دانلود مقاله نانوکامپوزیت های رسانا مبتنی بر پلیمر با غلظت بالای نانوصفحات گرافن
چکیده
در سال های اخیر چگالی توان ابزارهای الکترونیکی به تدریج افزایش پیدا کرده است، از این رو نیاز ضروری برای سیستم های رسانای الکتریکی کارامد بیشتر شده است. از یک منظر، یک استراتژی امیدوار کننده برای افزایش رسانایی الکتریکی کامپوزیت های پلیمری، ساخت و ایجاد شبکه های بهم پیوسته سه بعدی از نانو صفحات گرافن است. به سبب تنوع تجاری نانوصفحات گرافن، برخی پژوهشگران نیاز به غلظت های بیشتر از این نانوصفحات را گزارش کرده اند. هدف از این پژوهش توسعه نانوکامپوزیت هایی با قابلیت رسانایی الکتریکی مبتنی بر غلظت های بالا نانوصفحات گرافن(به عنوان مثال 12.5 و 25 درصد وزنی) و پلیمرهای متداول(به عنوان مثال پلی استایرن(PS) و آکریلونیتریل بوتادین استایرن(ABS)) است. علاوه بر این، اثرات غلظت های بالا نانوصفحات گرافن بر روی خصوصیات مکانیکی، رئولوژیکی و مورفولوژیکی نانوکامپوزیت ها بررسی شده است. نتایج نشان دادند که نانوصفحات گرافن به طور مستقیم در ویسکوزیته مختلط و همچنین در خصوصیات مکانیکی-دینامیکی ماتریس های پلیمری اثرگذار هستند. با افزودن نانوصفحات گرافن، افزایش قابل توجهی در رسانایی الکتریکی حجمی هر دو ماتریس پلیمری ذکر شده مشاهده و اثبات شد. با وجود این که ماتریس های پلیمری به عنوان مواد عایق عمل می کنند، نانوکامپوزیت هایی که شامل 25 درصد وزنی از نانوصفحات گرافن باشند برای هر دو ماتریس پلیمری(PS و ABS) به عنوان نیمه رسانا عمل می کنند. با این حال، خصوصیات مکانیکی مقاومت کششی و مقاومت ضربه، به دلیل افزایش سفتی نانوکامپوزیت ها به شدت کاهش پیدا می کند. این نتایج حاکی از قابلیت بالقوه استفاده از نانوکامپوزیت ها با میزان بالایی از نانوصفحات گرافن، احتمالا به عنوان جایگزینی برای مواد نیمه رسانای متداول در صنعت الکترونیک است، البته به شرط این که خصوصیات مکانیکی مورد نیاز عملکرد پایینی داشته باشند.
مقدمه
همراه با توسعه تکنولوژی های 5G، داده های عظیم، هوش مصنوعی و غیره، چگالی توان ابزارهای الکترونیکی نیز به صورت تدریجی افزایش پیدا کرده است، به همین دلیل تقاضا برای سیستم های کارامد با رسانایی الکتریکی و حرارتی مطلوب، به منظور اطمینان حاصل کردن از بازدهی، انعطاف پذیری، ایمنی، دوام، و پایداری بیشتر شده است[1, 2]. در همین راستا ، پژوهش های اخیر به استفاده از یون های فلزی به عنوان مواد پیشنهادی به منظور بهبود عملکرد ابرخازن ها و باتری ها تاکید دارند[3–5].
در عین حال، جست و جو برای مواد غیرفلزی که رسانایی الکتریکی مطلوبی داشته نیز برای کاربردهای متفاوت لازم و ضروری است[6]. در این سناریو، پلیمرها به جهت خصوصیات منحصر به فرد خود مانند وزن کم، قیمت پایین، انعطاف پذیری بالا، و فرایندپذیری عالی توجه زیادی را به خود جلب کرده اند[2]. با این حال، پلیمرهای متداول عموماً به عنوان مواد عایق در نظر گرفته می شوند، زیرا که مواد پلیمری به دلیل تعداد کم ذرات زیر اتمی، مقاومتی در برابر جریان الکترونی ایجاد کرده و انتقال جریان الکتریکی را سخت و دشوار می کنند.
نتیجه گیری
روش های اولیه تولید کامپوزیت های گرافن/پلیمر بر پایه اختلاط فیزیکی ساده غلظت های کم گرافن با پلیمر است. انتظار می رود که یک کامپوزیت رسانای گرافن/پلیمر در میزان گرافن کمتر، رسانایی الکتریکی بالاتری داشته باشد. با این وجود به دلیل خواص متمایز نانو صفحات گرافن، در مقایسه با گرافن، نیاز به افزودن غلظت های بالاتری از این پرکننده نانو است. از این رو، در این کار تحقیقاتی، نانوکامپوزیتها از ماتریسهای پلیمری مختلف (PS و ABS) و غلظتهای بالای نانو صفحات گرافن تولید شدند. بر اساس نتایج DMA، مشاهده شده است که، برای هر دو ماتریس پلیمری، افزودن نانو صفحات گرافن سبب افزایش تدریجی مدول ذخیره، مدول اتلاف و مقادیر Tg مرتبط با تشکیل پیوند در زنجیره پلیمری ماتریس شده، و کامپوزیت های سخت تری را تشکیل داد. خوشبختانه، بهبود و افزایش در رسانایی الکتریکی حجمی برای نانوکامپوزیت حاوی 25 درصد وزنی NPG، برای هر دو ماتریس پلیمری(PS و ABS) حاصل شد. افزایش چشمگیر برابر 10 مرتبه بزرگی در رسانایی الکتریکی حجمی مشاهده شد که در آن رسانایی الکتریکی حجمی از 10-14 S/m برای پلیمر خالص به 10-4 S/m برای نانوکامپوزیت حاوی 25 درصد وزنی NPG افزایش یافت. بنابراین، صحت تئوری انتقال ناگهانی مواد عایق به مواد نیمه رسانا تایید شد. نتایج ارائه شده حاکی از کاربردهای بالقوه نانوکامپوزیتهای توسعه یافته است، به این دلیل که نانوکامپوزیت ها عملکرد الکتریکی مناسبی از خود نشان داده (به عنوان مثال، رفتار نیمه رسانا) و این مسئله این مواد را تبدیل به یک گزینه امیدوارکننده در کاربردهای الکترونیکی آینده می کند. با این وجود، شایان ذکر است که افزودن غلظت های بالای NPG در ماتریس های پلیمری خصوصیات مکانیکی آن ها را کاهش داده، و کاربرد آن ها را در سیستم های مورد نیاز به عملکرد مکانیکی بالا محدود می کند.
Abstract
The power density of electronic devices has been progressively increased in the last years, thus raising the urgent demand for the efcient systems of electrical conductivity. In a sense a promising strategy to increase the electrical conductivity of polymer composites is to construct interconnected three-dimensional graphene nanoplatelets networks. Due to the variety commercialized graphene nanoplatelets, some researchers have reported the need to incorporate higher concentrations. This research aims to develop nanocomposites with electrical conductivity potential, based on high concentrations of graphene nanoplatelets (i.e., 12.5 and 25 wt%) and conventional polymers (i.e., polystyrene (PS) and acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS)). Moreover, it will investigate the efects of the high concentrations of graphene nanoplatelets on the mechanical, rheological and morphological properties of the nanocomposites. The results showed that the graphene nanoplatelets directly interfere in the complex viscosity and in the dynamic–mechanical properties of the polymers matrices. A signifcant increase in volume electrical conductivity was verifed in both polymeric matrices when graphene nanoplatelets were added. While polymeric matrices acted as insulating materials, the nanocomposites containing 25 wt% of graphene nanoplatelets acted as semiconductors, for both matrices (PS and ABS). However, the mechanical properties of the tensile strength and impact were strongly reduced, due to the increased stifness of the nanocomposites. These results indicated a potential application of these nanocomposites with high contents of graphene nanoplatelets in the electronics feld, possibly as an alternative to conventional semiconductor materials, provided that the required mechanical properties are of low performance.
Introduction
Along with the technological development in 5G, big data, artifcial intelligence, etc., the power density of electronic devices has been progressively increased, thus raising the urgent demand for efcient systems with electrical and thermal conductivity to ensure the efciency, reliability, safety, durability, and stability [1, 2]. In this sense, recent research works emphasized the use of metallic ions as candidate materials to improve the performance of supercapacitors and batteries. [3–5].
At the same time, searching for non-metallic materials that conduct electricity well has become essential for diferent applications [6]. In this scenario, polymers have attracted great attentions owing to their impressive properties, such as light weight, low cost, high fexibility and excellent processibility [2]. Although, traditional polymers are generally considered insulating materials, since they promote resistance to the fow of electrons because of the low number of subatomic particles, making electrical charges difcult to transit.
Conclusions
The primary methods for preparing graphene/polymer composites is based on simple physical mixing of very low concentration of graphene with polymer. An outstanding electrically conductive graphene/polymer composite is expected to have higher electrical conductivity at a lower graphene loading. However, due to the distinct properties of the graphene nanoplatelets, when compared to graphene, it is necessary to add higher concentrations of this nanofller. Wherefore, in this research work, nanocomposites were produced from diferent polymer matrices (PS and ABS) and high concentrations of graphene nanoplatelets. By DMA results, it was observed that, for both polymer matrices, the addition of graphene nanoplatelets gradually increased the storage modulus, loss modulus and Tg values associated with the formation of cross-links in the polymeric chain of the matrices, forming stifer composites. Due to the addition of NPGs, the complex viscosity decreased in the PS nanocomposites, due to the lubricating efect of the graphene nanoplatelets. On the other hand, in the ABS nanocomposites, the complex viscosity increased, probably due to the molecular confguration of ABS, the lateral presence of acrylonitrile and longer chains, hindering the fow of graphene sheets between the polymer chains. The mechanical properties of tensile strength and impact strength were strongly reduced with the addition of NPGs, due to the increased stifness of the nanocomposites. Fortunately, an expressive enhancement in volume electrical conductivity was obtained for the nanocomposites with 25 wt% of NPG, for both matrices (PS and ABS). It was found a surprising increase up to 10 orders of magnitude, increasing from 10–14 S/m for pure polymer matrices to 10–4 S/m for nanocomposites containing 25 wt% NPG. Therefore, the sharp transition from insulating materials to semiconducting materials was confrmed. The results presented shed light on the potential applications of the developed nanocomposites, since they exhibited good electrical performance (i.e., semiconductor behavior) becoming a promising candidate in future electronics applications. However, it is worth mentioning that the addition of high concentrations of NPG in these polymeric matrices decreased their mechanical properties, limiting their applications in systems with high mechanical performance.
چکیده
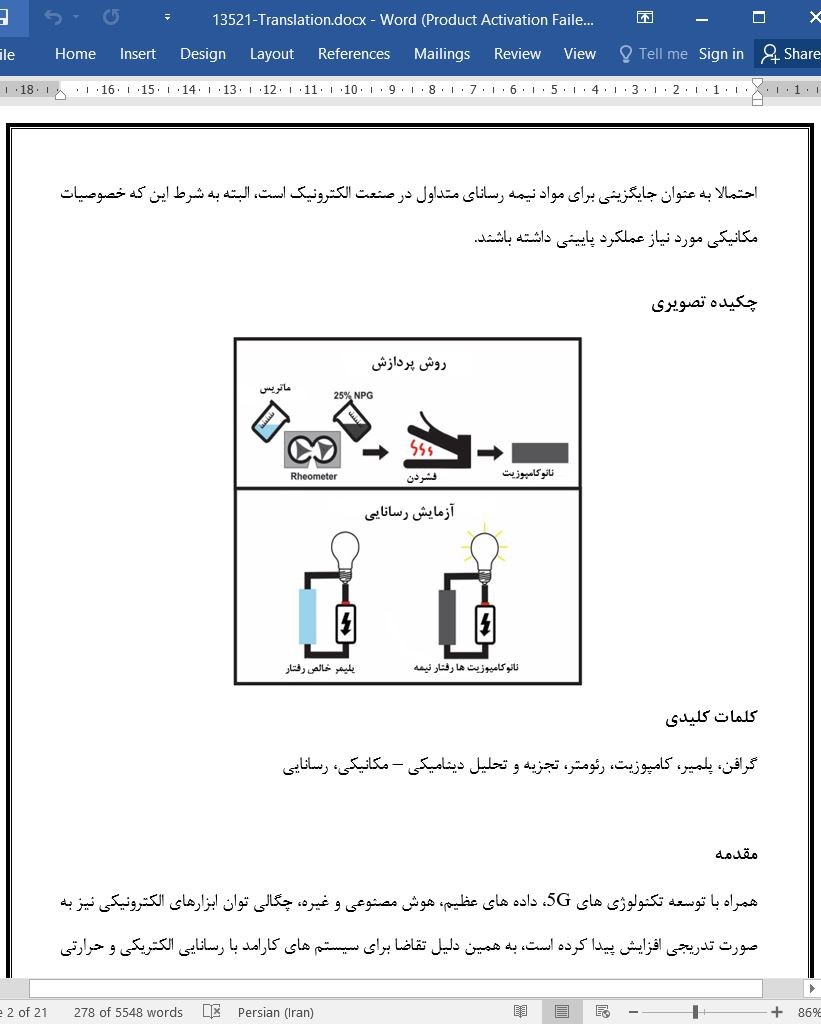
چکیده تصویری
مقدمه
تجربی
مواد
روش ها
تعیین مشخصات
نتایج و بحث
نتیجه گیری
منابع
Abstract
Introduction
Experimental
Materials
Methods
Characterization
Results and discussion
Conclusions
References
این محصول شامل پاورپوینت ترجمه نیز می باشد که پس از خرید قابل دانلود می باشد. پاورپوینت این مقاله حاوی 22 اسلاید و 4 فصل است. در صورت نیاز به ارائه مقاله در کنفرانس یا سمینار می توان از این فایل پاورپوینت استفاده کرد.
در این محصول، به همراه ترجمه کامل متن، یک فایل ورد ترجمه خلاصه نیز ارائه شده است. متن فارسی این مقاله در 9 صفحه (1600 کلمه) خلاصه شده و در داخل بسته قرار گرفته است.
علاوه بر ترجمه مقاله، یک فایل ورد نیز به این محصول اضافه شده است که در آن متن به صورت یک پاراگراف انگلیسی و یک پاراگراف فارسی درج شده است که باعث می شود به راحتی قادر به تشخیص ترجمه هر بخش از مقاله و مطالعه آن باشید. این فایل برای یادگیری و مطالعه همزمان متن انگلیسی و فارسی بسیار مفید می باشد.
بخش مهم دیگری از این محصول لغت نامه یا اصطلاحات تخصصی می باشد که در آن تعداد 40 عبارت و اصطلاح تخصصی استفاده شده در این مقاله در یک فایل اکسل جمع آوری شده است. در این فایل اصطلاحات انگلیسی (تک کلمه ای یا چند کلمه ای) در یک ستون و ترجمه آنها در ستون دیگر درج شده است که در صورت نیاز می توان به راحتی از این عبارات استفاده کرد.
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش و pdf بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- پاورپوینت فارسی با فرمت pptx
- خلاصه فارسی با فرمت ورد (word)
- متن پاراگراف به پاراگراف انگلیسی و فارسی با فرمت ورد (word)
- اصطلاحات تخصصی با فرمت اکسل