دانلود مقاله شیوه های HRM با مشارکت بالا نوآوری تدریجی و بنیادین را ترغیب می کند
چکیده
مطالعهای که به بررسی رابطه بین شیوه HRM با مشارکت بالا و قابلیت نوآوری به گونه ای که توسط به اشتراکگذاری دانش میانجی شود، وجود ندارد. بنابراین، انگیزه این مقاله، مطالعه و بررسی نقشهای میانجی بالقوه به اشتراک گذاری دانش صریح و ضمنی در روابط شیوه HRM با مشارکت بالا و قابلیت نوآوری تحت تعدیلکننده احتمالی آشفتگی بازار است. از تجزیه و تحلیل ساختارهای گشتاوری برای اعتبارسنجی و آزمون مدل ساختاری بر اساس نظرسنجی پرسشنامه ای از 333 شرکت کننده در 119 شرکت تولیدی و خدماتی ویتنامی از ماه می تا جولای 2021 استفاده شد. داده های جمع آوری شده با استفاده از نرم افزار SPSS و AMOS نسخه 22 بررسی و تحلیل شدند. نتیجه، فرضیههای پیشنهادی مربوط به نقش میانجی KS در رابطه شیوههای HRM- نوآوری را تایید می کند. همچنین، ویژگی بسیار مهم آشفتگی بازار را در هدایت تسلط شیوه HRM با مشارکت بالا بر نوآوری تدریجی و بنیادین نشان میدهد. این مقاله به طور قابل ملاحظه ای بینش مربوط به نقش زمینه ساز شیوه HRM با مشارکت بالا، مکانیسم میانجی فعالیت های KM، تأثیر تنظیم کننده آشفتگی بازار در پیش بینی و تقویت نوآوری بنیادین و تدریجی را افزایش می دهد، در نتیجه نظریه HRM و مدیریت نوآوری را مطرح می کند.
1. مقدمه
قابلیت نوآوری به طور گسترده به عنوان یک شایستگی پویا پذیرفته شده است که شرکت ها را قادر می سازد، خدمات و محصولات خود را با هدف برآوردن نیازهای مشتریان تطبیق و تکامل دهند(لی، 2021؛ گای و همکاران، 2022). بنابراین، شرکتها در تلاش هستند تا قابلیت نوآوری خود را بهبود بخشند تا در مقابله با آشفتگیهای خارجی و محیطهایی که ممکن است اثرات منفی بر عملکرد سازمانی داشته باشند، موفق شوند (کائو و همکاران، 2021؛ اده و همکاران، 2022). با این حال، مانعی برای سازمانها در بازارهای در حال توسعه و نوظهور وجود دارد تا به نوآوران واقعی تبدیل شوند تا مقلد، زیرا اکثر این شرکتها، شرکت هایی با اندازه متوسط و کوچک هستند، که دارای محدودیت منابع و سرمایه برای نوآوری موفق هستند(لی و همکاران، 2020؛ گای و همکاران، 2021). چنین وضعیتی محققان و متخصصان را ملزم کرده است تا جهت شناسایی پیشایندهای دقیق تر، مکانیسم جدید و راه حل های بهینه برای بهبود شایستگی نوآوری برای سازمان ها در این کشورها تلاش بیشتری کنند(لی و همکاران، 2021؛ تان و همکاران، 2022). در میان منابع پیشبینی کننده قابلیت نوآوری شرکتها، محققان بر نقش حیاتی سرمایه انسانی و دانش به عنوان نیروهای استراتژیک سازمانها جهت پیگیری و بهبود شایستگی نوآوری خود تاکید میکنند (سینگ و همکاران، 2021؛ گای و همکاران، 2022). در نتیجه، جهت تبیین ویژگی ها و تأثیرات این مولفه های احتمالی، این مقاله تلاش میکند تا تأثیرات مستقیم و غیرمستقیم شیوه مدیریت منابع انسانی(HRM) با مشارکت بالا را بر روی اشکال مشخص ظرفیت نوآوری که شامل نوآوری تدریجی و بنیادین است، را از طریق متغیرهای تعدیلگر به اشتراک گذاری دانش(KM) صریح و ضمنی توضیح دهد. پیشبینی میشود که این مطالعه به دلایل متعددی نظریه و اقدامات مدیریت نوآوری را با تبیین نوآوری های شیوههای HRM و KS افزایش دهد.
5.2. محدودیت ها و مسیرهایی برای تحقیقات آتی
این پژوهش علاوه بر اینکه در بهبود درک رابطه بین متغیرهای مکنون در مدل تحقیق نقش دارد، دارای محدودیتهای خاصی است که باید بر آنها غلبه کرد. اول، این تحقیق از رویکرد مقطعی برای آزمون روابط بین عوامل مکنون استفاده کرد، بنابراین ممکن است احتمال ظهور و تغییر همبستگیها در بلندمدت را نپذیرد. برای رفع این محدودیت و تایید یافته های تحقیق، به یک مطالعه طولی نیاز است. دوم، این مطالعه در یک کشور در حال توسعه اجرا میشود که ممکن است پیامدهای بالقوهای برای نتایج تحقیقات در مقایسه با سایر محیطهای تحقیقاتی داشته باشد. بنابراین، این مقاله توصیه میکند که مطالعات آتی باید همبستگی بین عوامل ذکر شده را در زمینه جدید مانند کشورهای توسعهیافته آزمون کنند تا نتایج تحقیق تبیین و تقویت شود. سوم، ادبیات بر نوآوری باز به عنوان رویکردی جامع برای مدیریت نوآوری با "تشویق و بررسی سیستماتیک طیف وسیعی از منابع داخلی و خارجی برای فرصتهای نوآوری، یکپارچه سازی آگاهانه آن اکتشاف با قابلیتها و منابع شرکت، و بهرهبرداری گسترده از آن فرصتها از طریق کانالهای چندگانه تاکید دارد(وست و گالاگر، 2006، ص.2).به عقیده اسکوردالیس و همکاران (2020)، اگر نوآوری باز به طور موثر اجرا شود، پویایی آن می تواند منجر به رشد قابل توجهی برای SMEها شود، حتی آنها را به رهبران جهان تبدیل کند. بنابراین، تحقیقات آتی باید به بررسی و تبیین نقش بالقوه شیوه HRM با مشارکت بالا در ایجاد فرهنگی که پویایی نوآوری باز را ترویج می کند، بپردازند. در نهایت، تلاش و استراتژی نوآوری سازمانها در بازارهای نوظهور و در حال توسعه تحت تاثیر آشفتگیهای محیطی و محدودیتهای منابع قرار دارد(لی و همکاران، 2022). این مقاله پیشنهاد میکند که کارهای آتی باید بر بررسی مولفه های موجود مانند شیوههای HRM و منابع دانش برای ترویج مدلهای نوآوری مناسب مانند نوآوری صرفه جویانه برای غلبه بر چالشهای کمبود منابع تمرکز کنند.
به طور کلی، این مقاله با پیشنهاد یک مدل کامل برای ترکیب شیوه HRM با مشارکت بالا و انواع خاصی از نوآوری از طریق متغیر میانجی KS صریح و ضمنی و نقش تعدیل کننده آشفتگی های بازار، نظریه نوآوری را مطرح می کند. این مقاله بخاطر تلاش هایش جهت کشف و ارائه بینش عمیق تر از یک رویکرد جدید جهت ارتقا نوآوری بنیادین و تدریجی برای شرکت های موجود در بازارهای نوظهور، ارزشمند و متمایز از دیگر تحقیقات است.
Abstract
There is a lack of study examining the relationship between high-involvement HRM practice and innovation capability as mediated by knowledge sharing. So, the motivation of this paper is to study and explore potential intermediating roles of explicit and tacit knowledge sharing in linking high-involvement HRM practice and innovation capability under the possible moderator of market turbulence. Analysis of Moment Structures was used to measure validation and test the structural model based on the questionnaire surveys of 333 participators in 119 Vietnamese manufacturing and service enterprises from May to July 2021. The collected data were inspected and analyzed using SPSS and AMOS software version 22. The result advocates the proposed hypotheses relating to the intermediating role of KS in the HRM practices-innovation relationship. It spotlights the crucial character of market turbulence in driving the domination of high-involvement HRM practice on incremental and radical innovation. This paper remarkably increases the insights of the precursor role of high-involvement HRM practice, intermediating mechanism of KS activities, and the regulating influence of market turbulence in predicting and fostering radical and incremental innovation, thereby pushing forward the theory of HRM and innovation management.
1. Introduction
Innovation capability is widely accepted as a dynamic competence allowing firms to adjust and evolve their services and products aimed at meeting customers’ needs (Le, 2021; Gui et al., 2022). Accordingly, firms are attempting to improve its innovation capability to succeed in dealing with the external turbulences and environments that might induce negative effects on organizational performances (Cao et al., 2021; Edeh et al., 2022). However, it is an obstacle for organizations in developing and emerging markets to become real innovators rather than imitators due to majority of these firms are medium and small size, with the lack of resources and capital for successful innovation (Lei et al., 2020; Gui et al., 2021). Such situation has required researchers and practitioners to devote more effort to detecting the finer antecedents, new mechanism, and optimal solutions to improve innovation competence for organizations in these nations (Le, 2021; Than et al., 2022). Among the source of predicting innovation capability of firms, scholars highlight the crucial role of human and knowledge capital as the strategic forces for organizations to pursue and improve its innovation competence (Singh et al., 2021; Gui et al., 2022). Consequently, to shed light on the characters and influences of these possible constructs, the paper attempts to elucidate the direct and indirect effects of high-involvement human resource management (HRM) practice on specified forms of innovation capacity that is incremental and radical innovation via the mediators of explicit and tacit knowledge sharing (KS). This study is anticipated to increase the theory and initiatives of innovation management by clarifying the contributions of HRM practices and KS by several reasons.
5.2. Limitations and directions for future research
Besides contributing to improving the understanding of the relationship between latent variables in the research model, the research has certain constraints that require to be overcome. Firstly, the research utilized the cross-sectional approach for testing the relations among the latent factors, so it might not rule out likelihood that the correlations will emerge and change in the long run. A longitudinal study is necessary to address this restriction and confirm the research findings. Second, this study is implemented in a developing country setting, which may have potential implications for research results compared to other research settings. Therefore, the paper recommends that future studies should persist in testing the correlation between the mentioned factors in the new context such as developed countries to clarify and strengthen the research results. Third, literature highlighted open innovation as a holistic approach to innovation management by “systematically encouraging and exploring a wide range of internal and external sources for innovation opportunities, consciously integrating that exploration with firm capabilities and resources, and broadly exploiting those opportunities through multiple channels (West and Gallagher, 2006, p. 2). According to Skordoulis et al. (2020), if open innovation is executed effectively, its dynamics can lead to significant growth for SMEs, even becoming the world leaders. Therefore, future research should explore and clarify the potential role of high-involvement HRM practice in creating a culture that promotes open innovation dynamics. Finally, innovation effort and strategy of organizations in emerging and developing markets tend to be influenced by environmental turbulences and resource-constraints (Le et al., 2022). The paper suggests that future works should focus on exploring available constructs like HRM practices and knowledge resources to promote appropriate innovation models such as frugal innovation to overcome challenges of resource scarcity.
Generally, this paper significantly pushes forward theory of innovation by proffering a complete model to combine high-involvement HRM practice and particular forms of innovation through the mediator of explicit and tacit KS and moderating role of market turbulences. The paper is distinctive and valuable by its efforts in exposing and bringing a deeper insight of a new approach to boost incremental and radical innovation for enterprises in the emerging markets.
H1a. High-involvement HRM practice considerably predicts radical innovation.
H1b. High-involvement HRM practice considerably predicts incremental innovation.
H2a. High-involvement HRM practices are positively associated with tacit KS.
H2b. High-involvement HRM practices are positively associated with explicit KS.
H3a.b. Tacit KS behaviors remarkably affect incremental and radical innovation.
H3c.d. Explicit KS behaviors remarkably affect incremental and radical innovation.
H4a.b. KS behaviors intermediate the high-involvement HRM practice’s influences on incremental and radical innovation.
H5a.b. Market turbulence strengthens the impact of explicit and tacit KS on radical innovation.
H5c.d. Market turbulence strengthens the impact of explicit and tacit KS on incremental innovation.
H1a: شیوه HRM با مشارکت بالا، به طور معناداری، نوآوری بنیادین را پیش بینی می کند.
H1b: شیوه HRM با مشارکت بالا، به طور معناداری، نوآوری تدریجی را پیش بینی می کند.
H2a: شیوه های HRM با مشارکت بالا، ارتباط مثبت با KS ضمنی دارد.
H2b: شیوه های HRM با مشارکت بالا، ارتباط مثبت با KS صریح دارد.
H3a.b: رفتارهای KS ضمنی به طور قابل توجهی بر نوآوری تدریجی و بنیادین تأثیر می گذارد.
H3c.d: رفتارهای KS صریح به طور قابل توجهی بر نوآوری تدریجی و بنیادین تأثیر می گذارد.
H4a.b: رفتارهای KS ، تأثیرات عملکرد HRM با درگیری بالا را بر نوآوری افزایشی و رادیکال میانجی می کند.
H5a.b: آشفتگی بازار، تأثیر KS صریح و ضمنی را بر نوآوری بنیادین تقویت می کند.
H5c.d: آشفتگی بازار، تأثیر KS صریح و ضمنی را بر نوآوری تدریجی تقویت می کند.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. مروری بر ادبیات پیشین
2.1. تاثیر شیوه های HRM با مشارکت بالا بر قابلیت نوآوری
2.2. نقش میانجی KS بین شیوه HRM با مشارکت بالا و نوآوری
2.3. نقش تعدیلگر آشفتگی بازار در رابطه نوآوری-KS
3. روش شناسی تحقیق
3.1. نمونه و جمع آوری داده ها
3.2. مقیاس اندازه گیری
3.3. روش های تحلیل داده
4. تحلیل داده و نتایج
4.1. مدل اندازه گیری
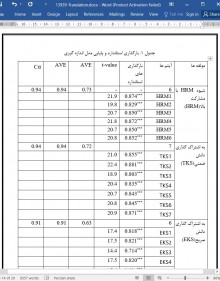
4.1.1. روایی همگرا
4.1.2. روایی افتراقی
4.1.3. برازش مدل اندازه گیری
4.2. مدل ساختاری و یافته ها
4.2.1. آزمون اثرات مستقیم
4.2.2. آزمون اثرات میانجی
4.2.3. اثرات تعدیل کننده
5. بحث
5.1. کاربردهای نظری و عملی
5.2. محدودیت ها و مسیرهایی برای تحقیقات آتی
منابع
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Review of the literature
2.1. The impact of high-involvement HRM practices on innovation capability
2.2. Intermediating role of KS between high-involvement HRM practice and innovation
2.3. Moderating role of market turbulence in the KS-innovation relationship
3. Research methodology
3.1. Sample and data collection
3.2. Measurement
3.3. Data analysis methods
4. Data analysis and results
4.1. Measurement model
4.1.1. Convergent validity
4.1.2. Discriminant validity
4.1.3. Satisfactory of measurement model
4.2. Structural model and findings
4.2.1. Test direct effects
4.2.2. Test mediating effects
4.2.3. Test moderating effects
5. Discussions
5.1. Theoretical and practical contributions
5.2. Limitations and directions for future research
Acknowledgments
References
این محصول شامل پاورپوینت ترجمه نیز می باشد که پس از خرید قابل دانلود می باشد. پاورپوینت این مقاله حاوی 29 اسلاید و 5 فصل است. در صورت نیاز به ارائه مقاله در کنفرانس یا سمینار می توان از این فایل پاورپوینت استفاده کرد.
در این محصول، به همراه ترجمه کامل متن، یک فایل ورد ترجمه خلاصه نیز ارائه شده است. متن فارسی این مقاله در 12 صفحه (2200 کلمه) خلاصه شده و در داخل بسته قرار گرفته است.
علاوه بر ترجمه مقاله، یک فایل ورد نیز به این محصول اضافه شده است که در آن متن به صورت یک پاراگراف انگلیسی و یک پاراگراف فارسی درج شده است که باعث می شود به راحتی قادر به تشخیص ترجمه هر بخش از مقاله و مطالعه آن باشید. این فایل برای یادگیری و مطالعه همزمان متن انگلیسی و فارسی بسیار مفید می باشد.
بخش مهم دیگری از این محصول لغت نامه یا اصطلاحات تخصصی می باشد که در آن تعداد 50 عبارت و اصطلاح تخصصی استفاده شده در این مقاله در یک فایل اکسل جمع آوری شده است. در این فایل اصطلاحات انگلیسی (تک کلمه ای یا چند کلمه ای) در یک ستون و ترجمه آنها در ستون دیگر درج شده است که در صورت نیاز می توان به راحتی از این عبارات استفاده کرد.
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش و pdf بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- پاورپوینت فارسی با فرمت pptx
- خلاصه فارسی با فرمت ورد (word)
- متن پاراگراف به پاراگراف انگلیسی و فارسی با فرمت ورد (word)
- اصطلاحات تخصصی با فرمت اکسل