دانلود مقاله فری مغناطیس در نانوذرات فریت کبالت (CoFe2O4)
چکیده
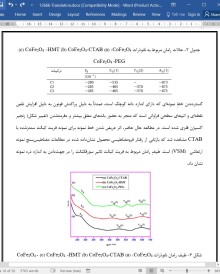
در این تحقیق، نانوذرات فریمغناطیس فریت کبالت (CoFe2O4) با بهرهگیری از روش همرسوبی سنتز شد. خواصِ مغناطیسی و فیزیکی-شیمیایی محصول نهایی بر اساسِ بکارگیری سورفکتانتهای ستیل تریاتیل آمونیم برومید (CTAB)، هگزامتیلن تترامین (HMT) و پلیاتیلنگلایکول (PEG-400) بررسی شد. الگوی افتراقسنجی پرتو ایکس (XRD) و حالات فعال رامان حاکی از تشکیل ساختار مکعبی فریت کبالت بود. همچنین تصاویر میکروسکوپ الکترونی روبشی (SEM) نشان داد که محصول نهایی ساختاری کروی دارد و اندازه ذرات در آن متفاوت است. پیکهای تابش فوتولومینسنس قوی تاییدی بر کیفیت محصول بود. ارتعاش اکسیژن فلزی فروسرخ در اعداد موج cm-1 615 و 426 به ترتیب در مکانهای تتراهدرال و اکتاهدرال سیستم فریت کبالت خودش را نشان داد. معلوم شد که رفتار الکتروشیمیایی محصول به اندازه دانه وابسته است و با استفاده از CTAB بالاترین ظرفیت ویژه مشاهده گردید. علاوه بر این، رفتار فری مغناطیس در دمای اتاق با استفاده از مطالعات مغناطیسسنج نمونه ارتعاشی (VSM) تایید شد. همچنین با استفاده از PEG حد مغناطش اشباع به emu/g 66 رسید. ذراتی که دارای اندازه دانه و بلورهای بزرگتری بودند، رفتار مغناطیسی بهتری از خود نشان دادند.
1-مقدمه
خواص فیزیکی و شیمیایی فریت سبب توجه محققین به تحقیق بیشتر در زمینه خواص نوری-الکتریکی، الکتریکی و مغناطیسی فریت شده است. به دلیل اندازه کوچکِ اسپینلهای نانویی فریت و همچنین باریکه توزیع اندازه دانه و مساحت سطحِ بزرگ آن، توجهات به سوی فریت جلب شده است. نانوذرات فریت کبالت (CoFe2O4) بخشِ اعظم کاربردها در زمینه رفتارهای مغناطیسی فریت را به دلیل خواص نامعمولش نظیر ناهمسانگردی بالای بلورهای مغناطیسی (J/m3 105 × 3- 8/1 در دمای K 300) وادارندگی (coercivity) و مغناطشِ زیاد به خود اختصاص داده است. از سوی دیگر اکسید کبالت و اکسید آهن نیز به دلیل خواص منحصربفرد و هزینه پائین سنتز آنها، با استقبال گستردهای روبرو شدهاند. تکنیکهای متعددی نظیر عملیات حرارتی، جانشینی شیمیایی و سردسازی ناگهانی و ... برای تنظیم خواص فریت کبالت به کار رفته است. به طور کلی، در ساختار اسپینل معکوس بالکِ فریت کبالت، یونهای Co2+ مکانهای اکتاهدرال بی (B) را ترجیح میدهند و یونهای Fe3+ مکانهای تتراهدرال ای (A) را در سیستم فریت ترجیح میدهند. توزیع کاتیونها در سیستم فریت باعث میشود تا نانوذراتِ فریت حاصل از نظر خواص خود برای کاربردهای پیشرفته منحصربفرد باشند. خاصیت مغناطیسی فریت به طور مستقیم به نوع کاتیونها و توزیع آنها در مکانهای اکتاهدرال و تتراهدرال وابسته است و بالعکس. اسپینهای الکترون فریت مغناطیسی به شکل موازی با مکانِ شبکه بلوری و غیرموازی بین دو مکان زیرشبکهای استقرار مییابند در حالیکه خالص مغناطش برابر تفاوت میان دو مکان یادشده است. ساختار اسپینل فریت کبالت یک ماده فازی مناسب برای سیستمهای حساس مغناطیسی، تصویربرداری رزونانس مغناطیسی (MRI)، تصویربرداری بافتی و دیگر کاربردهای دوستدار محیط زیستی است. علاوه بر این به دلیل استحکام مکانیکی بالا و ناهمسانگردی سایشی، میتوان از فریت کبالت برای اتصال به موادِ فعال در سیالات فریمغناطیس، تجهیزات مایکروویو و کاربردهای جذبی استفاده کرد. نانوفریتهای دارای ساختار سلسلهمراتبی، نامعمول و مورفولوژی جدید نظیر نانوذرات، نانومیلهها، نانومکعبها، نانوکمربندها و نانوگلها کمک میکند تا ماده موردنظر مطابق با کاربردهای آتی تنظیم شود. روشهای متعددی برای سنتز نانوفریتها توسعه یافتهاند که شامل روش هیدروترمال، سل-ژل، ساچمهزنی، احیای شیمیایی، سنتز با مایکروویو، همرسوبی و آلیاژسازی مکانیکی میشود. از میان روشهای فوق، روش همرسوبی سمیت کمتری دارد و روشی سریع و با ظرفیت بالا است.
4- نتیجهگیری
تاثیر سورفکتانتهای CTAB، HMT و PEG بر خواص فیزیکی-شیمیایی و مغناطیسی نانوذرات فریت کبالت سنتزشده به روش همرسوبی مطالعه شد. نتایج افتراقسنجی پرتو ایکس (XRD) حاکی از یک ساختار اسپینل مکعبی با قرارگیری اتمها در مرکز هر وجه (fcc) بود. تصاویر میکروسکوپ الکترونی روبشی (SEM)مورفولوژی کروی نانوذرات و اندازه ذرات نابرابر آنها را آشکار کرد. طیف رامان نیز حالت فعال رامان را مطابق با تعویض سورفکتانتها نمایش داد. خاصیت لومینسنس صرفاً به اندازه ذره محصول نهایی وابسته بود. پیکِ اکسیزن فلزی قوی برای هر سه نمونه تایید شد. بالاترین ظرفیت ویژه در بین نمونهها به نمونه سنتزشده با سورفکتانت CTAB مربوط بود و نشان داد که نانومواد همواره قادر به داشتن ظرفیت ویژه بالایی هستند. فریمغناطیس در دمای اتاق برای نمونههای سنتزشده با سورفکتانت PEG-400 به دلیل اندازه ذره بزرگتر آنها از همه بیشتر بود. این یافتهها به خوبی معلوم کرد که سورفکتانتهای بکاررفته در فرآیند سنتز، ابزاری مهم در تعیین خواص نانوفریتها هستند.
Abstract
Ferrimagnetic cobalt ferrite (CoFe2O4) nanoparticles were synthesized by employing co-precipitation method. Product physico-chemical and magnetic properties with respect to cetyl trimethylammonium bromide (CTAB), hexamethylenetetramine (HMT) and polyethylene glycol (PEG-400) surfactants were investigated. XRD pattern and Raman characteristic active modes revealed the cubic cobalt ferrite structure formation. SEM images explored spherical shaped product with different particle size. Identified strong PL emission peaks confirmed the product quality. IR metal oxygen vibration at 615 and 426 cm−1 revealed tetrahedral and octahedral site of cobalt ferrite system. Product electrochemical behavior was found to be size dependent and high specific capacitance was observed using CTAB. Room temperature ferrimagnetic behavior was confirmed through VSM studies. High saturation value as 66 emu/g was found using PEG. Particles with larger crystallite and particle size exhibited improved magnetic behavior.
1. Introduction
The ferrite physical and chemical properties grasp the researcher’s interest to carry out research over a deep insight of analyzing the different ferrite magnetic, electric and optoelectric properties [1–5]. Nano-sized spinel ferrites have been focused due to its smaller particle size and narrow size distribution with larger surface area [1]. Nano-sized cobalt ferrite (CoFe2O4) filled up the major applications due to its unusual properties like magnetocrystalline high anisotropy (1.8–3 × 105 J/m3 at 300 K), good coercivity and enhanced magnetization [2]. Separately, cobalt oxide and iron oxide are also attracted for their unique properties and low cost [3,4]. Numerous techniques such as heat treatment, chemical substitution and sudden cooling etc. has been adopted to tune cobalt ferrite properties [5,6]. Generally, in bulk cobalt ferrite inverse spinel structure, Co2+ ions preferred octahedral B site and Fe3+ ions preferred tetrahedral A site of ferrite system. The cations distribution in ferrite system made the respective ferrite nanoparticles being significant in their unique properties for advanced applications. The ferrite magnetic property is directly depending on cations type and distribution in octahedral and tetrahedral sites and vice versa. The magnetic ferrite electron spins are arranged parallel within the crystal lattice site and anti-parallel between two sublattice sites whiles the net magnetization is the difference between two sites. The cobalt ferrite spinel structure is a hopeful phase material for magneto-sensitive systems [7], magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), tissue imaging and other environmental friendly applications [8]. Due to its high mechanical strength and wear anisotropy, it could be tied to the active materials in ferrofluids, microwave devices and adsorption applications [9]. The hierarchical, unusual and novel morphology nanoferrites such as nanoparticles, nanorods, nanocubes, nanobelt and nanoflowers help to adapt the corresponding material for future generation potential applications [10,11]. Several methods have been developed to synthesize nanoferrites including hydrothermal, sol–gel, ball milling, chemical reduction, microwave synthesis, mechanical alloying and co-precipitation etc. Among these methods, co-precipitation method has less toxic and fast and high yield synthesis method [12,13].
4. Conclusions
The physico-chemical and magnetic properties of cobalt ferrite via simple co-precipitation route using the surfactants CTAB, HMT and PEG was investigated. XRD results revealed the cubic face centered spinel structure. SEM images revealed the spherical morphology with uneven particle sizes. A well defined Raman active mode with surfactant corresponding shift was revealed by Raman spectra. The luminescent property purely depends on particle size of the products. The strong metal oxygen signature was confirmed for all the three samples. The highest specific capacitance was observed for the sample synthesized by using CTAB which revealed that the nano sized materials are always capable of possessing high specific capacitance. The room temperature ferrimagnetism was observed for the sample synthesized by using the surfactant PEG400 due to its larger particle size. These results elucidated that the surfactants used in the product processing method is an important tool to control the properties of nanoferrites.
چکیده
1-مقدمه
2-مواد و روشها
3- نتایج و بحث
4- نتیجهگیری
منابع
ABSTRACT
1. Introduction
2. Materials and methods
3. Results and discussion
4. Conclusions
References
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه