دانلود مقاله بررسی محرک های نوآوری بازاریابی در شرکت های کوچک و متوسط (SMEs)
چکیده
نوآوری بازاریابی نشان دهنده مسیری برای کسب مشروعیت، استمرار و رشد برای SME هایی است که معمولاً تحت محدودیت منابع در محیط های نامطمئن و رقابتی فعالیت می کنند. با این حال، درک ما از عوامل سازمانی نوآوری بازاریابی توسط SMEها محدود است. ادبیات را با استفاده از مجموعه داده های طولی (5 ساله) که از اداره ملی آمار استرالیا(ABS) به دست آوردیم، و ارائه تصویری جامع از عوامل سازمانی که بر شانس نوآوری بازاریابی SMEها تأثیر می گذارند، پیش می بریم. به طور کلی تحلیل رگرسیون لجستیک انجام شده بر 4378 مشاهدات شرکت-سال، چارچوب نظری ما را تایید می کند و نشان می دهد که چگونه نوآوری بازاریابی SME ها از عوامل سازمانی، منابع، نوآوری و سنجش عملکرد نشات می گیرد. یافتههای ما مسیر روشنی بین شیوههای سازمانی و شیوههای بازاریابی نوآورانه برای مدیران شرکت های کوچک و متوسط فراهم می کند.
1. مقدمه
اهمیت نوآوری بازاریابی را نمی توان دست کم گرفت. نوآوری در بازاریابی نشان دهنده منبعی از تمایز و رشد رقابتی برای اکثر شرکت ها، به ویژه برای شرکت های کوچک و متوسط(SMEs) است. بر خلاف سازمانهای بزرگتر که مدلهای کسبوکار آنها تثبیت شده است، SMEها معمولاً با مسئولیت نوبودگی، کوچک بودن و مبارزه برای مشروعیت محدود میشوند (ایگرز، 2020؛ کراوس و همکاران، 2007). علاوه بر این، شرکتهای کوچک و متوسط معمولاً در محیطهای بسیار رقابتی و با محدودیت منابع فعالیت میکنند (کلاس و همکاران، 2022). در چنین شرایطی، نوآوری بازاریابی در شرکتهای کوچک و متوسط مکانیسمی حیاتی برای بقا و کسب مزیت رقابتی می باشد(کراسکو-کارواجال و همکاران، 2022؛ هاک- دپاگن و همکاران، 2021؛ نایدو، 2020؛ او دایر و همکاران، 2009).
علیرغم اهمیت نوآوری بازاریابی، متخصصان معمولا درک درستی از پیشایندها و پیامدهای نوآوری بازاریابی ندارند(پرچیس و والری، 2020). با تمرکز بر عوامل تعیین کننده سازمانی نوآوری بازاریابی SME به این شکاف دانش می پردازیم. بر اساس ویژگیهای منحصربهفرد SMEها، یک چارچوب نظری پیشنهاد می دهیم که برگرفته از تئوری نهادی، نظریه وابستگی به منابع، نوآوری محصول/خدمات و ادبیات سنجش عملکرد استراتژیک است. چارچوب خود را بر اساس دادههای طولی (5 ساله) بهدستآمده از اداره ملی آمار استرالیا(ABS) (شامل 4378 مشاهدات سال- شرکت) می آزماییم. با استفاده از تحلیل رگرسیون لجستیک، از این پیشنهاد خود پشتیبانی می کنیم که نوآوری بازاریابی SME از فشارهای سازمانی، وابستگی به منابع، نوآوری محصول/خدمات و الزامات سنجش(اندازه گیری) عملکرد نشات می گیرد.
مطالعه حاضر با توجه به دیدگاه جامع ما در مورد نوآوری بازاریابی SME، کمک های قابل توجهی به ادبیات نوآوری بازاریابی SME می کند. اگرچه ادبیات عوامل تعیین کننده خاص نوآوری بازاریابی را تشریح می کند، مطالعات نسبتا کمی به طور همزمان به بررسی مجموعه جامعی از محرک های نوآوری بازاریابی در سطح سازمان پرداخته اند. نشان میدهیم که محرکهای نوآوری بازاریابی میتوانند از عوامل سازمانی متعددی نشات گیرند. به طور نظری، حیطه پیشایندهای نوآوری بازاریابی SME را گسترش می دهیم. به طور عملی، نتایج ما مدیران SME را قادر می سازد تا عوامل نوآوری بازاریابی را صریحا مشخص کنند که شفافیت و تمرکز بر برنامهریزی آتی و تعیین هدف را امکان پذیر می سازد.
6. بحث و کاربردها
پیتر دراکر، استاد مدیریت معتقد است که علت وجودی هر کسب و کاری ایجاد مشتری است و در نتیجه دو اصل اساسی هر کسب و کاری، بازاریابی و نوآوری است (وبستر، 2009). تمرکز ما بر فصل مشترک بازاریابی و نوآوری است؛ حوزه ای که در حال رشد است (هنسلر و همکاران، 2021). مطالعه حاضر، تلاشی اکتشافی برای درک عوامل تعیینکننده نوآوری بازاریابی توسط SME های استرالیایی است(بررسی نتایج نوآوری بازاریابی فراتر از محدوده تحقیق حاضر است).
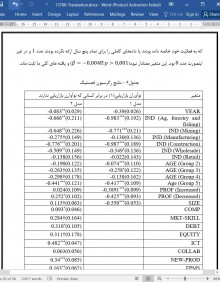
میزان رقابت به طور قابلتوجهی نوآوری بازاریابی را در مطالعه حاضر پیشبینی میکند، اگرچه این اثر کوچک به نظر میرسد. با این وجود، این نتیجه حاکی از آن است که فشارهای رقابتی (تقلیدی) احتمال اتخاذ نوآوری های بازاریابی را افزایش می دهد. این نتیجه با منطق "ترس از دست دادن" مطابقت دارد که به موجب آن SME ها از عقب افتادن از تلاش های بازاریابی رقبای خود می ترسند. یک مفهوم نظری این یافته این است که نوآوری بازاریابی SME می تواند جهت گیری واکنشی داشته باشد، که مکمل دیدگاه اودایر و همکاران (2009) است که بازاریابی SME می تواند فعال یا واکنشی باشد.
Abstract
Marketing innovation represents a pathway for achieving legitimacy, viability, and growth for SMEs that typically operate with resource constraints in uncertain and competitive environments. However, our understanding of the organizational determinants of marketing innovation by SMEs is limited. We advance the literature by drawing on a longitudinal (5-year) data set obtained through an Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS) national-level panel and offering a comprehensive picture of the organizational determinants that affect the likelihood of marketing innovation by SMEs. Logistic regression analysis conducted on 4378 firm-year observations generally supports our theoretical framework and reveals how marketing innovation by SMEs is driven by institutional, resource, innovation, and performance measurement factors. Our findings offer SME managers a clear line of sight between organization-wide practices and innovative marketing practices.
1. Introduction
The importance of marketing innovation cannot be underestimated. Innovation in marketing represents a source of competitive differentiation and growth for most firms, particularly for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Unlike larger organizations that have established business models, SMEs are typically constrained by liabilities of smallness and newness, and a struggle for legitimacy (Eggers, 2020; Kraus et al., 2007). Moreover, SMEs typically operate in highly competitive and resource constrained environments (Clauss et al., 2022). Under such circumstances, marketing innovation at SMEs represents a crucial mechanism for survival and gaining a competitive advantage (CarrascoCarvajal et al., 2022; Hock-Doepgen et al., 2021; Naidoo, 2010; O’Dwyer et al., 2009).
Despite the importance of marketing innovation, practitioners generally lack an understanding of the antecedents and consequences of marketing innovation (Purchase & Volery, 2020). We address this knowledge gap by focusing on the organizational determinants of SME marketing innovation. Based on the unique characteristics of SMEs, we advance a theoretical framework that draws across the institutional theory, resource dependence theory, product/service innovation and, strategic performance measurement literatures. We test our framework on longitudinal (5-year) data obtained through the Australian Bureau of Statistics’ (ABS) national-level panel of SMEs (comprising 4378 firmyear observations). Using logistic regression analysis, we find support for our position that SME marketing innovation is driven by institutional pressures, resource dependencies, product/service innovation, and performance measurement requirements.
The present study offers significant contributions to the SME marketing innovation literature given our holistic perspective on SME marketing innovation. Although the literature outlines specific determinants of marketing innovation, relatively few studies simultaneously examine a comprehensive set of organization-wide drivers of marketing innovation. We demonstrate that the triggers of marketing innovation can arise from numerous organizational factors. Theoretically, we broaden the scope of the antecedents of SME marketing innovation. From a practical standpoint, our results enable SME managers to clearly visualize the catalysts of marketing innovation, permitting clarity and focus for future planning and goal setting.
6. Discussion and implications
Management guru Peter Drucker believes that the raison d’ˆetre of any business is to create a customer and thus the two fundamental functions of any business are marketing and innovation (Webster, 2009). We focus on the intersection of marketing and innovation; a domain that is growing (Henseler et al., 2021). The current study is an exploratory attempt to understand the determinants of marketing innovation by Australian SMEs (examining the outcomes of marketing innovation is beyond the scope of the present investigation).
The degree of competition significantly predicts marketing innovation in the present study, though this effect seemed small. Nonetheless, this result implies that competitive (mimetic) pressures seem to enhance the likelihood of adopting marketing innovations. This result is consistent with the ‘fear of missing out’ logic whereby SMEs fear falling behind their competitors’ marketing efforts. A theoretical implication of this finding is that SME marketing innovation can have a reactionary orientation, which complements O’Dwyer et al.’s (2009) view that SME marketing can be either proactive or reactive.
H1: The degree of competition is positively associated with the likelihood of marketing innovation.
H2: The adoption of marketing skills is positively associated with the likelihood of marketing innovation.
H3a: Debt seeking behavior is positively associated with the likelihood of marketing innovation.
H3b: Equity seeking behavior is positively associated with the likelihood of marketing innovation.
H4: The degree of ICT integration is positively associated with the likelihood of marketing innovation.
H5: Inter-organizational collaboration is positively associated with the likelihood of marketing innovation.
H6: Product or service innovation is positively associated with the likelihood of marketing innovation.
H7a: The use of financial performance measures is positively associated with the likelihood of marketing innovation.
H7b: The use of strategic performance measures is positively associated with the likelihood of marketing innovation.
H1. میزان رقابت با احتمال نوآوری بازاریابی ارتباط مستقیم دارد.
H2. پذیرش مهارت های بازاریابی با احتمال نوآوری بازاریابی ارتباط مستقیم دارد.
H3a. رفتار استقراض طلبی(تامین مالی از طریق استقراض) با احتمال نوآوری بازاریابی ارتباط مستقیم دارد.
H3b. رفتار سهام طلبی(تامین مالی از طریق فروش سهام) با احتمال نوآوری بازاریابی ارتباط مستقیم دارد.
H4 . میزان یکپارچگی ICT با احتمال نوآوری بازاریابی ارتباط مثبت دارد.
H5: همکاری میان سازمانی، ارتباط مثبت با احتمال نوآوری بازاریابی دارد.
H6. نوآوری محصول یا خدمات ارتباط مثبت با احتمال نوآوری بازاریابی دارد.
H7a: استفاده از معیارهای عملکرد مالی با احتمال نوآوری بازاریابی ارتباط مثبت دارد.
H7b: استفاده از معیارهای عملکرد استراتژیک با احتمال نوآوری بازاریابی ارتباط مثبت دارد.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. نوآوری بازاریابی در SMEs و عوامل تعیین کننده آن: مروری بر تحقیقات پیشین
3. چارچوب مفهومی و فرضیه ها
3.1. فشارهای نهادی و نوآوری بازاریابی
3.2. وابستگی به منابع و نوآوری بازاریابی
3.3. نوآوری محصول یا خدمات
3.4. سنجش(اندازه گیری) عملکرد/نظارت
4. طرح تجربی
4.1. جمع آوری داده و نمونه
4.2. اندازه گیری متغیر
4.3. متغیرهای کنترل
4.4. مدل های رگرسیون و استواری
5. تحلیل و نتایج
5.1. آمار توصیفی
5.2. نتایج رگرسیون لجستیک
6. بحث و کاربردها
منابع
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Marketing innovation in SMEs and its determinants: A literature review
3. Conceptual framework and hypotheses
3.1. Institutional pressures and marketing innovation
3.2. Resource dependence and marketing innovation
3.3. Product or service innovation
3.4. Strategic performance measurement/monitoring
4. Empirical design
4.1. Data collection and sample
4.2. Variable measurement
4.3. Control variables
4.4. Regression models and robustness
5. Analysis and results
5.1. Descriptive statistics
5.2. Logistic regression results
6. Discussion and implications
References
این محصول شامل پاورپوینت ترجمه نیز می باشد که پس از خرید قابل دانلود می باشد. پاورپوینت این مقاله حاوی 25 اسلاید و 6 فصل است. در صورت نیاز به ارائه مقاله در کنفرانس یا سمینار می توان از این فایل پاورپوینت استفاده کرد.
در این محصول، به همراه ترجمه کامل متن، یک فایل ورد ترجمه خلاصه نیز ارائه شده است. متن فارسی این مقاله در 10 صفحه (2300 کلمه) خلاصه شده و در داخل بسته قرار گرفته است.
علاوه بر ترجمه مقاله، یک فایل ورد نیز به این محصول اضافه شده است که در آن متن به صورت یک پاراگراف انگلیسی و یک پاراگراف فارسی درج شده است که باعث می شود به راحتی قادر به تشخیص ترجمه هر بخش از مقاله و مطالعه آن باشید. این فایل برای یادگیری و مطالعه همزمان متن انگلیسی و فارسی بسیار مفید می باشد.
بخش مهم دیگری از این محصول لغت نامه یا اصطلاحات تخصصی می باشد که در آن تعداد 55 عبارت و اصطلاح تخصصی استفاده شده در این مقاله در یک فایل اکسل جمع آوری شده است. در این فایل اصطلاحات انگلیسی (تک کلمه ای یا چند کلمه ای) در یک ستون و ترجمه آنها در ستون دیگر درج شده است که در صورت نیاز می توان به راحتی از این عبارات استفاده کرد.
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش و pdf بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- پاورپوینت فارسی با فرمت pptx
- خلاصه فارسی با فرمت ورد (word)
- متن پاراگراف به پاراگراف انگلیسی و فارسی با فرمت ورد (word)
- اصطلاحات تخصصی با فرمت اکسل