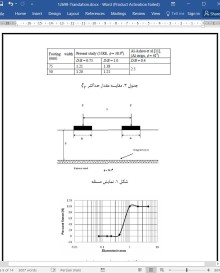
دانلود مقاله اثر تداخلی دو پی نواری مجاور بر روی ماسه مسلح
چکیده
در این تحقیق، تعدادی از آزمون های مدل جهت مطالعه اثر تداخلی دو پی نواری مجاور بر روی بستر ماسه خشک مسلح اینور انجام شده اند. یک لایه ژئوگرید تک محوری به منظور مسلح کردن بستر شالوده مورد استفاده قرار گرفته است. جهت مطالعه اثر تداخلی میان دو پی، در ابتدا، ظرفیت باربری یک پی مجزا به دست آمده و سپس ظرفیت باربری پی های با فاصله نزدیک به هم، تعیین شده است. تحقیق آزمایشگاهی نشان می دهد که ظرفیت باربری یک پی بر روی خاک مسلح با افزایش D/B کاهش می یابد، که D و B نشان دهنده عمق میلگرد گذاری و عرض پی هستند. ضریب ظرفیت باربری ناشی از وزن واحد خاک با افزایش عرض پی، کاهش می یابد. در این مقاله، اثر فاصله مرکز به مرکز (S) میان دو پی بر روی ظرفیت باربری و نشست آنها مورد بررسی قرار می گیرد. رفتار نشست پی های تداخلی از روندی مشابه با ظرفیت باربری تبعیت می کند. نتایج بر حسب ضرائب کارایی ارائه شده و تغییرات آنها با تغییر در مقدار S، به دست آمده است. مشاهدات آزمایشگاهی کنونی تطابق مطلوبی با نتایج آزمایشگاهی و تئوریک موجود در مراجع دارند.
1. مقدمه
در بسیاری از موارد، امکان قرار دادن شالوده ها با فاصله تقریبا نزدیک جهت قراردادن عناصر سازه ای یا جهت محدود کردن بارهای شالوده، غیر قابل اجتناب است. در این گونه موارد، تداخل نواحی شکست می تواند موجب تغییر ظرفیت باربری و رفتار بار- نشست پی ها نسبت به شرایط پی مجزا شود. بنابراین، مسئله اندرکنش میان پی های مجاور از اهمیت اجرایی بالایی برخوردار است، به طوری که در بسیاری از موارد پی ها در با یکدیگر دچار اندرکنش شده و به ندرت اثر مجزا نسبت به یکدیگر دارند. اثر تداخلی بر روی ظرفیت باربری نهایی دو پی نواری مجاور به صورت تئوریک توسط استورات [1] با در نظر گرفتن روش تعادل حدی مطالعه شده است که می توان این تحقیق را به عنوان یک تحقیق پیشگامانه در این حوزه محسوب می شود. در این تحلیل بر خلاف نظریه های موجود برای یک پی مجزا، یک گوه محدود غیر پلاستیک جزئی در زیر پایه شالوده در نظر گرفته شده است. به منظور ارزیابی اثر تداخل، فرض شده است که ناحیه زیر دو پی تداخلی در برگیرنده یک گوه غیر پلاستیک کوچک و بخشی دیگر شامل یک ناحیه برش پلاستیک است. شکل سطح شکست به صورت ترکیبی از یک مارپیچ لگاریتمی و خطم مستقیم در این روش در نظر گرفته شده است. سپس، با استفاده از مکانیزم شکست مشابه با رویکرد استفاده شده توسط استوارت [1]، وست و استوارت [2] از روش ویژگی های تنش به منظور به دست آوردن جواب تداخل دو پی نواری استفاده کرده اند. مقادیر ضرایب کارایی به دست آمده توسط وست و استوارت بر اساس روش ویژگی ها برای φ=35 کوچکتر از مقادیر به دست آمده توسط استوارت با استفاده از روش تعادل حدی هستند؛ که φ نشان دهنده زاویه اصطکاک داخلی بوده و ضریب کارایی توسط نسبت بار تحمل شده توسط یک پی در صورت وجود پی های دیگر نسبت به پی تکی با اندازه مشابه تعریف می شود. مارتی اثرتداخلی شالوده های سطحی را بر روی خاک ماسه ای مطالعه کرده است، اما پی ها به صورت همزمان در معرض بارگذاری قرار نگرفته اند به طوری که یکی از پی ها در ابتدا نسبت به ظرفیت باربری ایمن آن در معرض بارگذاری قرار گرفته و بار بر روی پی مجاور دیگر به میزان بار نهایی افزایش یافته است. سپس به منظور مطالعه اثر تداخل دو پی مجاور بر روی خاک غیر مسلح، برخی از ارزیابی ها توسط محققان مختلف انجام شده اند ([4],[5],[6],[7],[8],[9]). با این حال، با توجه به مطالعات نظریه و آزمایشگاهی موجود، می توان دریافت که بزرگی ظرفیت باربری نهایی و همچنین نشست پی در فاصله نزدیک بر اساس تداخل با شالوده دیگر افزایش می یابد. بنابراین اهمیت تحقیق در مورد کاهش نشست پی های تداخلی با تقویت بستر سنگی غیر قابل کتمان به نظر می رسد به طوری که این موضوع بر رفتار پی های تداخلی حاکم می شود. کینگ و همکاران و ال اشو و همکاران به صورت آزمایشگاهی در مورد اثر تداخل بر ظرفیت باربری پی های نزدیک به هم واقع بر بستر ماسه ای مسلح مطالعه کرده اند. مطالعه فشار، نشست و ویژگی های کجی پی های نزدیک به هم بر روی بستر خاک مسلح توسط کومار و ساران مطالعه شده است. کومار و ساران یک روش تحلیلی را جهت تعیین فشار متناظر با یک نشست برای پی های نواری نزدیک به هم بر روی ماسه مسلح شده ارائه کرده اند. در این تحقیق، مطالعه آزمایشگاهی بر روی اثر تداخل میان دو پی نواری سطحی مجاور توسط برخی از آزمایشات مدل مقیاس بندی شده آزمایشگاهی بر روی بستر ماسه ای خشک با تراکم متوسط و مسلح شده اینور انجام شده اند. ماسه اینور به صورت گسترده در بخش جنوبی هندوستان در دسترس قرار دارد. بنابراین، مطالعه تداخل پی ها بر روی ماسه اینور حائز اهمیت بوده است. پی های نواری مدل از فولاد نرم ساخته شده اند که مانند پی های صلب رفتار کرده و سختی بستر با چسباندن صفحه ماسه ای زیر پی ها تضمین شده است. یک لایه از ژئوگرید تک محوری جهت تقویت خاک مورد استفاده قرار گرفته است. اثر برخی از پارامتر ها مانند عمق لایه میلگرد گذاری (D) و فاصله مرکز به مرکز میان پی ها در این مقاله مطالعه شده است.
Abstract
In this study, a number of model tests were conducted to study the interference effect of two near-by strip footings on dry, reinforced Ennore sand bed. Single layer of uniaxial geogrid was used for reinforcing the foundation bed. To study the interference effect between the two footings, first, the bearing capacity of single isolated footing was obtained and later on, that of closely spaced footings was determined. The experimental study indicates that the bearing capacity of single footing on the reinforced soil decreases with increase in D/B, where D and B are the depth of reinforcement and width of footing, respectively. The bearing capacity factor due to the unit weight of soil is found to decrease with increase in the width of footing. The effect of centre to centre spacing (S) between two footings, on their bearing capacity and settlement is mainly focused in this paper. The settlement behaviour of the interfering footings is found to follow the same trend as the bearing capacity. The results are presented in terms of efficiency factors and their variation was obtained with the change in S. The present experimental observations are generally found in good agreement to those theoretical and experimental results available in the literature.
1 Introduction
On many occasions, it is unavoidable to place footings with quite close spacing, to accommodate the structural details or to limit the footing loads. In such cases, the interference of failure zones could alter the bearing capacity and load-settlement behaviour of footings from the isolated footing condition. Therefore, the problem of interaction between adjacent footings is of great practical significance, as several times the footings in field generally interfere with each other to some extent and are rarely isolated. The interference effect on the ultimate bearing capacity of two nearby strip footings was studied theoretically by Stuart [1] considering limit equilibrium method, which could be considered as the pioneering work in this area. In this analysis, in contrast with the available theories for an isolated rough footing, a partial non-plastic trapped wedge was considered below the footing base. In order to examine the effect of interference, the zone below the two interfering rough footings was assumed to comprise of partly a small non-plastic wedge and partly a plastic shear zone. The shape of failure surface was chosen as a combination of logarithmic spiral and straight line in this approach. Later, by using the failure mechanism similar to that earlier used by Stuart [1], West and Stuart [2] employed the method of stress characteristics so as to obtain the solution for the interference of two strip footings. The values of the efficiency factors obtained by West and Stuart [2], on the basis of method of characteristics for φ = 350 , were shown to be smaller than those obtained earlier by Stuart [1] by using the limit equilibrium method; where φ is the angle of internal friction of soil and the efficiency factor is defined by the ratio of load carried by the single footing in presence of the other footing to that of the single isolated footing of same size. Murthy [3] studied the interference effect of surface footings on sand, but both the footings were not loaded simultaneously, i.e. one of the two footings was first loaded to its safe bearing capacity and the load on the other adjacent footing was then increased up to the ultimate load. Later on, in order to study the effect of the interference of two closely spaced footings on unreinforced soil, a number of investigations were conducted by various researchers ([4], [5], [6], [7], [8], [9]). However, from the available theoretical and experimental studies, it is now understood that the magnitude of ultimate bearing capacity as well as settlement of foundation generally increases at close spacing on account of the interference of other footing. Therefore, the importance of study on the reduction of settlement of interfering footings by reinforcing the soil bed cannot be ignored as it mainly governs the behaviour of interfering footings. Khing et al. [10] and Al-Ashou et al. [11] studied experimentally the effect of interference on the bearing capacity of closely spaced footings resting on reinforced sand bed. The study of pressure, settlement and tilt characteristics of closely spaced footings on reinforced soil bed was studied by Kumar and Saran [12]. Kumar and Saran [13] also presented an analytical method to determine the pressure corresponding to a given settlement for closely spaced strip footings on reinforced sand. In present investigation, the experimental study on the effect of interference between two adjacent surface strip footings was carried out by conducting a number of laboratory scaled model tests on dry, medium dense, reinforced Ennore sand bed. Ennore sand is widely available in the southern part of India. Therefore, the study of interference of footings on Ennore sand was found to be significant. The model strip footings are made of mild steel, which were expected to behave like rigid footings and the roughness of base was ensured by gluing sand paper beneath the footings. Single layer of uniaxial geogrid was used for reinforcing the soil. The effect of a range of parameters such as depth of reinforcement layer (D).
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. تعریف مسئله
3. خصوصیات خاک پی و تجهیزات آزمایشگاهی
4. روند آزمایشگاهی
5. نتایج و بحث ها
5.1 پی تکی مجزا
5.1 پی های تحت تداخل
6. مقایسه
7. نتیجه گیری
منابع
Abstract
1 Introduction
2 Definition of the Problem
3 Properties of Foundation Soil and Experimental Set-up
4 Experimental Procedure
5 Results and Discussions
5.1 Single Isolated Footing
5.1 Footings under Interference
6 Comparison
7 Conclusion
References
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه