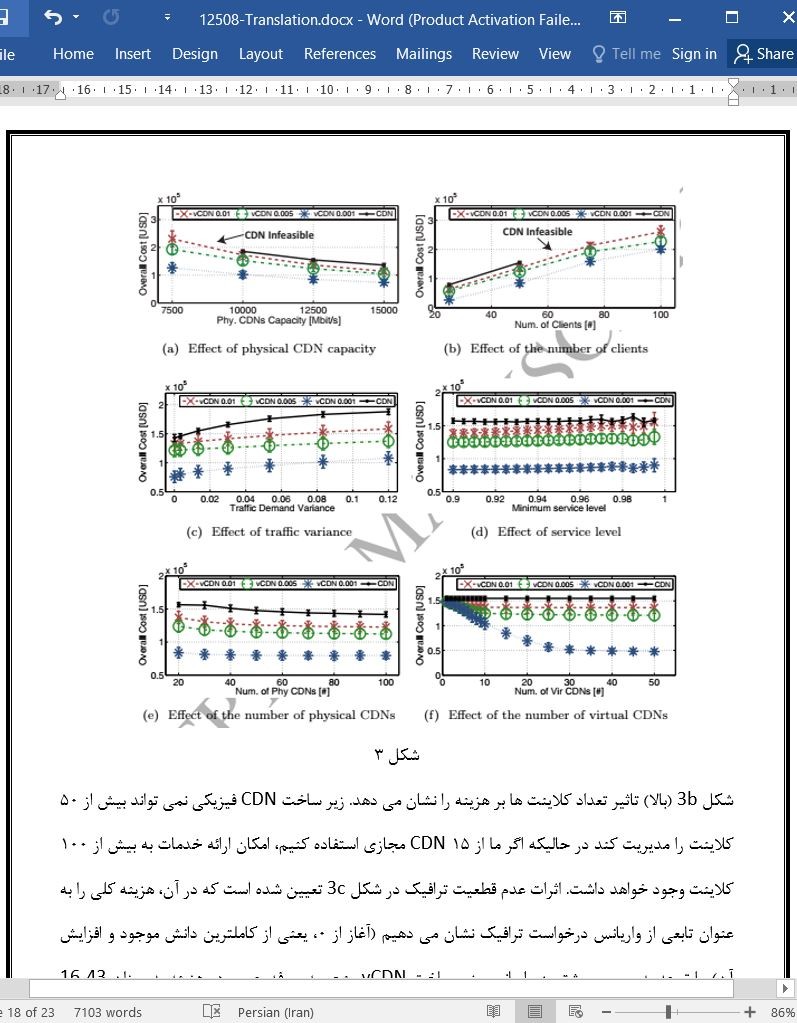
دانلود مقاله برنامه ریزی بهینه شبکه های توزیع محتوای مجازی در درخواست های ترافیک نامعین
چکیده
شبکه های توزیع محتوا (CDN ها)، به عنوان یکی از پرکاربردترین شبکه ها شناخته شده اند که در آنها، پارادایم نوظهور مجازی سازی توابع شبکه (NFV) از اهمیت خاصی برخوردار است. در حقیقت، مجازی سازی انعطاف پذیری را افزایش می دهد زیرا تخصیص منبع گره های CDN مجازی بر حسب نیاز، می تواند تغییرات درخواست ترافیک ناگهانی را تطبیق دهد. با این وجود، مواردی وجود دارد که در آنها، برنامه های فیزیکی هنوز باید در اولویت قرار گیرند. بنابراین، ما یک معماری ترکیبی را بین دو راهکار متصور می شویم که با آن می توانیم از مزایای هر دو راهکار بهره ببریم. بر اساس این دلایل، در این مقاله یک مدل برنامه ریزی احتمالی دو مرحله ای را ارائه می نماییم که اپراتورهای CDN می توانند از آن برای محاسبه تصمیم برنامه ریزی شبکه بلند مدت، بکارگیری برنامه های CDN فیزیکی در شبکه و/یا منابع لیزینگ برای گره های CDN مجازی در مراکز داده بهره ببرند. یافته های کلیدی حاکی از آن هستند که در طیف گسترده ای از گزینه های قیمت گذاری و پروفایل های ترافیک، NFV می تواند به طور قابل توجهی هزینه های شبکه را کاهش دهد تا اپراتورهای شبکه خدمات توزیع محتوا را ارائه نمایند.
1. مقدمه
موفقیت جهانی برنامه های وب پر محتوا مانند شبکه های اجتماعی یا خدمات پخش زنده بر حسب تقاضا، اپراتورهای شبکه را وادار کرده است تا حجم بالایی از پول را برای داشتن زیر ساخت های ارتباطی به روز در این زمینه سرمایه گذاری کنند (1). بطور خاص، امروزه شبکه های توزیع محتوا (CDN ها) به یک فناوری جدایی ناپذیر (و تثبیت شده) تبدیل شده اند که درخواست های ترافیک مشتریان را مدیریت می کنند و در عین حال، از سطح بالای عملکرد و اطمینان پذیری که فراهم کنندگان خدمات به دنبال آن هستند، برخوردارند (2).
اگرچه CDN یک زیر ساخت کارآمد برای ارسال دقیق تر مدل محتوای محبوب به مناطق کاربران است، به سرمایه گذاری زیادی نیاز دارد. به عنوان مثال، زیر ساخت آکامی (Akami) از بیش از 61000 سرور تشکیل شده است که در 1000 شبکه و 70 کشور در سراسر دنیا به کار گرفته شده اند (3). برای کاهش هزینه های سرمایه ای و بهبود عملکرد CDN ها، اخیرا سازمان هایی از قبیل نیروی ضربت مهندسی اینترنت (IETF) و موسسه استانداردهای مخابراتی اروپا (ETSI) یک فرآیند استانداردسازی را برای دو معماری جایگزین زیر آغاز کرده اند:
ارتباط داخلی شبکه توزیع محتوا (CDNI)
شبکه توزیع محتوای مجازی (vCDN)
5. نتیجه گیری
در این مقاله، ما مساله برنامه ریزی تصادفی را برای توزیع محتوا در نظر گرفتیم و مزایای بالقوه مجازی سازی توابع شبکه را برای توزیع محتوا مورد بررسی قرار دادیم. ما یک معماری ترکیبی را ارزیابی نمودیم که در آن، هم گره های فیزیکی و هم گره های مجازی در دسترس مالک CDN خواهند بود تا سرویس توزیع محتوا را ارائه کند. وی برنامه ریزی را در زیر ساخت CDN بر اساس یک برنامه زمانی بلند مدت انجام خواهد داد و تنها یک تخمین احتمالی از درخواست های ترافیک آینده در ذهن خواهد داشت.
مطالعه پیش رو نشان داد که یک راه حل ترکیبی، که در آن هم گره های فیزیکی و هم گره های مجازی به کار برده می شوند، می تواند بطور قابل توجهی هزینه های اپراتور در زمینه خرید و عملیاتی سازی زیر ساخت توزیع را کاهش دهد. بطور خاص، مشاهده نمودیم که با بررسی ارزانترین قیمت vCDN، بیش از 65% سود حاصل شده است. نقش آفرینی این مطالعه، ارائه الگوریتم های راه حل کارآمد برای مساله برنامه ریزی تصادفی دو مرحله ای است که می تواند اندازه های واقعی یک توپولوژی را مقیاس بندی کند. به جای حل مساله معادل قطعی در فرم گسترده، الگوریتم ال شکل پیشنهادی و روش ابتکاری حریصانه می توانند یک راه حل موثر را ارائه کنند و بیش از 95 درصد، در مقایسه با حل کننده MILP در زمان صرفه جویی نمایند.
Abstract
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) have been identified as one of the relevant use cases where the emerging paradigm of Network Functions Virtualization (NFV) will likely be beneficial. In fact, virtualization fosters flexibility, since on-demand resource allocation of virtual CDN nodes can accommodate sudden traffic demand changes. However, there are cases where physical appliances should still be preferred, therefore we envision a mixed architecture in between these two solutions, capable to exploit the advantages of both of them. Motivated by these reasons, in this paper we formulate a two-stage stochastic planning model that can be used by CDN operators to compute the optimal long-term network planning decision, deploying physical CDN appliances in the network and/or leasing resources for virtual CDN nodes in data centers. Key findings demonstrate that for a large range of pricing options and traffic profiles, NFV can significantly save network costs spent by the operator to provide the content distribution service.
1. Introduction
The worldwide success of content-rich web applications like social networks or on-demand streaming services has forced network operators to invest a significant amount of money in order to keep up-to-date their communication infrastructures [1]. In particular, Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) have nowadays become a necessary (and well-established) technology to efficiently serve the traffic demands that consumers are generating, while supporting the high level of performance and reliability that providers are demanding [2].
Although CDN is an effective infrastructure to move replicas of popular contents closer to the users’ locations, it requires significant investments to be built and operated. As an example, the Akamai infrastructure comprises more than 61 000 servers deployed in 1 000 networks and 70 countries worldwide [3]. To reduce the capital expenditures and improve the performance of CDNs, organizations such as the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) and the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) have recently begun a standardization process for two alternative architectures:
• Content Delivery Network Interconnection (CDNI);
• Virtual Content Delivery Network (vCDN).
5. Conclusion
In this paper we tackled the stochastic planning problem for content delivery to study potential benefits that Network Functions Virtualization can provide for content distribution purposes. We considered a mixed architecture where both physical as well as virtual CDN nodes can be used by a CDN owner to implement the content distribution service. The owner performs the planning choice for the physical CDN infrastructure on a long-term time schedule, possessing only a stochastic estimate of future traffic demands.
Our study shows that a mixed solution where both virtual an physical CDN nodes are used can dramatically reduce the overall costs sustained by the operator to purchase and operate the distribution infrastructure. In particular, we observed that gains can be up to 65% when considering the cheapest vCDN price. Our contribution is also to formulate efficient solution algorithms for the two-stage stochastic planning problem that can scale to realistic topology sizes. Rather than solving the deterministic equivalent problem in the extensive form, our proposed L-shaped algorithm and the greedy heuristic can efficiently find a solution, saving up to 95% of time compared to the MILP solver.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. کار مرتبط
2.1 مجازی سازی توابع شبکه
2.2 شبکه های توزیع محتوا
2.3 بهینه سازی تصادفی
3. توزیع بهینه محتوا در NFV
3.1 مدل سیستم و فرضیات آن
3.2 مدل بهینه سازی
3.3 الگوریتم های برنامه ریزی CDN تصادفی
3.3.1 الگوریتم ال شکل
3.3.2 الگوریتم حریصانه
4. نتایج عددی
4.1 سناریوی شبکه نمونه
4.2 مزایای NFV
4.3 تاثیر قیمت vCDN
4.4 زمان محاسبه
5. نتیجه گیری
منابع
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Network Functions Virtualization
2.2. Content Delivery Networks
2.3. Stochastic Optimization
3. Optimal Content Delivery in NFV
3.1. System Model and Assumptions
3.2. Optimization Model
3.3. Stochastic CDN Planning Algorithms
3.3.1. L-Shaped Algorithm
3.3.2. Greedy Algorithm
4. Numerical Results
4.1. Example network scenario.
4.2. NFV Benefits
4.3. Effect of the vCDN Price
4.4. Computing time
5. Conclusion
References
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه