دانلود مقاله استفاده از مدل سازی مسیر PLS در تحقیقات تکنولوژی جدید
خلاصه
هدف - مدل سازی مسیر حداقل مربعات جزئی (PLS) ، یک روش مدل سازی معادلات ساختاری مبتنی بر واریانس (SEM) است که به طور گسترده در کسب وکار و علوم اجتماعی کاربرد دارد. توانایی آن برای مدلسازی ترکیب ها و عوامل مختلف آن را به یک ابزار آماری نیرومند در تحقیقات تکنولوژی جدید تبدیل کرده است
بررسی ها،بحث ها و پیشرفت های اخیر منجر به تغییرات اساسی در درک و استفاده از PLS شده است. هدف این مقاله، بحث در مورد این مسائل است. طراحی / روش شناسی / رویکرد - این مقاله بینش جدیدی را به ارمغان می آورد و نگاه تازه ای به مدل سازی مسیر PLS ارائه می دهد. همچنین این مقاله تحولات جدیدی مانند PLS سازگار، تجزیه و تحلیل های ترکیبی تایید کننده و نسبت همبستگی heterotrait-monotrait را ارائه می دهد.
یافته ها - درصورتی کهSEM در بردارنده ی هم عوامل و هم ترکیبات باشد، روش انتخابی مدل سازی مسیر PLSخواهد بود. آزمایش های جدیدی وجود دارند که بواسطه ی آنها میتوان مناسب بودن مدل سازی مسیر PSL را تائید نمود.
اصالت / ارزش - این مقاله دستورالعمل های به روز شده در خصوص نحوه استفاده از PLS و نحوه گزارش دهی و تفسیر نتایج آن را ارائه می دهد. کلمات کلیدی PLS، مدلسازی معادلات ساختاری،دستورالعمل ها ،تست مدل
مقدمه
مدلسازی معادلات ساختاری (SEM) مجموعه ای از تکنیکهای آماری است که در کسب و کار و علوم اجتماعی بسیار محبوب شده است. توانایی آن برای مدل سازی متغیرهای پنهان، محاسبه نمودن انواع مختلف خطاهای اندازه گیری و بررسی کلی نظریه ها ، این مدلسازی را برای پاسخگویی به بسیاری از سوالات تحقیقاتی مناسب نموده است. .
دو نوع SEM وجود دارند : SEM مبتنی بر کواریانس و SEM مبتنی بر واریانس. SEM مبتنی بر کوواریانس، پارامترهای مدل را با استفاده از ماتریس واریانس- کواریانس تجربی برآورد میکند ، و اگر مدل فرض شده شامل یک یا چند عامل مشترک باشد، از این روش استفاده میشود. در مقابل، SEM مبتنی بر واریانس ابتدا پروکسی ها را به صورت ترکیبهای خطی از متغیرهای مشاهده شده ایجاد می کند و سپس پارامترهای مدل را با استفاده از این پروکسی ها تخمین می زند. اگر مدل فرض شده حاوی ترکیب باشد، SEM مبتنی بر واریانس روش انتخابی مناسب است.
از میان روشهای SEM مبتنی بر واریانس، مدل سازی مسیر حداقل مربعات جزئی (PLS) به عنوان " توسعه یافته ترین و کلی ترین سیستم "در نظر گرفته شده است (مک دونالد، 1996، ص 240) و "گلوله نقره ای" نامیده شده است (Hair et al.، 2011).PLS به طور گسترده ای در تحقیقات سیستم های اطلاعاتی (Marcoulides and Saunders، 2006)، مدیریت استراتژیک (Hair et al.، 2012a) ، بازاریابی (Hair و همکاران، b 2012) و مواردی فراتر از اینها استفاده می شود.محققان همه رشته ها توانایی PLS برای مدل سازی هر دومورد عامل ها و ترکیب ها را بخوبی درک کرده اند واین موضوع PLS را به روشی ( متودی) کارآمد بویژه در تحقیقات فن آوری های جدید و تحقیقات سیستم های اطلاعاتی تبدیل کرده است. در حالی که عوامل را می توان برای مدل سازی متغیرهای پنهان تحقیقات رفتاری از جمله نگرشها یا صفات شخصیتی مورد استفاده قرار داد ، ترکیب ها همچنین می توانند برای مدل سازی مفاهیم قوی (Höök و Löwgren، 2012)، یعنی انتزاع مصنوعات مانند ابزارهای مدیریت، نوآوری ها یا سیستم های اطلاعاتی استفاده شوند. در نتیجه، مدل سازی مسیر PLS ابزار آماری مطلوبی در مطالعات عوامل موفقیت است (Albers، 2010).
بحث
فراوانی بحث ها و پیشرفت ها در مورد مدل سازی مسیر PLS نیازمند نگاه تازه به این تکنیک و همچنین دستورالعمل های جدید برای آن است. یک جنبه مهم این تلاش، پاسخ به سوال «چه چیزی تغییر کرده است؟» می باشد. پاسخ این سوال در جدول 2 آمده است، که به مقایسه دیدگاه های سنتی و مدرن در PLS میپردازد. این به ویژه برای محققانی که در گذشته در خصوص مدل سازی مسیر PLS مطالعه کرده اند و مایلند اطلاعات خود را به روز کنند، مفید است.
این واقعیت که نحوه ی استفاده از PLS امروزه بسیار متفاوت از گذشته شده است پیامدهایی را برای کاربران نرم افزار PLS بهمراه داشته است. کاربران بایستی از به روز ترین نسخه های نرم افزار PLS از جمله SmartPLS استفاده کنند که جدیدترین پیشرفت ها را در زمینه PLS ارائه میکند. ممکن است کاربران ترجیح دهند از ADANCO استفاده نمایند (Henseler and Dijkstra, 2015) ، که یک نرم افزار جدید SEM مبتنی بر واریانس است که شامل مدل سازی مسیر PLS نیز می شود.
مدولاسیون مدل سازی مسیر PLS همانطور که در بخش دوم توضیح داده شد ، امکان جایگزینی یک یا چند مرحله توسط روش های دیگر را ارائه می دهد. به عنوان مثال ، برآوردگر حداقل مربعات در مرحله ی سوم میتواند توسط شبکه های عصبی جایگزین شود (Buckler and Hennig-Thurau, 2008; Turkyilmaz et al., 2013). الگوریتم PLS را می توان در مرحله 1 با استفاده از مولد های نشانگر شاخص جایگزین مانند تجزیه و تحلیل مولفه های اصلی (Tenenhaus، 2008)، تجزیه و تحلیل اجزای ساختاری جمعی (Hwang and Takane, 2004; Henseler, 2012)، تجزیه و تحلیل همبستگی متعارف کلیت یافته (Tenenhaus and Tenenhaus, 2011) و یا حتی مجموع نمرات ساده جایگزین نمود. از آنجا که در این موارد الگوریتم PLS تکراری نمی تواند به عنوان نام دهنده (eponym) عمل کند، نمیتوان بیش از این در مورد مدل سازی مسیر PLS صحبت نمود. با این حال، این روش هنوز هم SEM مبتنی بر واریانس است.
Abstract
Purpose Partial least squares (PLS) path modeling is a variance-based structural equation modeling (SEM) technique that is widely applied in business and social sciences. Its ability to model composites and factors makes it a formidable statistical tool for new technology research. Recent reviews, discussions, and developments have led to substantial changes in the understanding and use of PLS. The paper aims to discuss these issues.
Design/methodology/approach This paper aggregates new insights and offers a fresh look at PLS path modeling. It presents new developments, such as consistent PLS, confirmatory composite analysis, and the heterotrait-monotrait ratio of correlations.
Findings PLS path modeling is the method of choice if a SEM contains both factors and composites. Novel tests of exact fit make a confirmatory use of PLS path modeling possible.
Originality/value This paper provides updated guidelines of how to use PLS and how to report and interpret its results.
Introduction
Structural equation modeling (SEM) is a family of statistical techniques that has become very popular in business and social sciences. Its ability to model latent variables, to take into account various forms of measurement error, and to test entire theories makes it useful for a plethora of research questions.
Two types of SEM can be distinguished: covariance- and variance-based SEM. Covariance-based SEM estimates model parameters using the empirical variancecovariance matrix, and it is the method of choice if the hypothesized model consists of one or more common factors. In contrast, variance-based SEM first creates proxies as linear combinations of observed variables, and then estimates the model parameters using these proxies. Variance-based SEM is the method of choice if the hypothesized model contains composites.
Among variance-based SEM methods, partial least squares (PLS) path modeling is regarded as the “most fully developed and general system” (McDonald, 1996, p. 240) and has been called a “silver bullet” (Hair et al., 2011). PLS is widely used in information systems research (Marcoulides and Saunders, 2006), strategic management (Hair et al., 2012a), marketing (Hair et al., 2012b), and beyond. Its ability to model both factors and composites is appreciated by researchers across disciplines, and makes it a promising method particularly for new technology research and information systems research. Whereas factors can be used to model latent variables of behavioral research such as attitudes or personality traits, composites can be applied to model strong concepts (Höök and Löwgren, 2012), i.e. the abstraction of artifacts such as management instruments, innovations, or information systems. Consequently, PLS path modeling is a preferred statistical tool for success factor studies (Albers, 2010).
Discussion
The plethora of discussions and developments around PLS path modeling called for a fresh look at this technique as well as new guidelines. As important aspect of this endeavor, we provide an answer the question “What has changed?” This answer is given in Table II, which contrasts traditional and modern perspectives on PLS. It is particularly helpful for researchers who have been educated in PLS path modeling in the past, and who would like to update their understanding of the method.
The fact that PLS today strongly differs from how it used to be has also implications for the users of PLS software. They should verify that they use very current versions of PLS software such as SmartPLS, which have implemented the newest developments in the PLS field. Alternatively, they may want to use ADANCO (Henseler and Dijkstra, 2015), a new software for variance-based SEM, which also includes PLS path modeling.
The modularity of PLS path modeling as introduced in the second section opens up the possibility of replacing one or more steps by other approaches. For instance, the least squares estimators of the third step could be replaced by neural networks (Buckler and Hennig-Thurau, 2008; Turkyilmaz et al., 2013). One could even replace the PLS algorithm in Step 1 by alternative indicator weight generators, such as principal component analysis (Tenenhaus, 2008), generalized structured component analysis (Hwang and Takane, 2004; Henseler, 2012), regularized generalized canonical correlation analysis (Tenenhaus and Tenenhaus, 2011), or even plain sum scores. Because in these instances the iterative PLS algorithm would not serve as eponym, one could not speak of PLS path modeling any more. However, it still would be variance-based SEM.
خلاصه
مقدمه
ماهیت مدل سازی مسیر PLS
ویژگی های مدل
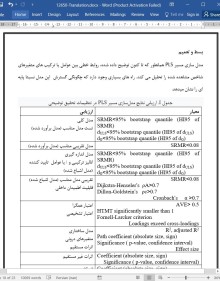
ارزیابی و گزارش تجزیه و تحلیل PLS
بسط و تعمیم
بحث
منابع
Abstract
Introduction
The nature of PLS path modeling
Model specification
Assessing and reporting PLS analyses
Extensions
Discussion
References