دانلود مقاله پیش بینی روند آتش سوزی در جنگل کاج سیاه با کمک هوش مصنوعی (پاین نیگرا آرنولد)
چکیده
مدلسازی روند آتشسوزی جنگل برای کنترل مؤثر آتشسوزیهای جنگلی و انجام اقدامات احتیاطی لازم پیش از شروع آتش سوزی امری بسیار مهم است. با این حال، مطالعات روند آتشسوزی در جنگل، مطالعات پیچیده ای است که به بسیاری از متغیرها وابسته بوده و معمولا شامل مجموعه داده های بزرگی میباش. به همین دلیل، قدرت پیش بینی و سرعت مدلهای کلاسیک در مواردی که دادههای بزرگ و بسیاری از متغیرها را شامل میشوند، پایینتر از مدلهای هوش مصنوعی هستند. علاوه بر این، مدلهای پیشبینی کلاسیک بر خلاف مدلهای هوش مصنوعی، ملزم به تأمین مفروضات آماری خاصی هستند. در واقع در این مطالعه، پیشبینی روند آتشسوزی سطحی، بهویژه میزان گسترش آتش و شدت آتش، در محل آغاز آتش سوزی با استفاده از دو روش هوش مصنوعی شامل مدل شبکه عصبی مصنوعی و مدل درخت تصمیم انجام شد و مدلهای توسعهیافته در این مطالعه از نظر برازش مورد آزمایش و بررسی قرار گرفتند. در نهایت، مدل رگرسیون کلاسیک برای پیشبینی روند آتشسوزی سطحی با دو مدل هوش مصنوعی فوق، مقایسه شد. یافتهها نشان داد که معیارهای دقت مدلهای هوش مصنوعی بهتر از مدل کلاسیک بوده است.
1. مقدمه
جنگل ها از مهم ترین منابع طبیعی در جهان هستند و نقش بسیار مهمی در حفظ تعادل اکولوژیکی و اکوسیستم های جنگلی ایفا می کنند و در واقع بسیاری از امکانات زیست محیطی و اقتصادی را برای زندگی انسان فراهم میآورد. آتشسوزی جنگلها از مخربترین مخاطرات برای طبیعت قلمداد میشوند که در واقع این امکانات فراهم شده توسط جنگل را مختل میسازند. شرایط شدید هواشناسی موجب افزایش اثرات مخرب آتش سوزی جنگلها میشود. آتش سوزی ها باعث پیچیدگی می شود و اغلب مبارزه با آن بسیار دشوار است. بنابراین، پیش بینی روند آتش سوزی برای مدیریت موفقیت آمیز، برنامه ریزی موثر منابع برای مبارزه با آنها و کاهش خسارات امری ضروری است (میتسوپولوزو همگاران 2017، یاوز و همکاران 2018، ; سوینک و همکاران 2020; ابید 2021). مدل های رگرسیون کلاسیک متعددی برای پیشبینی رفتار آتشسوزی جنگل ارائه شده است (فریر و جانسون، 1988; الکساندر و کروز 2006; سالیوان 2007; یاسمی و همکاران 2008; فرناندس، 2009; متیوز و همکاران 2012; کوچوک و همکاران 2012; کروز و همکاران 2017; کوچوک و همکاران 2018; بیلگیلی و همکاران 2019; الحاج خلف و همکاران 2021; کروز و همکاران 2022). مدل های دیگر آتش سوزی جنگل ها بر اساس روش یادگیری ماشینی شبکه های عصبی مصنوعی (فام و همکاران 2020) ویژگیهای آتش و گسترش آن را بررسی و معین میکنند (چتهونا و همکاران 2015).
تشخیص و نقشه برداری آتش، آب و هوای منطقه در زمان آتشسوزی و تغییرات آب و هوایی (Li و همکاران 2009; سن میگوئل آینز و همکاران. 2012)، احتمال آتش سوزی و خطر آن، ارزیابی خطر آتشسوزی، و پیش بینی رفتار آتش سوزی، در سال های اخیر، به دلیل پیشرفت در علوم آتش نشانی، دیجیتال و اطلاعات آماری، فناوری های سنجش از دور، از جمله GIS، و بحران رو به رشد اقلیمی اخیر، بسیار مورد توجه بودهاند (وکالیس و همکاران 2004؛ فینی و همکاران 2011; آریکاک و همکاران 2014; رودریگز و ریوا، 2014; پریسلر و همکاران 2014; گلداراگ و همکاران 2016; لری و همکاران 2016; هولینگ و همکاران، 2016; ژانگ و همکاران 2018; سیوریکایا و کوچوک، 2022). روش های احتمالی نظیر رگرسیون لجستیک، شبکه های عصبی، و رگرسیون منطق فازی در مطالعات آتش سوزی جنگل کاربرد گستردهای دارند (جعفری و همکاران 2019). مدل های سنتی برای پیش بینی خطر آتش سوزی و روند آن شامل مدل های خطی تعمیم یافته برمبنای توزیع لجستیک، پواسون و دوجمله ای منفی شکل گرفتهاند. با این حال، این مدل ها در پردازش حجم بزرگ داده های چند بعدی ناتوان هستند. محققین بر این باورند که روشهای آماری مبتنی بر هوش مصنوعی بهتر از روشهای سنتی در حل مسائل مرتبط با داده های کلان در مدل سازی آتش سوزی های جنگلی عمل میکنند. علاوه بر این، مدل های آماری سنتی بر خلاف هوش مصنوعی، فرضیات آماری خاصی را مورد بررسی قرار میدهند.
4. نتیجه گیری
در این مطالعه، پیشبینی روند آتشسوزی سطحی جنگلها بر اساس سرعت گسترش آتش و شدت آتش با استفاده از دو روش هوش مصنوعی شامل، یک شبکه عصبی مصنوعی و یک مدل درخت تصمیم صورت پذیرفت. علاوه بر این، عملکرد پیشبینی این دو روش با عملکرد مدل رگرسیون معمولی مقایسه شد. نتایج نشان داد که مدل شبکه عصبی مصنوعی در پیش بینی شدت آتش و سرعت گسترش آتش بهتر از دو مدل دیگر عمل کرد. مدل درخت تصمیم نیز عملکرد بسیار موفق تری نسبت به مدل رگرسیون در پیش بینی شدت آتش سوزی داشت. با این حال در خصوص پیش بینی میزان گسترش آتش، عملکرد مدل رگرسیون کمی بهتر از مدل درخت تصمیم بود. به طور کلی، شبکه عصبی مصنوعی قدرتمندترین مدل در پیش بینی شدت و سرعت گسترش آتش بود. در نتیجه میتوان گفت که مدلهای هوشی را می توان با موفقیت در پیش بینی روند آتش به کار بست. برای گسترش این مطالعه، سایر مطالعات پیشبینی شدت آتش و سرعت گسترش آتش را میتوان با سایر روشهای هوش مصنوعی و استفاده از متغیرهای اضافی یا متفاوت انجام داد. همچنین این مطالعه را میتوان در خصوص بررسی جنگلهای کاج برونیا در منطقۀ مدیترانه نیز انجام داد.
Abstract
Modeling forest fire behavior is very important for the effective control of forest fires and the setting up of necessary precautions before fires start. However, studies of forest fire behavior are complex studies that depend on many variables and usually involve large data sets. For this reason, the predictive power and speed of classical forecasting models are lower than of artificial intelligence models in cases involving big data and many variables. Moreover, classical forecasting models must satisfy certain statistical assumptions, unlike artificial intelligence methods. Thus, in this study, predictions were made of surface fire behavior, especially the rate of fire spread and the fire intensity, at the location at which fires started using two artificial intelligence methods, an artificial neural network and a decision tree. The accuracy of the developed models was fitted and tested. Finally, the classical regression model for predicting surface fire behavior was compared with the two artificial intelligence methods. The accuracy measures of the artificial intelligence models were found to be better than those of the classical model.
Forests are some of the most important natural resources in the world and play a key role in maintaining ecological balance, and forest ecosystems provide many ecological and economic services for human life. Forest fires are considered some of the most detrimental events that interrupt these services. Extreme meteorological conditions greatly increase the destructive effects of forest fires. The fires have complicated causes and are often very difficult to fight. Therefore, the prediction of fire behavior is essential for the successful management of fires, the effective planning of resources for fighting them, and the mitigation of the damage they cause (Mitsopoulos et al. 2017; Yavuz et al. 2018; Sevinc et al. 2020; Abid 2021). Various classical regression models have been developed to predict forest fire behavior (Fryer and Johnson 1988; Alexander and Cruz 2006; Sullivan 2007; Yassemi et al. 2008; Fernandes 2009; Matthews et al. 2012; Kucuk et al. 2012; Cruz et al. 2017; Kucuk et al. 2018; Bilgili et al. 2019; Alhaj-Khalaf et al. 2021; Cruz et al. 2022). Other models of forest fires based on the machine learning method of artificial neural networks (Pham et al. 2020) have predicted flame characteristics and fire spread (Chetehouna et al. 2015).
Fire detection and mapping, fire weather and climate change (Li et al. 2009; San-Miguel-Ayanz et al. 2012), fire probability and risk, fire hazard assessment, and fire behavior prediction have become very popular in recent years, driven by advances in fire sciences, digital and statistical information, the remote sensing technologies, including GIS, and the growing climate crisis (Vakalis et al 2004; Finney et al. 2011; Aricak et al. 2014; Rodrigues and Riva, 2014; Preisler et al. 2014; Goldarag et al. 2016; Lary et al. 2016; Huiling at al. 2016; Zhang et al 2018; Sivrikaya and Küçük, 2022). Probabilistic methods such as logistic regression, neural networks, and fuzzy logic regression are commonly used for forest fire studies (Jaafari et al. 2019). Traditional models for predicting fire risk and behavior include generalized linear models based on logistic, Poisson, and negative binomial distributions. However, these models cannot process multidimensional big data. Researchers have stated that artificial intelligence outperforms traditional statistical methods in solving the big data problem encountered in modeling forest fires. In addition, traditional statistical models must satisfy certain statistical assumptions, unlike artificial intelligence methods.
4. Conclusions
In this study, predictions were made of the surface forest fire behavior based on the rate of fire spread and the fire intensity using two artificial intelligence methods, an artificial neural network and a decision tree. Additionally, the prediction performances of the two methods were compared with the performance of the conventional regression model. The artificial neural network performed better than the other models in predicting both the fire intensity and the fire spread rate. The decision tree model had a considerably more successful performance than the regression model in predicting the fire intensity. However, when it came to predicting the fire spread, the regression model performed slightly better than the decision tree model. Overall, the artificial neural network was the most powerful model in predicting the fire intensity and the fire spread rate, and this demonstrated that artificial intelligence models can be used quite successfully in predicting fire behavior. To expand on this study, other studies of the prediction of the fire intensity and fire spread rate can be performed with other artificial intelligence methods and using additional or different variables. This method can also be used for Pinus brutia in Mediterranean region.
Wind speed
Rate of fire spread
Total fuel load
Air temperature
Ignition of fire line length
Needle moisture content
Fine fuel moisture content
Relative humidity
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. روش تحقیق
1-2 مکان تحقیق
2.2. اندازه گیری قبل از آتش سوزی های آزمایشی
2.3. آتش سوزیهای آزمایشی و داده ها
2.4. مدل های شبکه عصبی مصنوعی
2.4.1. مدل های شبکه عصبی دریافت چند لایه
5-2 مدلهای درخت تصمیمگیری
2.6. برازش مدل و مقایسه مدلهای روند آتش سوزی
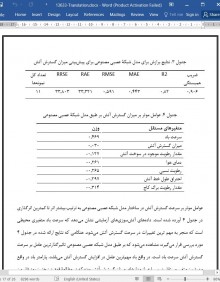
3. نتایج و بحث
3.1. توسعه یک مدل شبکه عصبی مصنوعی برای پیش بینی شدت آتش
3.2. توسعه مدل شبکه عصبی مصنوعی برای پیشبینی میزان گسترش آتش
3.3. توسعه یک مدل درخت تصمیم برای پیشبینی شدت آتش
3.4. توسعۀ مدل درخت تصمیم برای پیشبینی میزان گسترش آتش
4. نتیجه گیری
منابع
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study area
2.2. Measurements before the experimental fires
2.3. Experimental fires and data
2.4. Artificial neural network models
2.4.1. Multilayer perceptron neural network models
2.5. Decision tree models
2.6. Model fit and comparison of fire behavior models
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Development of an artificial neural network model for predicting fire intensity
3.2. Development of an artificial neural network model for predicting the fire spread rate
3.3. Development of a decision tree model for predicting fire intensity
3.4. Development of a decision tree model for predicting the fire spread rate
4. Conclusions
References
این محصول شامل پاورپوینت ترجمه نیز می باشد که پس از خرید قابل دانلود می باشد. پاورپوینت این مقاله حاوی 18 اسلاید و 4 فصل است. در صورت نیاز به ارائه مقاله در کنفرانس یا سمینار می توان از این فایل پاورپوینت استفاده کرد. ش
در این محصول، به همراه ترجمه کامل متن، یک فایل ورد ترجمه خلاصه نیز ارائه شده است. متن فارسی این مقاله در 7 صفحه (1800 کلمه) خلاصه شده و در داخل بسته قرار گرفته است.
علاوه بر ترجمه مقاله، یک فایل ورد نیز به این محصول اضافه شده است که در آن متن به صورت یک پاراگراف انگلیسی و یک پاراگراف فارسی درج شده است که باعث می شود به راحتی قادر به تشخیص ترجمه هر بخش از مقاله و مطالعه آن باشید. این فایل برای یادگیری و مطالعه همزمان متن انگلیسی و فارسی بسیار مفید می باشد.
بخش مهم دیگری از این محصول لغت نامه یا اصطلاحات تخصصی می باشد که در آن تعداد 50 عبارت و اصطلاح تخصصی استفاده شده در این مقاله در یک فایل اکسل جمع آوری شده است. در این فایل اصطلاحات انگلیسی (تک کلمه ای یا چند کلمه ای) در یک ستون و ترجمه آنها در ستون دیگر درج شده است که در صورت نیاز می توان به راحتی از این عبارات استفاده کرد.
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش و pdf بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- پاورپوینت فارسی با فرمت pptx
- خلاصه فارسی با فرمت ورد (word)
- متن پاراگراف به پاراگراف انگلیسی و فارسی با فرمت ورد (word)
- اصطلاحات تخصصی با فرمت اکسل