دانلود مقاله تاثیر ویژگی های حسابرسی داخلی بر اثربخشی کنترل داخلی نسبت به عملیات و سازگاری
چکیده
عملکرد حسابرسی داخلی (IAF) به مدیریت در بهبود کنترل داخلی نسبت به عملیات، گزارشدهی و سازگاری کمک میکند. در حالی که بسیاری از مطالعات، ارتباط بین IAF و کنترل داخلی گزارشگری مالی (ICFR) را بررسی کردهاند، مطالعات اندکی در مورد کنترل داخلی عملیات و سازگاری انجام شدهاند. این مقاله با استفاده از مجموعه داده منحصر به فردی از تایوان، ارتباط بین کیفیت عملکرد حسابرسی داخلی و نقص کنترل داخلی در عملیات و سازگاری را مورد بررسی قرار میدهد. نتایج نشان میدهند که گروه حسابرسی داخلی بزرگتر میتواند موجب بهبود عملکرد حسابرسی داخلی در مورد عملیات و سازگاری شود. در حالی که مهارت حسابرسان داخلی دارای مثبتی با اثربخشی کنترل داخلی بر سازگاری است، اما رابطهای با عملیات ندارد. این مطالعه با تبیین عوامل تعیین کننده دستیابی به اهداف عملیات و سازگاری، به تحقیقات در این زمینه کمک میکند. این کار، مفاهیم مهمی را برای ذینفعان و کارشناسان نیز فراهم میکند، زیرا کنترل شرکت بر عملیات و سازگاری میتواند به طور متقابل بر ICFR و در نهایت موفقیت کسب و کار تأثیر بگذارد.
1. مقدمه
عملکرد موثر حسابرسی داخلی ( IAF)، می تواند با کمک به مدیریت در راستای بهبود کنترل های داخلی، نظارت کیفی شرکت را تضمین کند. مسئولیت های اصلی حسابرسان داخلی، بررسی، ارزیابی و نظارت بر کفایت و اثربخشی اهداف کنترل داخلی نسبت به فرآیندها، گزارشات و تطبیقها است. در حالی که بسیاری از تحقیقات، کنترل داخلی را بالاتر از گزارش مالی در نظر میگیرند اما محدودیت های اطلاعاتی تضمین کرده اند که تاکنون تحقیقات تجربی نسبتاً کمی در مورد ارزیابی کنترل داخلی نسبت به عملیات و تطبیق عملیات انجام شدهاند. تحقیقات ما با استفاده از مجموعه داده منحصر به فردی از کشور تایوان، که در اختیار عموم نیست، ارتباط میان خصوصیات IAF و اثربخشی کنترل داخلی را نسبت به عملیات و سازگاری عملیات بررسی می کند. درک این ارتباط مهم است، زیرا رسیدن به اهداف عملیاتی و سازگاری عملیات احتمالاً قدرت نظارت حاکمیت شرکت و فرهنگ سازگاری را منعکس می کند که به طور دو طرفه بر ICFR آن اثر می گذارد و در نهایت منجر به موفقیت کلی میشود.
7. بحث و جمع بندی
بر اساس فرضیات خود درمی یابیم که کیفیت حسابرسی داخلی به صورتی که توسط مهارت و اندازه کارمندان IAF سنجیده میشود، ارتباط منفی با احتمال افشای ICDها دارد. به طور خاص، نتایج حاکی از این است که احتمال بیشتری وجود دارد مبنی بر این که یک شرکت با عملکرد حسابرسی داخلی قوی تر (یعنی یک تیم IAF بزرگ، کارمندان IAF با مدارک تحصیلی بیشتر، تجربیات حسابرسی و کاری بیشتر، و سطح آموزش بالاتر)، سیستم کنترل داخلی بهتری داشته باشد و در نتیجه احتمال کمتری وجود دارد مبنی بر این که ICDهایی با زمینه سازگاری با قوانین گزارش شوند. اگرچه یافته های ما مستعد نوعی از ICDها هستند. یعنی شواهدی پیدا کردیم مبنی بر این که کارمندان زیاد در IAF می تواند شانس ICDها در عملیات را کاهش دهد اما هیچ گونه پیدا نکردیم که نشان دهند مهارت کارمندان شانس ICDها در عملیات را کاهش می دهد. توضیح ممکنی که می توان داد این است که فعالیت های کنترلی در عملیات، در مقایسه با فعالیت های کنترلی در سازگاری با قوانین، از شرکتی به شرکت دیگر دیگر، تفاوت بیشتر دارند و در نتیجه به سختی می توان سازگاری میان شرکتها را اندازه گرفت. این مساله ممکن است منجر به خطای اندازه گیری و یافته های غیرمعنادار شود. در کنار این ها، فعالیت های کنترل داخلی در عملیات، در مقایسه با فعالیتهای کنترل داخلی در سازگاری، ممکن است نیازمند این باشند که حسابرسان داخلی، دانش خاص-شرکت بیشتری داشته باشند. در اکثر موارد، شاخص های (پروکسیهای) شایستگی ما، دانش کلی کارمندان IAF را در زمینه حسابرسی داخلی اندازه می گیرند و درنتیجه قادر نیستند ابعاد کاملی از صلاحیت را در نظر بگیرند. در نتیجه، یافته-های ما در مورد ICDهای مربوط به عملیات ممکن است قطعی نباشد و نیاز باشد که با احتیاط تفسیر شوند. با بررسی بیشتر این جنبه های خاص، کیفیت IAF تضمین میشود.
Abstract
The internal audit function (IAF) assists management in improving internal controls over operations, reporting, and compliance. While many studies examine the association between the IAF and the internal control over financial reporting (ICFR), little is known about internal control over operations and compliance. Using a unique dataset from Taiwan, this paper examines the association between IAF quality and internal control deficiencies in operations and compliance. The results suggest that a larger internal audit team can enhance internal audit performance for both operations and compliance, whereas internal auditor competence is positively associated with the effectiveness of internal control over compliance, but not operations. This study contributes to the literature by shedding light on the determinants of the achievement of operations and compliance objectives. It also provides important implications for stakeholders and practitioners, as a company’s control over operations and compliance may mutually influence its ICFR and ultimately its business success.
1. Introduction
An effective internal audit function (IAF) can ensure quality corporate governance by assisting management in improving internal controls (Chartered Institute of Internal Auditors, 2015). The key responsibilities of internal auditors are to examine, evaluate, and monitor the adequacy and effectiveness of internal control objectives over operations, reporting, and compliance (American Institute of Certified Public Accountants [AICPA], 2008; Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission [COSO], 2012; Institute of Internal Auditors [IIA], 2012).1 While many studies investigate internal control over financial reporting (ICFR) (e.g., Abbott et al., 2016; Ege, 2015; Lin et al., 2011; Prawitt et al., 2009), data constraints have ensured that so far there has been relatively little empirical research that assesses internal control over operations and compliance. Our study, using a unique, publicly unavailable dataset from Taiwan, examines the association between IAF characteristics and the effectiveness of internal control over operations and compliance. Understanding this relationship is critical, as the achievement of operations and compliance objectives is likely to reflect the strength of a company’s corporate governance and compliance culture, mutually influences its ICFR, and ultimately contributes to its overall success.
7. Discussion and conclusion
In accordance with our hypotheses, we find that internal audit quality, as proxied by IAF staff competence and size, has a negative association with the likelihood of the disclosure of ICDs. Specifically, the results suggest that a company with a stronger internal audit function (i.e., a large IAF team, IAF staff with more certifications, more audit work experience, and higher level of education) is more likely to have a better internal control system and thus less likely to report ICDs in compliance. Our findings, however, are subject to the type of ICDs. That is, we find evidence that a large IAF staff can reduce the likelihood of ICDs in operations, but we find no supporting evidence for IAF competence. A possible explanation is that control activities in operations vary from company to company more than those in regulatory compliance and thus are more difficult to measure consistently across companies. This difficulty may lead to measurement error and result in insignificant findings. Besides, internal control activities in operations may require more internal auditors’ company-specific knowledge than do those in compliance. For the most part, our competence proxies measure the IAF staff’s general knowledge in internal auditing and thus are not able to capture the complete dimensions of competence. Therefore, our findings on the ICDs related to operations may not be conclusive and need to be interpreted with caution. Further investigation into these specific aspects of IAF quality is warranted.
H1: The likelihood that a company reports an internal control deficiency in operations and/or compliance is negatively associated with IAF competence.
H2: The likelihood that a company reports an internal control deficiency in operations and/or compliance is negatively associated with IAF resources.
H1: احتمالا گزارشهای نقض کنترل داخلی در عملیات و/یا سازگاری رابطه منفی با مهارت IAF دارد.
H2: احتمال اینکه یک شرکت یک نقض کنترل داخلی را در عملیات و/یا سازگاری گزارش کند، رابطه منفی با منابع IAF دارد.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. پیشینه تحقیقات سازمانی و ملزومات کنترل داخلی در تایوان
3.بررسی تحقیقات و توسعه فرضیات
3.1 اهداف کنترل داخلی
3.2 کیفیت عملکرد حسابرسی داخلی
3.3 توسعه فرضیات
3.3.1 مهارت حسابرس داخلی
3.3.2 تعهد منابع IAF
4. طرح تحقیق
4.1 داده و نمونه
4.2. مدل نقاط ضعف کنترل داخلی و اندازهگیری متغیرها
5. نتایج
5.1. آمار توصیفی
5.2. تجزیه وتحلیل همبستگی
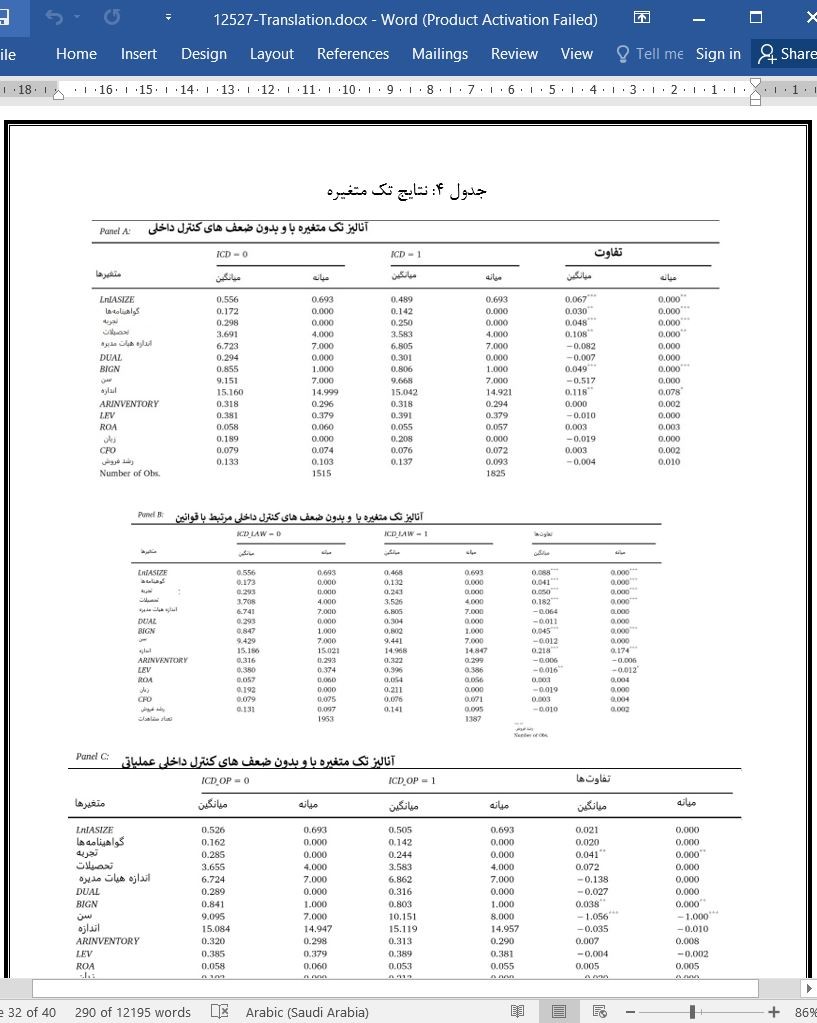
5.3. تجزیه و تحلیل تک متغیره
5.4. تجزیه و تحلیل پروبیت
6. تجزیه و تحلیل بیشتر
6.1. اندازه گیری جایگزین –ICDها
6.2. معیار جایگزین- معیار IAF تجمیع شده
6.3. تست سازگاری امتیاز گرایش
6.4. اثر متغیرهای IAF و ICDهای با-تاخیر
7. بحث و جمع بندی
منابع
ABSTRACT
1. Introduction
2. Institutional background and regulations of internal control in Taiwan
3. Literature review and hypothesis development
3.1. Internal control objectives
3.2. Internal audit function quality
3.3. Hypothesis development
3.3.1. Competence of internal auditor
3.3.2. Commitment of IAF resources
4. Research design
4.1. Data and sample
4.2. Internal control weakness model and measurements of variables
5. Results
5.1. Descriptive statistics
5.2. Correlation analysis
5.3. Univariate analysis
5.4. Probit analysis
6. Additional analysis
6.1. Alternative measurement – ICDs
6.2. Alternative measurement – aggregate IAF measure
6.3. Propensity-score matched test
6.4. The effect of lagged ICDs and IAF variables
7. Discussion and conclusion
References
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه