دانلود مقاله مطالعه عملکرد LDO بدون خازن با انواع مختلف مقاومت
چکیده
در این مقاله تاثیر استفاده از انواع مختلف مقاومت در رگولاتور (تنظیم کننده) ولتاژ با افت خروجی کم (LDO) و بدون خازن، از نظر ویژگی های اصلی عملکرد بررسی می شود. به منظور دستیابی به این امر، یک رگولاتور ولتاژ LDO 1.8 ولتی طراحی شده است و با استفاده از تکنولوژی CMOS 180 نانومتر شبیه سازی شده است و ولتاژ تغذیه آن 3.3 ولت است. شبیه سازی ها در سطح شماتیک در نرم افزار کیدنس برای پنج نوع مختلف مقاومت در یک LDO یکسان، انجام شده است و عملکرد آن ها از نظر دقت ولتاژ خروجی، پایداری و نسبت حذف منبع تغذیه (PSRR) مقایسه شده است. با توجه به نتایج شبیه سازی، تفاوتهای قابل توجهی در عملکرد LDOها با انواع مختلف مقاومت مشاهده شده است. LDO با مقاومت hpoly بهترین نتایج را از نظر پایداری نشان می دهد، در حالی که LDO با مقاومت pdiffb بالاترین PSRR را دارد.
1.معرفی
گسترش حوزه الکترونیک موبایل، رگولاتور ولتاژ با افت خروجی کم (LDO) را به یک بلوک سازنده مهم در سیستم مدیریت توان تبدیل کرده است، زیرا LDO می تواند طوری طراحی شود که از یک ولتاژ تغذیه محدود، ولتاژ خروجی دلخواه خاص برای مدارها را تامین کند. این امر کاربر را قادر می سازد تا از یک ولتاژ ورودی بزرگتر، یک ولتاژ خروجی را به روشی ساده و ارزان تنظیم کند [1] به طوری که از آن برای تقریب زدن یک منبع ولتاژ ایده آل در زندگی واقعی استفاده شود [2]. همان طور که در شکل 1 نشان داده شده است، یک مدار LDO پایه از چهار بخش اصلی تشکیل شده است. تقویت کننده خطا، ترانزیستور گذر، شبکه فیدبک و بار [2]. یکی از پیشرفت های اخیر در LDO ها بدون خازن کردن آن ها است. در LDOها، اغلب برای تامین پایداری و پاسخِ گذرای خوب، یک خازن خارجی بزرگ، که در شکل 1 با CL نشان داده شده است، مورد نیاز است. پایداری در طراحی LDOها، بسیار مهم است زیرا پهنای باند بهره واحد (UGBW) و مکان قطب ها مستقیما تحت تاثیر جریان بار IL هستند [3]. همچنین PSRR می تواند با استفاده از خازن بار بزرگ خارج از تراشه، بهبود یابد. هر چند عمدتا روش استفاده از خازن بزرگ، دارای عیب نیازمندی به استفاده از جزء خارجی است، بنابراین این ایراد مانعِ استفاده از LDO در رویکردهای سیستم-روی-تراشه می شود. به علاوه هزینه ساخت بالاتری دارد و مساحت کل برد مدار چاپی (PCB) افزایش می یابد [3]. بنابراین، طراحی یک LDO که پایداری خوب و PSRR بالایی دارد اما به یک خازن خارجی بزرگ نیاز ندارد مزیتی بزرگ برای سیستمی است که هدف آن حداقل کردن جزء خارجی و مساحت است، درست همان چیزی که این روزها در دستگاه های قابل حمل مورد توجه است.
5.نتیجه گیری
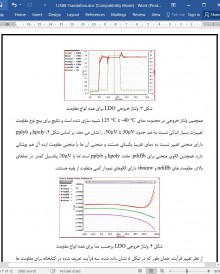
از نتایج، استنتاج می شود که هنگام استفاده از انواع مختلف مقاومت، تأثیرات قابل توجهی در عملکرد LDO به وجود می آید. همه ی پنج نوع مختلف مقاومت سطح دقت بالایی را برای ولتاژ خروجی نشان دادند که با تغییرات دما و در فرآیندهای مختلف تغییرات بسیار کوچکی دارد. در کل، از نظر پایداری hpoly بهترین نتایج قابل مقایسه با مقاومت ایده آل را دارد که دارای 1% اختلاف در حاشیه فاز و UGBW یکسان نسبت به مقاومت ایده آل است و pplyb نیز آن را از نزدیک دنبال می کند. از سویی دیگر از نظر PSRR، pdiffb بهترین نتایج را نشان می دهد که با یک افزایش قابل توجه در مقایسه با مقاومت ایده آل همراه است که میزان این افزایش تقریبا برابر با 11% در 1 kHz، 36% در 100 kHz و 67% در 1 MHz است. عیب مقاومت pdiffb، مقاومت ورقه نسبتا پایین تر آن در مقایسه با hpoly و pplyb است که باعث مصرف مساحت خیلی زیادی برای ایجاد مقادیر بزرگ مقاومت می شود، بنابراین برای LDOهایی که می خواهند جریان ساکن کمی داشته باشند، چندان مناسب نیست. با این وجود، اگر PSRR بالاترین اولویت باشد pdiffb بهترین گزینه است و با توجه به اینکه جریان بزرگ تر برای جبران مقدار مقاومت کمتر قابل قبول است، می توان مساحت کل این مقاومت را کاهش داد.
Abstract
This paper studies the impact of utilizing different resistor types in capacitor-less low drop-out (LDO) voltage regulator on its key performance characteristics. In order to achieve this, a 1.8 V LDO voltage regulator is designed and characterized using 180 nm CMOS technology with a supply voltage of 3.3 V. Simulations are done in schematic level using Cadence on five different types of resistor for the same LDO, and the performance in terms of output voltage accuracy, stability and power supply rejection ratio (PSRR) are compared. From the simulation results, significant differences are observed in the LDO's performance with different types of resistor. The LDO with hpoly resistor gives the best results in terms of stability while pdiffb resistor LDO produces the highest PSRR.
I. INTRODUCTION
The expansion of mobile electronics area makes a low dropout (LDO) voltage regulator an important building block in power management system as it can be designed to supply a specific desired output voltage needed by the circuits from limited supply voltage. It enables the user to regulate an output voltage from a higher input voltage in a simple and inexpensive way [1] as it is used to approximate an ideal voltage source in real life [2]. A basic LDO circuit consists of four main parts; the error amplifier, the pass transistor, the feedback network and the load as shown in Fig. 1 [2]. One of the recent improvement areas in LDOs is to make it capacitorless. In LDOs, a bulky external capacitor, denoted as CL in Fig. 1, is often needed to provide stability and good transient response. Stability is critical in LDO design since the unity gain bandwidth (UGBW) and the poles locations are directly affected by the load current IL [3]. The PSRR can also be improved by using the large off-chip load capacitor. However, the drawback of using it is mainly the need to use external component, hence preventing the LDO to be used in systemon-chip (SOC) solutions, besides higher cost and increased total printed circuit board (PCB) area [3]. Therefore, a LDO that has good stability and high PSRR but does not require a large external capacitor will provide a great advantage to a system which aims for minimum external component and minimal area, which is what portable device is all about these days.
V. CONCLUSION
From the results, it is concluded that there are significant impacts in LDO performance when using different types of resistor. All five different types of resistor produce high level of accuracy for the output voltage with very small variation across temperature and under different process. In overall, hpoly has the best results comparable to the ideal resistor in terms of stability, with 1% difference in phase margin and identical UGBW with the ideal resistor, followed closely by pplyb. In terms of PSRR on the other hand, pdiffb shows the highest result, with a significant increase of approximately 11% at 1 kHz, 36% at 100 kHz and 67% at 1 MHz as compared to the ideal resistor. The drawback of pdiffb resistor is its relatively much lower sheet resistivity compared to hpoly and pplyb, which results in very large area consumption for large resistance values, thus making it less suitable for LDOs which aim for low quiescent current. Nonetheless, if PSRR is the highest priority, pdiffb would make the best option given that bigger current is acceptable to compensate lower resistance value in order to reduce the total area of the resistor.
چکیده
1. معرفی
2. طراحی LDO
3. روش شناسی طراحی و تست
4 .نتایج و بحث
5. نتیجه گیری
منابع
Abstract
1. INTRODUCTION
2. LDO DESIGN
3. DESIGN AND TEST METHODOLOGY
4. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
5. CONCLUSION
REFERENCES
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه