دانلود مقاله پیاده سازی مدل شبکه صف بندی مارکوف با استفاده از چندین زنجیره بسته
چکیده
استراتژی ریاضیاتی ارزیابی عملکرد رایانه و سیستم ارتباطی را به تصویر می کشد و با ویژگی های تصادفی سیستم صف بندی مارکوف چند کلاسه همراه با زمان های سرویس وابسته به کلاس و وابسته به سرور سر و کار دارد. الگوریتمی طراحی شده است که در آن انتقال های کار توسط بیش از یک زنجیره مارکوف بسته انجام می شود. تولید توابع برای استخراج شکل بسته راه حل ها و راهکار حاصلضرب همراه با پارامترهایی چون پایداری، ثابت نرمالیزه کردن و توزیع های مجانبی پیاده سازی می شوند. برای چنین سیستمی همراه با N سرور و L زنجیره، راهکارها به طور قابل توجهی پیچیده تر از راهکارهای ارائه شده برای سیستم های دارای یک زنجیره فرعی هستند. در شبکه صف بندی چند کلاسه، یک کار از یک صف به صف دیگر به همراه برخی احتمالات پس از دستیابی به یک سرویس حرکت می کند. یک کلاس چندتایی از مشتری بسته یا باز می شود به طوری که هر کلاس دارای مجموعه پارامترهای صف بندی خاص خودش است. این پارامترها با تحلیل هر ایستگاه تحت این فرض انجام می شود که فرآیند ورود هر کلاس یک فرآیند مارکوف مستقل از حالت همراستا با توزیع زمان مختلف سرویس است. یک روش الگوریتمی از نمایش تولید تابع برای کلاس عمومی شبکه ها پیاده سازی شده است. براساس این روش الگوریتمی، نحوه تعامل زنجیره های فرعی باز و بسته با یکدیگر در چنین سیستمی اثبات شده است. به ویژه، تکنیک های محاسباتی برای محاسبه مدل مارکوف برای زنجیره های متعدد فراهم شده است و نشان داده شده است که این الگوریتم ها به سرعت به طور نمایی همگرا می شوند.
1. مقدمه
نمایش و تحلیل سیستم صف بندی چند پردازنده ای توجه زیادی را در سال های اخیر به خود جلب کرده است. پارامترهای شبکه با استفاده از الگوریتم های به شکل حاصلضرب محاسبه می شوند و تقریب راهکار نیز در برخی موارد در نظر گرفته می شود. عملکرد شبکه می بایست توسط یک زنجیره مارکوف و اندازه بزرگ فضای حالت آن مشخص شود که پیچیدگی زمان نقصی برای حل سیستم های خطی محسوب می شود. روش های محاسباتی برای توزیع تعادل اصلی کارها همراه با سرورهای نمایی و توزیع مرزی نیز در شبکه صف بندی بسته به دست می آیند. تعداد محدود کارها تنها از طریق شبکه عبور می کند و ورود و خروج های جدید اجازه ورود به شبکه صف بندی بسته را ندارند. الگوریتم به شکل حاصلضرب در مورد چندین زنجیره فرعی بسته به دست می آید و الگوریتم محاسباتی برای کلاس های عمومی شبکه های صف بندی ارائه شده است. انتقال مسیریابی توسط یک زنجیره مارکوف مشخص می شود که به درون چندین زنجیره فرعی قابل تجزیه است. در موارد محدودی شبکه همراه با زنجیره های فرعی برای انتخاب یک شبکه باز معرفی می شود. چندین حالت انباشتگی و توزیع های مرزی آن ها در بخش نتیجه گیری مورد بحث قرار می گیرند.
5. نتیجه گیری
در این مقاله یک روش تکراری برای چندین زنجیره بسته به کار گرفته شده است. در تجزیه و تحلیل، مراحل شامل ارزیابی تمامی حالت های مورد نظر فرآیند مارکوف هستند. در شبکه صف بندی چند کلاسه، رفتار انتقالی زنجیره مارکوف تحلیل می شود و این حقیقت را نشان می دهد که یک کار که سرویس را در سرور i تکمیل می کند به سرور j بعدی با احتمال pij می رود. اندازه گیری عملکرد توسط الگوریتم محاسباتی مورد ارزیابی قرار می گیرد. معیارهای همگرایی آزمایش می شوند و نرخ انتقال بین بلوک ها به دست می آید. براساس روش الگوریتمی، ثابت شده است که چگونه زنجیره های فرعی باز و بسته در چنین سیستمی با یکدیگر تعامل می کنند.
کاربردها: روش پیشنهادی در سیستم های چند لایه سرویس اینترنتی قابل استفاده است. خود شباهتی در ترافیک سرعت بالای پکت قابل تحلیل است و اندازه گیری های ترافیک اترنت برای تحلیل عملکرد برای شبکه های سرعت بالای آتی قابل مدل سازی است.
Abstract
Mathematical strategy portrays the performance evaluation of computer and communication system and it deals with the stochastic properties of the multiclass Markovian queueing system with class-dependent and server-dependent service times. An algorithm is designed where the job transitions are characterized by more than one closed Markov chain. Generating functions are implemented to derive closed form of solutions and product form solution with the parameters such as stability, normalizations constant and marginal distributions. For such a system with N servers and L chains, the solutions are considerably more complicated than those for the systems with one sub-chain only. In Multi-class queueing network, a job moves from a queue to another queue with some probability after getting a service. A multiple class of customer could be open or closed where each class has its own set of queueing parameters. These parameters are obtained by analyzing each station in isolation under the assumption that the arrival process of each class is a state-dependent Markovian process along with different service time distributions. An algorithmic approach is implemented from the generating function representation for the general class of Networks. Based on the algorithmic approach it is proved that how open and closed sub-chain interact with each other in such system. Specifically, computation techniques are provided for the calculation of the Markovian model for multiple chains and it is shown that these algorithms converge exponentially fast.
1 Introduction
Representation and analysis of multiprocessor Queueing system have drawn more attention in the recent years. By product-form algorithms the network parameters are computed and approximating solution is also considered in some cases. The network performance has to be characterized by a Markov chain and its large size of the state space, time intricacy is a drawback for solving linear systems. The computational methods for basic equilibrium distribution of jobs with exponential servers and the marginal distribution are also derived in the closed queueing network. Finite number of jobs only can pass through the network, new arrivals and departures are not permitted to enter into the closed queueing network. The product form algorithm is derived in the case of multiple closed sub chains and computational algorithm is presented for general classes of queueing networks. The routing transition is characterized by a Markov chain which is decomposable into multiple sub chains. In limited cases, network with closed sub chain is introduced for choosing an open network. Several aggregate states and their marginal distributions are discussed in the conclusion.
5 Conclusion
In this paper an iterative method is implemented for multiple closed chains. In disagglomeration steps involve the enumeration of all the states underlying Markov process. In Multi-class queueing network the transition behavior of the Markov chain is analysed and based on that it reveals the fact that a job completing the service at server i will go next to server j with probability pi j . The performance measures are evaluated by the computational algorithm. Convergence criteria are tested and rate of transition between blocks is obtained. Based on the algorithmic approach it is proved that how open and closed sub-chain interact with each other in such system.
Applications The proposed scheme can be implemented in multiple-tier Internet service systems. Self-Similarity in High-Speed Packet Traffic be analyzed and Ethernet Traffic Measurements can be modeled for the Performance analysis for future high speed networks.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. مروری بر ادبیات
2-1 بررسی و توضیح
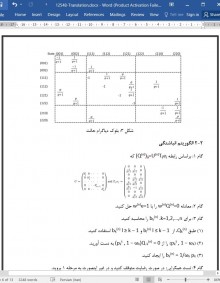
2-2 الگوریتم انباشتگی
2-3 احتمالات حالت تعادل
2-4 الگوریتمی برای تحلیل مقدار میانگین شبکه های صف بندی چند زنجیره ای بسته
3. محاسبه عددی
4. نمایش گرافیکی
5. نتیجه گیری
منابع
Abstract
1 Introduction
2 Literature Survey
2.1 Scrutiny and Delineation
2.2 Agglomeration Algorithm
2.3 Equilibrium State Probabilities
2.4 Algorithm for Mean Value Analysis of a Closed Multichain Queueing Networks
3 Numerical Calculation
4 Graphical Representation
5 Conclusion
References
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه