دانلود مقاله ارزیابی SAR تلفن همراه در مجاورت دستگاه تنظیم کننده ضربان قلب کاشته شده در بدن انسان
چکیده
اخیرا، تداخل الکترومغناطیسی (EMI) تنظیم کننده ضربان قلب ایمپلنت شده با تلفن همراه بسیار مورد بررسی قرار گرفته است. برای این دستگاه، انجمن متخصصان ملی ژاپن توصیه کرده است که تلفن همراه را در فاصله ای امن از دستگاه تنظیم کننده ضربان قلب قرار دهید. بعلاوه، ارزیابی تعامل بین موج الکترومغناطیسی (EM) و بدن انسان در حال انجام است. بنابراین، جذب انرژی EM توسط بدن انسان به ویژه در اطراف تنظیم کننده ضربان قلب، که در این حالت تلفن همراه در جیب پیراهن بیمار حامل دستگاه قرار دارد، کاملا ارزیابی شده است. محاسبه ی توزیع نرخ جذب خاص (SAR) اطراف مدل دستگاه تنظیم کننده ضربان، که در یک مدل نیم تنه مستطیلی متوازی الاضلاع قرار داده شده است، و هنگامی که یک مدل تلفن همراه در مجاورت آن قرار دارد، فراهم شده است. بعلاوه، SAR به صورت تجربی نیز به کار رفت، تا این محاسبات عددی ارزیابی شوند. تاکید می شود که توزیع SAR می تواند از حضور یا غیاب مدل تنظیم کننده ضربان، تخمین شود. بعلاوه، نتایج اندازه گیری توزیع SAR با محاسبات سازگار می باشند، بنابراین اعتبار آن تایید شده است.
1 . مقدمه
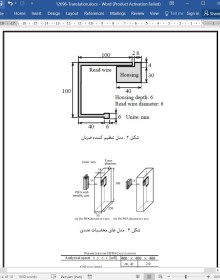
تنظیم کننده ضربان قلب ایمپلنت شده، یکی از شاخص ترین لوازم مورد استفاده برای درمان آریتمی قلب می باشد. سیستم تنظیم کننده، پالس های ضربان قلب را از طریق الکترودهای کاشته شده کنترل می کند، و در صورت تشخیص آریتمی آرام، قلب را با پالس های ولتاژ تحریک می کند.
اخیرا، تداخل الکترومغناطیسی (EMI) تنظیم کننده از تلفن همراه، به طور گسترده مورد بررسی قرار گرفته است [1]- [3]. این بررسی ها نشان می دهند که موج های الکترومغناطیسی موجب تداخل با مدارهای الکترونیکی داخلی، از طریق رابط بین محفظه ی تنظیم کننده، و سیم سربی الکترود، می گردد. بنابراین، رابط نقشی اساسی برای EMI ، به دلیل تلفن های همراه، ایفا می کند. در این حالت، تنظیم کننده ، با توجه به موج های الکترومغناطیس، به عنوان آنتن دریافت کننده عمل می کند. به منظور اجتناب از EMI، متخصصان ملی توصیه کرده اند که تلفن همراه را در فاصله ای مناسب از تنظیم کننده نگهداری کنید [4].
به طور تصادفی، هنگامی که بیمار سوار یک قطار شلوغ می شود، یا تصادفا تلفن همراه را در جیب پیراهن خود قرار می دهد، تلفن همراه می تواند به تنظیم کننده ایمپلنت شده نزدیک باشد. در این حالت، علاوه بر EMI تنظیم کننده، با توجه به مشارکت موج های EM در اثر حرارتی، جذب انرژی الکترومغناطیس در بدن انسان به ویژه در اطراف تنظیم کننده باید در نظر گرفته شود.
5 . نتیجه گیری
SAR میانگین 10-g در اطراف مدل تنظیم کننده ی ضربان قلب ایمپلنت شده درون یک فانتوم نیم تنهی، هنگامی که PIFA بر روی یک پایه ی فلزی، در مجاورت نیم تنه قرار دارد، محاسبه شد. اختلاف توزیع SAR در حضور و غیاب مدل تنظیم کننده، ارزیابی شد. این روند به صورت تجربی نیز بررسی شده است. به منظور بررسی بیشتر، در محاسبات SAR، فانتوم نیم تنه با یک مدل واقعی انسان جایگزین خواهد شد.
Abstract
Recently, electromagnetic interference (EMI) of an implanted pacemaker with a mobile phone was largely investigated. As for the pacemaker, the Japan National Authorities have recommended to keep the mobile phone in safe distance from the cardiac pacemaker. Meanwhile, evaluation of the interaction between the electromagnetic (EM) wave and human body was in progress. Therefore, the absorption of EM energy to the human body especially around the pacemaker, where the mobile phone was in a chest pocket of the pacemaker holder, was thoroughly evaluated. We provided the calculation of specific absorption rate (SAR) distributions around the pacemaker model that implanted into a rectangular parallelepiped torso model, when a mobile phone model is placed in the vicinity. In addition, the SAR was also experimentally performed to validate the such numerical calculations. We confirmed that SAR distributions could be estimated from the presence or absence of pacemaker model. Moreover, the measurement results of the SAR distribution suited to the calculation, thus its validation was achieved.
I. INTRODUCTION
Implanted cardiac pacemaker is one of the most significant devices used for treatment of cardiac arrhythmia. The pacemaker system monitors the pulses of the heartbeat through an implanted electrodes and stimulates the heart by voltage pulses if a slow arrhythmia is detected. Recently, the electromagnetic interference (EMI) of the pacemaker from mobile phone has widely been investigated [1]-[3]. These investigations shown that the electromagnetic waves caused interference to internal electronic circuits through the connector between the pacemaker housing and the lead wire of the electrode. Therefore, the connector played a major role for the EMI due to the mobile phones. In this case, a pacemaker acted as a receiving antenna with respect to the EM waves from the mobile phone. In order to avoid the EMI, national authorities have recommended to keep the mobile phone in safe distance from the cardiac pacemaker [4].
Incidentally, mobile phone may be close to an implanted pacemaker when the patient gets on a crowded train, or accidentally puts a mobile phone in own chest pocket. In this case, besides the EMI of the pacemaker, the absorption of electromagnetic (EM) energy in the human body especially around the pacemaker must be considered, owing to the contribution of EM waves to the heat effect.
V. CONCLUSIONS
10-g averaged SAR around the pacemaker model implanted into a torso phantom was calculated when the PIFA mounted on the metallic case was placed in vicinity of the torso. The difference of the SAR distribution was confirmed upon the presence of the pacemaker model. This tendency has also been validated by the measurement. As for further investigations, the torso phantom will be replaced with a realistic human model for calculations of the SAR.
چکیده
1 . مقدمه
2 . تحلیل عددی
3 . نتایج عددی
4 . ارزیابی های تجربی
5 . نتیجه گیری
منابع
Abstract
1. INTRODUCTION
2. NUMERICAL ANALYSIS
3. NUMERICAL RESULTS
5. EXPERIMENTAL VALIDATIONS
5. CONCLUSIONS
REFERENCES
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه