دانلود مقاله الگوریتم کارای انرژی توزیع شده جهت تضمین پوشش شبکه های حسگر بی سیم
چکیده
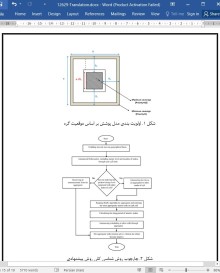
مصرف انرژی، عمر شبکه و پوشش بهعنوان چالشهای اصلی در شبکههای حسگر بیسیم محسوب میشوند. این تحقیق روشی را پیشنهاد میکند که سطح شبکه را به سلولهای مربعی بر اساس محدوده جغرافیایی شبکهبندی میکند. گره پردازش کننده بیشترین انرژی، بهعنوان یک ادغام کننده در هر سلول انتخاب میشود. با توجه به سطح پوشش و انرژی باقیمانده، الگوریتم کرم شبتاب جهت انتخاب و حفظ مناسبترین گره در هر سلول عمل کرده درحالیکه بقیه گرهها را غیرفعال میکند. منحصر به فرد بودن الگوریتم کرم شبتاب تکاملی پیشنهادی، تضمین پوشش مؤثر و مطلوب شبکه است. از Omnet++ جهت مطالعه شبیهسازی استفادهشده است و نتایج آنها با نتایج مدل های TCO و ACO حریصانه مقایسه شدهاند. یک پوشش بهمراتب بزرگتر توسط روش پیشنهادی با گرههای کمتر و %30 کاهش تقاضای انرژی ارائه شده است. مزیت افزوده شده، افزایش عمر شبکه است.
1. مقدمه
سال های اخیر شاهد پیشرفت سریع و کاربرد جهانی تکنولوژی سیستم ارتباط بیسیم بوده است. موقعیت دقیق گرهها به صورت از پیش تعیین شده نیست. این مشخصه طراحی خاص، امکان استفاده از گرههای حسگر را در مکان های خطرناک و راه دور مهیا میکند. یک شبکه حسگر بیسیم دارای تعدادی گره است که از ویژگی هایی خاص مانند توانایی حسی، ایجاد ارتباط، مشاهده رخداد های نسبی یا پدیده های خاص در یک محیط عملیاتی مشخص و واکنش مؤثر در برابر آنها برخوردار هستند. هدف این سیستم، جمع آوری فرآیند و انتقال داده برای ایستگاه پایه است. هر گونه محدودیت فیزیکی در گرهها منحصر به محدودیت های متناظر در انرژی، پوشش و عمر عملیاتی میشود. گرههای حسگر دارای انرژی کم بوده و نمیتوان آنها را مجدداً شارژ کرده و یا پس از قسمت اولیه تغییر داد. بنابراین، با گذشت زمان، انرژی آن رو به نزول گذاشته و موجب غیرفعال سازی برخی گرهها میشود. این موضوع از طرفی موجب ایجاد حفره هایی در ناحیه مورد بررسی میشود. هر حسگر دارای قابلیت خود ساخته جهت حس کردن یک ناحیه پوشش محدود در محیط کاربردی با شعاع گره محدود مورد نظر است. بر این اساس در نواحی بدون پوشش گره، برخی از حفره ها ایجاد میشوند. دسته یا رده کاربردی مورد انتظار برای سیستم پیشنهادی، بهعنوان عامل اصلی محسوب میشود که موجب اجرای وظیفه طراحی برای گرههای مشخص میشود. ابزار نظامی سیستم بهعنوان موردی در نظر گرفته میشود که طی آن نیاز به پوشش بالای شبکه احساس میشود. این موضوع نیازمند کارکرد همزمان چندین عامل جهت تضمین پوشش مناسب برای هر ناحیه حوزه حسگر است.
با این حال، درصد حداقل پوشش در شرایط عملیاتی مختلف مانند شرایطی که به پایش دامنه های حساس مانند اکوسیستم ها و حیات وحش پرداخته و یا به پایش دما در مجموعه های تجاری و مسکونی بزرگ می پردازند، حائز اهمیت است. شبکههایی با پوشش بیشتر در برابر نقایص عملکردی در گرهها، پشتیبانی میشوند. به همین دلایل، باید توجه داشت که در فاز طراحی، برنامه های مختلف نیازمند پوشش مناسب شبکه هستند که ممکن است نیازمند یک سیستم سنجیده با داشتن قابلیت جهت غلبه بر چالش های پوشش باشند.
6. نتیجه گیری
الگوریتم کرم شبتاب تکاملی بهعنوان مبنای مدل استفادهشده در این مقاله جهت بهینهسازی پوشش در شبکههای حسگر بیسیم انتخاب شده است. این روش مبتنی بر شبکهبندی شبکه بر اساس محدوده جغرافیایی است. علاوه براین، یک گره با بیشترین انرژی باقیمانده در هر سلول بهعنوان ادغام کننده انتخاب میشود. هدف، برداشتن گرهها با بیشترین سطح انرژی باقیمانده و ناحیه پوشش در هر سلول جهت فعال ماندن و غیرفعال شدن دیگر گرهها است. الگوریتم کرم شبتاب تکاملی جهت انتخاب مناسبترین گره، استفاده میشود. این موضوع امکان تضمین سطح پوشش بسیار بزرگتر برای تکنیک پیشنهادی را مهیا میکند. این موضوع امکان تضمین ایجاد حداقل گرههای فعال همزمان و حداکثر سطح پوشش شبکه را فراهم میکند. مصرف انرژی کاهش یافته و در نتیجه عمر شبکه نیز افزایش می یابد. نتایج مدل سازی شبیهسازی نشان می دهند که افزایش تعداد گرههای فعال موجب افزایش میانگین پوشش شبکه میزان %30 در مقایسه با دو روش دیگر میشود. از این رو، سطح پوشش بسیار بیشتر توسط روش پیشنهادی ایجاد میشود. الگوریتم پیشنهادی با نرم افزار Omnet++ شبیهسازی شده و نتایج آنها با نتایج الگوریتم های TCO و ACO-حریصانه جهت صحت سنجی نتایج، مقایسه شده است.
Abstract
Energy consumption, network lifetime and coverage are the major challenges in wireless sensor networks. This study proposes a method that grids network area into square cells on a geographical basis. The node possessing the highest energy is selected as an aggregator in each cell. Given the cover area and remaining energy, the firefly algorithm functions to select and actively maintain the most suitable node in each cell while deactivating others. The uniqueness of the proposed evolutionary firefly algorithm is to ensure the desirable and effective network coverage. Omnet++ was applied for simulation study, the results of which were compared with those from both TCO and ACO-Greedy models. A significantly greater coverage was provided by the proposed method with fewer nodes and 30% decrement in energy demand. The added advantage was the elongation of network lifetime.
1 Introduction
Recent years has witnessed a rapid development and universal application of wireless communication system technology. The precise location of nodes, more often than not, is not predetermined. This specific design characteristic makes it possible for the sensor nodes to be used in dangerous and remote places. A wireless sensor network consists of a number of nodes that have certain characteristics like sensing ability, establishment of communication, observation of relative incidents or specific phenomena within a certain operational environment and effective reaction against them. The aim is to collect process and transfer data for a base station [1]. Any physical limitation in the nodes is bound to result in corresponding limitations in energy, coverage and operational lifetime. The sensor nodes have low energy and cannot be recharged or changed after the initial instalment [2]. Therefore, as the time passes, its energy runs down, causing some nodes to deactivate. This in turn produces holes in the region under investigation. Each sensor has an in-built capability to sense a limited coverage area within the functional context with a limited radius of node in question. It is on such basis that in regions without node coverage, some holes are produced. The category or class of application that the proposed system is expected to select is the principal factor that dictates the specific nodes to perform the design function [3]. The system's military utility is a case in point where there would be a need for high network coverage. The latter necessitates simultaneous functioning of several sensors to ensure sufficient coverage for each sensor's catchment area.
A certain minimum coverage percentage is however required in different operational settings such as those that monitor sensitive domains such as eco-systems and wild life or monitoring temperature in huge residential and commercial complexes. Those networks with a greater coverage are, to certain extent, protected against performance deficiency in nodes. For these very reasons, it should be born in mind during the designing phase that various applications require a suitable network coverage [4] that might necessitate a specifically defined, tailor-made system having capability to overcome the coverage challenges.
6 Conclusion
The evolutionary firefly algorithm was the basis of the model used in this paper to optimise coverage in wireless sensor networks. The methodology is based on a gridding network on a geographical basis. Moreover, a node with the highest remaining energy in each cell is selected as an aggregator. The objective is to pick the nodes with the highest level of remaining energy and coverage area in each cell to stay active, while others to become inactive. The evolutionary firefly algorithm is used to select the most appropriate node. This makes it possible for the proposed technique to ensure considerably a must greater coverage area. The latter makes it possible to ensure the establishment of simultaneous minimal active nodes and maximal network coverage area. The energy consumption is decreased and the lifetime of the network is enhanced as a result. The results of simulation modelling show that increasing the number of active nodes increases an average of 30% network coverage compared with that of the other two methods. A much greater coverage area is therefore provided by the proposed method. The proposed algorithm was simulated with the Omnet++ software, the results of which were compared with those of the TCO and ACO-Greedy algorithms to validate the results.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. تحقیقات مرتبط
3. مقدمات
3.1 مدل شبکه
3.2 الگوریتم کرم شبتاب
4. روش پیشنهادی
5. شبیهسازی و نتایج
6. نتیجه گیری
منابع
Abstract
1 Introduction
2 Related works
3 Preliminaries
3.1 Network model
3.2 Firefly algorithm
4 Proposed method
5 Simulation and results
6 Conclusion
References
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه