دانلود مقاله تجزیه و تحلیل الگوریتم های پوشش دهنده هدف متصل شده بهینه برای شبکه های حسگر بی سیم صنعتی
چکیده
پیشرفت های اخیر در فن آوری های بی سیم تا حد زیادی موجب ظهور شبکه های حسگر بی سیم صنعتی (IWSN ها) شده است. برای تسهیل انطباق IWSN ها با برنامه های کاربردی صنعتی، پوشش کامل شبکه ها و قابلیت اتصال به شبکه باید به منظور اطمینان و تامین نیازهای زمان واقعی مورد توجه قرار گیرد. با وجودی که الگوریتم (CTC) پوشش دهنده ی هدف متصل شده در شبکه های حسگر عمومی به طور گسترده مورد مطالعه قرار گرفته است، توجه کمی به آشکار شدن کاربردها و محدودیت های استراتژی های پوشش متفاوت از دیدگاه صنعتی صورت گرفته است. در این مقاله، ویژگی های چهار استراتژی جدید پوشش بهینه را با انتخاب دقیق چهار الگوریتم پوشش داده شده تحلیل می کنیم:
(1) پوشش حریص وزن دهی شده ارتباطی ، (2) پوشش اکتشافی متصل شده بهینه ، (3) پوشش و هدف متصل همپوشانی شده ، (4) پوشش دامنه قابل تنظیم . از طریق یک مقایسه دقیق از لحاظ طول عمر شبکه، زمان پوشش، مصرف انرژی متوسط، نسبت گره های مرده و غیره، ویژگی های ایده های طراحی اولیه استفاده شده برای بهینه سازی پوشش و اتصالات شبکه IWSN، درج شده است. برای به دست آوردن پوشش شبکه بهینه، پارامترهای شبکه ی مختلف در یک محیط پر نویز شبیه سازی شده است. مناسب ترین زمینه صنعتی برای هر الگوریتم نیز بر اساس خصوصیات پوشش تعیین شده است. مطالعه ما با هدف ارائه بینش مفیدی برای انتخاب یک استراتژی مناسب پوشش و دستیابی به شاخص های عملکرد مورد انتظار در برنامه های مختلف صنعتی برای طراحان IWSN انجام شده است.
1. مقدمه
اخیرا، شبکه های حسگر بی سیم صنعتی (IWSN ها) که شامل بسیاری از گره های حسگر هستند، به عنوان یک ابزار قدرتمند برای سیستم اتوماسیون صنعتی (IAS) تکامل یافته اند. علیرغم IAS های قدیمی که از طریق سیم ارتباط برقرا می کردند، حسگرهای IWSN میتوانند بر روی تجهیزات صنعتی نصب شده و برای اطمینان از عملکرد عادی، پارامترهای بحرانی را مانیتور کنند. همچنین، هر سنسور قابلیت ارتباط بی سیم را برای ارائه خدمات تحویل داده دارد. با توجه به عدم وجود کابل، استفاده از گره های حسگر ارزان و کوچک، به انعطاف پذیری و بهره وری انرژی IAS کمک می کند.
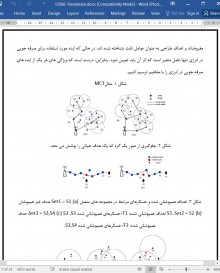
برنامه های کاربردی صنعتی نیاز به قابلیت اطمینان بالا دارند، بنابراین هر گونه سنجش تجهیزات و فرآیندهای ضروری باید اولویت بندی شود و بدون وقفه باشد. به عنوان یک نرم افزار پیشرو در IAS، کنترل نظارت و کسب اطلاعات نیاز به سطح بالایی از قابلیت اطمینان از نظر یکپارچگی داده ها و گزارش به موقع دارد. بنابراین، یک IWSN باید تداوم پوشش هدف و اتصال را در میان تمام گره های حسگر و یک گره سینک تضمین کند. بنابراین، یک IWSN باید تداوم پوشش هدف و اتصال را در میان تمام گره های حسگر و یک گره سینک تضمین کند. این مورد اغلب به عنوان مشکل مربوط به پوشش هدف (CTC) یاد می شود، جایی که هر هدف گسسته در شبکه باید در محدوده حساسیت حداقل یک گره حسگر باشد و حداقل یک مسیر برای اتصال هر گره منبع به گره سینک وجود داشته باشد. با این حال، در محیط های صنعتی، ناحیه پوشش یک گره حسگر، و همچنین مسیر اتصال، ممکن است از دارای نویز، تداخل کانال و انتشار چندمسیری باشد. علاوه بر این، تامین انرژی مسلما محدودیت اصلی گره های حسگر بی سیم است. از این رو، مشکل CTC با صرفه جویی در مصرف انرژی تبدیل به مسئله ی مهمی شده است که نیاز به توجه فوری دارد.
5. نتیجه گیری و کار آینده
در این مقاله، ما استراتژی های مختلف پوشش انرژی را تحلیل کرده ایم که برای محیط های صنعتی طراحی شده اند. از طریق مقایسه ی چهار الگوریتم CTC، ویژگی های هر استراتژی تحت شرایط مختلف ترسیم می شوند. از آنجا که رسیدن به عملکرد پوشش یکسان دشوار است، در انتخاب الگوریتم های پوشش باید در نظر گرفته شود که تمرکز بر چه فاکتوری (سرعت پوشش، حداکثر طول عمر، و غیره) در یک محیط عملیاتی نیاز است. باید توجه بیشتری به بهبود عملکرد تعیین شده توسط تمرکز اصلی بشود. سپس می توان برای دستیابی به عملکرد نسبی پارامترهای دیگر تلاش کرد. بر اساس تحلیل ما، دید مفیدی به طراحان IWSN برای انتخاب یک استراتژی پوشش مناسب داده شده است. در آینده، برای تکمیل شکاف بین شبیه سازی ایده آل و سیستم های پوشش دنیای واقعی، کار بیشتری مورد نیاز است. به عنوان مثال، حرکت کردن نیز باید به IWSN معرفی شود. گره های حسگر استاتیک ممکن است توسط لرزش تجهیزات صنعتی مختل شوند، که می تواند باعث تغییر در توپولوژی شبکه شود. بنابراین، نتایج شبیه سازی شده توسط الگوریتم های CTC با صرفه جویی در انرژی باید گسترش یابد تا تأثیرات احتمالی برنامه های صنعتی واقعی را شامل شود.
Abstract
Recent breakthroughs in wireless technologies have greatly spurred the emergence of industrial wireless sensor networks (IWSNs). To facilitate the adaptation of IWSNs to industrial applications, concerns about networks' full coverage and connectivity must be addressed to fulfill reliability and real-time requirements. Although connected target coverage (CTC) algorithms in general sensor networks have been extensively studied, little attention has been paid to reveal both the applicability and limitations of different coverage strategies from an industrial viewpoint. In this paper, we analyze characteristics of four recent energy-efficient coverage strategies by carefully choosing four representative connected coverage algorithms: 1) communication weighted greedy cover; 2) optimized connected coverage heuristic; 3) overlapped target and connected coverage; and 4) adjustable range set covers. Through a detailed comparison in terms of network lifetime, coverage time, average energy consumption, ratio of dead nodes, etc., characteristics of basic design ideas used to optimize coverage and network connectivity of IWSNs are embodied. Various network parameters are simulated in a noisy environment to obtain the optimal network coverage. The most appropriate industrial field for each algorithm is also described based on coverage properties. Our study aims to provide IWSNs designers with useful insights to choose an appropriate coverage strategy and achieve expected performance indicators in different industrial applications.
I. INTRODUCTION
RECENTLY, industrial wireless sensor networks (IWSNs), which consist of many sensor nodes, have evolved as a powerful tool for an industrial automation system (IAS). Different from traditional IAS realized through wired communications, sensors of an IWSN can be installed on industrial equipment and monitor critical parameters to ensure normal operations [1]. Also, each sensor has wireless communication capability to provide data delivery service. Due to the absence of cables, the use of inexpensive and tiny sensor nodes contributes to the flexibility and energy efficiency of IAS [2].
Industrial applications require a high measure of reliability, so any sensing of essential equipment or processes must be prioritized and free of interruption. As a leading application of IAS, supervisory control and data acquisition require a high level of reliability in terms of data integrity and timely reporting [3]. Therefore, an IWSN should guarantee uninterrupted target coverage and connectivity among all sensor nodes and a sink node [4]. This is often referred to as the connected target coverage (CTC) problem, where each discrete target in the network must be within the sensing range of at least one sensor node, and where at least one routing path must be found to connect any source node to the sink node [5]. However, in industrial environments, the coverage area of a sensor node, as well as the link connectivity, may suffer from noise, cochannel interferences, and multipath propagation. In addition, energy is arguably the main constraint of wireless sensor nodes [6]–[8]. Therefore, the energy-efficient CTC problem has become an important issue that urgently needs to be addressed.
V. CONCLUSION AND FUTURE WORK
In this paper, we have analyzed different energy-efficient coverage strategies designed for industrial environments. Through comparing four representative CTC algorithms, properties of each strategy are embodied under different conditions. Since coverage performance is difficult to obtain uniformly, the selection of coverage algorithms should consider which factor (convergence speed, maximum lifetime, etc.) is the focus in a specific practical application. Attention should be paid to improve the performance determined by the main focus. Efforts can then be made to achieve the relative performance of other parameters. Based on our analysis, useful insights are given for IWSN designers to choose an appropriate coverage strategy.
In the future, additional work is required to bridge the gap between ideal simulations and real-world coverage systems. For instance, mobility should be introduced to an IWSN. Static sensor nodes may be disturbed by the vibration of industrial equipment, which could cause a change in network topology. Therefore, simulation results achieved by energy-efficient CTC algorithms should be extended to include possible influences of real industrial applications.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. کارهای مرتبط
3. الگوریتم های CTC بهینه
4. شبیه سازی
5. نتیجه گیری و کار آینده
منابع
Abstract
1. INTRODUCTION
2. RELATED WORK
3. ENERGY-EFFICIENT CTC ALGORITHMS
4. SIMULATION
5. CONCLUSION AND FUTURE WORK
REFERENCES
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه