دانلود مقاله تشخیص تنگی دریچه ائورت با تحلیل همبستگی صداهای قلب فیلتر شده با موجک
چکیده
روش گوش دادن مرسوم توسط پزشکان عمومی (GP) همچنان با مشکلاتی همراه است و اغلب تنها در مراحل پیشرفته بیماری های مربوط به دریچه های قلب نتایج قابل توجهی فراهم می کند. امروزه تنگی و نارسایی های دریچه با دستگاه های اولتراسونیک دقیق اما پرهزینه تشخیص داده می شوند. هدف از این پژوهش ارائه یک روش جدید برای آنالیز صدای قلب به منظور تشخیص تنگی دریچه آئورت (AVS) بر اساس رویکرد تکنیک موجک و همبستگی است.
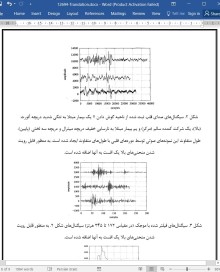
صدای قلب 81 بیمار (43 بیمار مبتلا به AVS، 11 شاهد سالم-REF و 27 بیمار مبتلا به بیماریهای دریچه ای دیگر –OVD) با یک استتوسکوپ الکترونیکی ضبط شده و بعد از فیلتر کردن با موجک، انولوپ ها محاسبه شدند. سه همبستگی بر اساس این انوولوپ ها اجرا شدند: 1) درون AVS، 2) درون گروه ترکیبی AVS+REF و 3) درون گروه ترکیبی AVS+OVD که به ضرایب همبستگی rAvS، rAVS/REF و rAVS/OVD منجر شدند.
نتایج نشان می دهند که rAvS، به میزان قابل توجهی بالاتر از rAVS/REF و rAVS/OVD است(P<0.01). این اختلافات در الگوهای صوتی بین گروه ها نشان می دهد که روش معرفی شده امکان تشخیص خودکار AVS را فراهم می اورد.
ما یک روش جدید برای طبقه بندی صدای قلب طراحی کردیم که به نظر می رسد که برای تشخیص بیماریهای دریچه قلب مناسب بوده و استفاده از ان برای پزشکان عمومی کم هزینه و آسان است.
1. مقدمه
برای سالیان درازی گوش دادن تنها روش تشخیص بیماری ها مربوط به دریچه-های قلبی بود. در ابتدا تشخیص تنها با گوش انجام می شد، اما بعدا از ثبت مکانیکی صداهای قلب برای تشخیص تغییرات پاتولوژیکی استفاده شد. با اختراع اکورادیوگرافی استفاده از روش سخت و حساس فونورادیوگرافی اهمیت خود را از دست داد. با ریزتر شدن سیستم های الکترونیکی امروزه ساخت تجهیزات قابل حمل برای گوش دادن و ضبط صداهای قلب امکان پذیر شده است. بسیاری از این تجهیزات یا نرم افزارهای موجود تشخیص را انجام نمی دهند بلمه تنها سیگنال های و طیف های فرکانسی را نمایش می دهند.
طبقه بندی صداهای قلبی ناشی از بیماری های دریچه ای بسیار پیچیده است. گوش دادن نیازمند تجربه فراوان و یک محیط آرم و ساکت است. به ندرت تنها یک دریچه دچار بیماری می شود، اغلب دو یا تعداد بیشتری از دریچه ها متاثر می شوند که می تواند از نوع تنگی یا نارسایی باشد. اینها تشخیص را بسیار دشوار می سازند.
5. نتیجه گیری
ما یک روش وابسته به موجک و همبستگی ارائه کرده ایم که برای تشخیص خودکار بیماری تنگی دریچه آئورت قابل استفاده است. به نظر می رسد که این روش جدید برای طبقه بندی صدای قلب برای تشخیص بیماری های دریچه قلب مناسب باشد و به دلیل هزینه پایین و آسان بودن توسط پزشکان عمومی قابل استفاده است.
Abstract
Traditional auscultation performed by general practitioners (GP) remains problematic and often gives significant results only in a late stage of the heart valve disease. Valve stenoses and insufficiencies are nowadays diagnosed with accurate but expensive ultrasonic devices. This study is aimed to develop a new heart sound analysis method for diagnosing aortic valve stenoses (AVS) based on a wavelet and correlation technique approach.
Heart sounds recorded from 81 patients (43 AVS patients, 11 healthy controls - REF and 27 patients with other valve diseases - OVD) with an electronic stethoscope were wavelet filtered and envelopes were calculated. Three correlations on the basis of these envelopes were performed: (1) within AVS, (2) within mixed group AVS+REF and (3) within mixed group AVS+OVD leading to the mean correlation coefficients rAvS, rAVS/REF and rAVS/OVD•
The results show that rAvs is significantly higher than rAvs1REF and rAvs1ovo (p<0.01). These differences in sound patterns between the groups show that the introduced method provides an automatic diagnostics of AVS.
We developed a new method of heart sound classification that seems to be suited for diagnosing valve diseases and application in a low cost and easy to use system for GPs.
I. INTRODUCTION
Auscultation was for a long time the only method to detect diseases of the heart valves. At first a diagnosis was perfonned only by ear, later on mechanical recordings of heart sounds with plotters were applied for diagnosing pathological changes. With the establishment of the echocardiography the application of the unwieldy, difficult to operate and sensitive phonocardiography devices became less important. With miniaturization of electronic systems it is now possible to develop mobile devices for auscultation and to store heart sounds digitally. Most of these common available devices or software solutions do not perform a diagnosis, they only display the signals and the frequency spectra.
Classification of heart sounds of different valve diseases is very complex [1]. Auscultation requires experience and a quiet environment. Rarely only one single valve is diseased, often two or more valves are affected and may either be insufficient and/or stenotic. This makes the diagnosis more difficult.
V. CONCLUSION
We developed a wavelet and correlation based method which is applicable for an automatic diagnostics of aortic valve stenoses. This new method of heart sound classification seems to be suited for diagnosing valve diseases and application in a low cost and easy to use system for GPs.
چکیده
1 .مقدمه
2. روش شناسی
3. نتایج
4. بحث
5. نتیجه گیری
منابع
Abstract
1. INTRODUCTION
2. METHODOLOGY
3. RESULTS
4. DISCUSS~ON
5. CONCLUSION
REFERENCES
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه