
دانلود رایگان مقاله الگوریتم Firefly برای تشخیص نفوذ شبکه
چکیده
تشخیص نفوذ شبکه فرآیند شناسایی فعالیت مخرب در یک شبکه با تحلیل رفتار ترافیک شبکه است. تکنیک های داده کاوی به طور گسترده ای در سیستم تشخیص نفوذ (IDS) برای تشخیص ناهنجاری ها استفاده می شود. کاهش ابعاد نقش حیاتی در IDS بازی می کند، زیرا شناسایی ناهنجاری ها از ویژگی ترافیک شبکه با ابعاد بزرگ، فرایندی زمان بر است. انتخاب مشخصه بر سرعت تحلیل و کار پیشنهادی، استفاده از فیلتر و روش مبتنی بر پوشش با استفاده از الگوریتم firefly در انتخاب ویژگی تاثیر می گذارد. ویژگی های حاصل از آن به طبقه بندی C4.5 و شبکه های بیزین (BN) با مجموعه داده KDD CUP 99 منتهی می شود. نتایج تجربی نشان می دهد که 10 ویژگی برای تشخیص نفوذ، نشان دهنده کفایت دقت بهبود یافته است. کار پیشنهادی با کارهای موجود نشان داده شده است که نشان دهنده پیشرفت قابل ملاحظه ای است.
1. مقدمه
سیستم تشخیص نفوذ (IDS) یکی از اجزای مهم سیستم های اطلاعات امن است. مزاحمان ومخلان در شبکه در حال تلاش برای دسترسی به منابع غیر مجاز در شبکه هستند. این امر برای نظارت و تجزیه و تحلیل فعالیت های کاربر و رفتار سیستم بسیار مورد نیاز است. به سادگی با اصلاح پیکربندی پارامترهای سیستم، رفتار سیستم می تواند بی وقفه باشد. از این رو سیستم باید از ویژگی های نظارت دوره ای و الگوهای رفتاری آن برای فعالیت های عادی و غیر طبیعی ارائه شود. دو نوع IDS [13] وجود دارد که مبتنی بر استقرار در زمان واقعی و مکانیزم تشخیص است. IDS مبتنی بر استقرار به IDS مبتنی بر میزبان (HIDS) و IDS مبتنی بر شبکه (NIDS) طبقه بندی شده است. HIDS فعالیت های داخلی یک سیستم محاسباتی را نظارت می کند. NIDS به طور پویا log های ترافیک شبکه را در زمان واقعی برای شناسایی نفوذهای بالقوه در یک شبکه با استفاده از الگوریتم های تشخیص مناسب کنترل می کند. IDS بر اساس مکانیزم تشخیص به تشخیص سوء استفاده، تشخیص غیرمتعارف و IDS ترکیبی طبقه بندی شده است. تشخیص سو مصرف از مجموعه قوانین و یا امضاهای از پیش تعیین شده برای شناسایی حملات شناخته شده استفاده می شود. تشخیص ناهنجاری یک پروفایل فعالیت نرمال، برای تشخیص حملات ناشناخته با چک کردن این موضوع می باشد که آیا وضعیت سیستم پروفایل از فعالیت نرمال تثبیت شده تغییر می کند یا خیر. هیبرید IDS حملات شناخته شده وناشناخته را تشخیص می دهد. امروزه انواع IDS از تکنیک های داده کاوی برای تشخیص نفوذ استفاده می کنند. اکثر NIDS های موجود، با استفاده از تمام ویژگی های ساخته شده از ترافیک شبکه، حملات را شناسایی می کنند. اما برای تشخیص حملات، تمام خصوصیات لازم نیست. کاهش تعداد خواص یا ویژگی ها می تواند زمان تشخیص را کاهش دهد و میزان تشخیص را نیز افزایش می دهد. در این کار، ما روشی مبتنی بر فیلتر و پوشش را برای انتخاب ویژگی های مناسب برای تشخیص نفوذ شبکه ترکیب کردیم. انگیزه کار کاهش تعداد ویژگی ها با عملکرد بهبود یافته برای نرخ تشخیص غیر ترکیبی است. کار پیشنهادی بر روی NIDS تمرکز دارد. اگر چه تکنیک های مختلف در مکتوبات برای NIDS در مورد انتخاب ویژگی ها، طبقه بندی ها وجود دارد، روش پیشنهادی بر روی رویکرد اکتشافی موسوم به تکنیک firefly برای انتخاب ویژگی و C۴ ۵ در مقایسه با طبقه بندی کننده شبکه بیزین متمرکز می باشد.
باقی مانده این مقاله به شرح زیر است. بخش دوم، کار مرتبط در مکتوبات را مشخص می کند. شرح مجموعه داده ها در بخش سوم ارائه شده و بخش چهارم ارائه کار پیشنهاد شده برای تشخیص نفوذ است. نتایج و بحث ها در بخش V و به دنبال آن اظهارات نهایی در بخش VI صورت می گیرد.
2. کار مرتبط
NIDS فعالیت شبکه را بر اساس اطلاعات بارگیری و ویژگی های آماری ترافیک شبکه را نظارت می کند. یک نظرسنجی دقیق از روش های موجود در ارائه روش ها و کاربرد آنها در ابزارهای NIDS توسط Monowar و همکاران انجام شده است. [13]. همچنین آنها حملات کامل مربوط به HIDS و NIDS را ذکر کرده اند. علاوه بر این، آنها بر نیاز به استخراج ویژگی های موثر تأکید کردند که نقش مهمی در تشخیص نفوذ دارند. روش های تشخیص همراه با معیارهای مورد استفاده برای ارزیابی عملکرد NIDS مورد بحث قرار گرفت. یک شبکه عصبی مبتنی بر NIDS توسط Gowrison و همکاران [7] همراه با الگوریتم تقویت شده با پیچیدگی محاسباتی کمتر پیشنهاد شده است. همچنین آنها ارتباط میان ترکیبی از ویژگی ها و حملات را در قالب دستور نشان دادند [29]. آزمایشات انجام شده بر روی KDDCUP'99 انجام شد. یک کار مشابه نیز توسط Weiming و همکاران [22] با روش های پارامتری مبتنی بر Adaboost آنلاین انجام شده است.
عدم نظارت سیستم تشخیص ناهنجاری برای تشخیص نفوذ توسط Jungsuk و همکاران [9] با داده های بدون برچسب انجام شد. علیرغم مزایا، هنوز هم سخت است که آنها را در یک محیط شبکه واقعی قرار دهیم. برای غلبه بر معایب کار مبتنی بر خوشه بندی، Deepak و همکاران. [6] یک رویکرد ترکیبی را پیشنهاد می کند که ترکیبی از خوشه بندی K-Medoids و طبقه بندی Naie-Bayes است. در ابتدا کارشنان جمع آوری داده ها برای تشکیل یک گروه انجام شد و پس از آن یک طبقه بندی برای شناسایی نفوذ در شبکه استفاده شد. تکنیک های داده کاوی توسط Vaishali و همکاران [18] و Uday و همکاران. [3] برای شناسایی الگوهای شناخته شده و ناشناخته حملات مورد استفاده قرار گرفت.
با توجه به ترکیبات مختلف ویژگی های پرونده های ترافیک شبکه، روش های بهینه سازی توسط محققان معرفی شده است. Revathi و همکاران [16] کار خود را با استفاده از تکنیک هوشمندانه برای حل مشکل پیچیده بهینه سازی و پیش پردازش داده انجام دادند. الگوریتم های مبتنی بر ژنتیک توسط Skalak و همکاران [ ۴ ] مورد استفاده قرار گرفتند که در آن جهش تصادفی برای انتخاب ویژگی ها با رویکرد ابتکاری صعود برای IDS بکار گرفته شد. بیش از یک طبقه بندی ضعیف توسط Akhilesh و همکاران [1] توسط مجموعه ای از شبکه عصبی مصنوعی (ANN) و شبکه بیسیم با نسبت افزایش (GR) ویژگی انتخاب برای تشخیص نفوذ استفاده می شود. تجزیه و تحلیل مولفه اصلی (PCA) یکی از روش های ابزار انتخاب ویژگی ها بود. یکی از این روش ها توسط Keerthi et al [10] برای کاهش ابعاد استفاده شد. آنها با آزمایش PCA با استفاده از الگوریتم های طبقه بندی تصادفی و C4.5 با KDD CUP و UNB ISCX آزمایش های انجام شده را انجام دادند. در کار خود، دقت طبقه بندی به دست آمده توسط 10 مولفه اصلی با 41 ویژگی با استفاده از طبقه بندی C4.5 مقایسه شد.
روش انتخاب ویژگی مبتنی بر پوشش توسط وی و همکاران [ ۲۰ ] پیشنهاد شد و آزمایش ها بر روی داده های KDD "۹۹" انجام شد. در کار آن ها، به جای ساختن تعداد زیادی از مشخصه ها از ترافیک شبکه گسترده، هدف نویسندگان انتخاب بهترین ویژگی ها و استفاده از آن ها برای تشخیص حملات نفوذ به شیوه ای سریع و موثر است. آن ها ابتدا از انتخاب ویژگی براساس روش فیلتر و روش پوشش استفاده کردند. انتخاب ویژگی مبتنی بر فیلتر برای ویژگی های مهم براساس ارتباط بین خصوصیت و ویژگی های مهم براساس رتبه بندی انتخاب می شود. انتخاب ویژگی مبتنی بر پوشش از برخی از روش های جستجو برای انتخاب زیر مجموعه از ویژگی ها و زیر مجموعه های انتخاب شده با استفاده از شبکه C4.5 و بیزین استفاده کرد. با این حال، Siva و همکاران. [26] از جستجوی ژنتیکی به عنوان یک استراتژی جستجو برای انتخاب ویژگی های مبتنی بر پوشش استفاده کرد تا زیرمجموعه مطلوب را انتخاب کند. اما Lei Yu و همکاران [12] یک مدل همبستگی مبتنی بر فیلتر ایجاد کرده اند تا ویژگی ها را سریعتر انتخاب کنند بدون اینکه از کارایی استفاده کنند. طبقه بندی ها بر اساس ماشین های بردار پشتیبانی و شبکه های عصبی توسط Sung و همکاران [2] با 13 ویژگی انتخاب شده مورد استفاده قرار گرفت. یک مدل محاسباتی موازی و تکنیک انتخاب ویژگی الهام گرفته از طبیعت توسط Natesan و همکاران [27] پیشنهاد انتخاب و طبقه بندی کارآمد برای به دست آوردن میزان تشخیص بهینه سازی شده انجام شد. همچنین نقشه کاهش مدل برنامه نویسی برای انتخاب زیر مجموعه های بهینه با پیچیدگی محاسباتی کم استفاده می شود. IDS با استفاده از تئوری مجموعه (Rough (rst)همراه با SVM توسط چن و همکاران ساخته شد که در آن rst برای انتخاب ویژگی های مهم استفاده شد [ ۱۵ ]. مجموعه داده NSL-KDD که تنوع KDDCUP'99 است توسط Dhanabal et al استفاده شده است. [11] که کار آنها از نظر دیگران از نظر استفاده از داده ها متفاوت است.
3. توصیف DATASET
در این کار، ما از مجموعه داده KDD CUP 99 [14] استفاده کردیم که شامل انواع عادی و حمله (22 نوع مختلف) است. هر رکورد از داده ها از گروهی از بسته ها که بیش از ۲ پنجره دوم اتصال که به یک مقصد ایجاد شده است، ساخته شده است. هر رکورد داده دارای 41 ویژگی (34 عدد، 4 باینری و 3 عدد) است. 9 ویژگی اول نشان دهنده اطلاعات آماری اولیه بسته ها بر روی یک اتصال است، ویژگی های بعدی 13 ویژگی محتوای بسته ها را نشان می دهد، و 9 ویژگی دیگر نشان دهنده اطلاعات ترافیکی است. 9 ویژگی های دیگر ویژگی های میزبان را نشان می دهد. انواع مختلفی از حمله وجود دارد که در طی یک زمان وارد شبکه می شوند و حملات به چهار طبقه اصلی زیر تقسیم می شوند. آنها به طور خلاصه شرح داده می شوند:
• Denial of Service (Dos): مهاجمان سعی می کند از استفاده از یک سرویس از کاربران قانونی جلوگیری کند.
• از راه دور به محلی (R2L): مهاجم دارای حساب کاربری در دستگاه قربانی نیست، بلکه تلاش می کند دسترسی به آن را داشته باشد.
• کاربر به ریشه (U2R): مهاجم دارای دسترسی محلی به دستگاه قربانی است و تلاش می کند تا امتیازات فوق العاده کاربر را به دست آورد.
• Probe: مهاجم تلاش می کند اطلاعاتی در مورد میزبان هدف به دست آورد.
Abstract
Network intrusion detection is the process of identifying malicious activity in a network by analyzing the network traffic behavior. Data mining techniques are widely used in Intrusion Detection System (IDS) to detect anomalies. Dimensionality reduction plays a vital role in IDS, since detecting anomalies from high dimensional network traffic feature is time-consuming process. Feature selection influences the speed of the analysis and the proposed work, deploys filter and wrapper based method with firefly algorithm in the wrapper for selecting the features. The resulting features are subjected to C4.5 and Bayesian Networks (BN) based classifier with KDD CUP 99 dataset. The experimental results show that 10 features are sufficient to detect the intrusion showing improved accuracy. The proposed work is compared with the existing work showing promising improvements.
I. INTRODUCTION
Intrusion detection system (IDS) is an important component of secure information systems. Intruders in the network are trying to access to the unauthorized resources in the network. It is highly required to monitor and analyse the activities of the user and the system behaviours. Simply by modifying the configuration of the system parameters, the behaviour of the system could be erratic. Hence the system has to be provided with the features for the periodic monitoring and its behavioural patterns both for normal and abnormal activities.There are two types of IDS [13], which are based on deployment in real time and detection mechanism. The IDS based on deployment is categorized into Host based IDS (HIDS) and Network based IDS (NIDS). HIDS monitors the internal activities of a computing system. NIDS dynamically monitors the logs of network traffic in real time to identify the potential intrusions in a network using appropriate detection algorithms. The IDS based on detection mechanism is categorized into misuse detection, anomaly detection and hybrid IDS. Misuse detection uses the predefined set of rules or signatures to detect known attacks. Anomaly detection builds a normal activity profile to detect unknown attacks by checking whether the system state varies from the established normal activity profile. Hybrid IDS detects known and unknown attacks. Nowadays, all kinds of IDS use the data mining techniques for detecting intrusions. Most of the existing NIDS detect attacks by using all attributes constructed from network traffic. But, not all the attributes are needed for detecting attacks. Reduced number of attributes or features can reduce the detection time and increases the detection rate also. In this work, we combined filter and wrapper based approach to select appropriate features for detecting Network Intrusion. The motivation of the work is in reducing the number of features with improved performance for an uncompromised detection rate. The proposed work focuses on NIDS. Though various techniques exist in the literature for NIDS in terms of selection of features, classifiers, the proposed work concentrates on the Meta heuristic approach called firefly technique for feature selection and C4.5 classifier and compared with Bayesian network classifier.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. Section II outlines the related work in the literature. The dataset description is given in the section III and the section IV presents proposed work for intrusion detection. The results and discussions are made in the Section V followed by the concluding remarks in section VI.
II. RELATED WORK
NIDS monitors the network activity based on payload information and statistical features of network traffic. A detailed survey of the existing methods outlining the methods, and their applicability associated with the tools in NIDS is done by Monowar et al. [13]. Also they listed the complete attacks related to the HIDS and NIDS. In addition, they emphasized the need for the extraction of the effective features which play major role in the detection of intruders. The detection methods along with the metrics used to assess the performance of the NIDS was discussed. A neural network based NIDS was proposed by Gowrison et al. [7] along with boosting algorithm with less computational complexity. Also they demonstrated the relation between the combination of features and attacks in the form of grammar [29]. The experiments were conducted on KDDCUP’99. A similar work is also carried out by Weiming et al. [22] with online Adaboost-based parameterized methods.
Unsupervised anomaly detection system for detecting intruders was carried out Jungsuk et al. [9] with the unlabelled data. Despite the advantages, it is still hard to deploy them into a real network environment. To overcome the disadvantages of the clustering based work, Deepak et al. [6] proposed a hybrid approach which is the combination of K-Medoids clustering and Naïve-Bayes classification. In their work, first they applied clustering on all data to form a group and after that applied a classifier for classification purpose to identify intrusion in the network. Data mining techniques were deployed by Vaishali et al. [18] and Uday et al. [3] to detect both known and unknown patterns of attacks.
Due to the various combinations of the features in the network traffic records, the optimization techniques were introduced by the researchers. Revathi et al. [16] carried their work using swarm intelligence technique to solve complex optimization problem and for data preprocessing. Genetic based algorithms were used by Skalak et al. [4] where the random mutation was deployed to select or deselect the features with hill climbing heuristic approach for the IDS. More than one weak classifiers are used by Akhilesh et al. [1] by the ensemble of Artificial Neural Network (ANN) and Bayesian Net with Gain Ratio (GR) feature selection technique for intrusion detection. Principal Component Analysis (PCA) was one of the instrumental methods to select the features. One such approach was used by Keerthi et al. [10] for dimensionality reduction. They carried out experiments with PCA using Random forest and C4.5 classifier algorithms with KDD CUP and UNB ISCX dataset. In their work, classification accuracy obtained by 10 principal components was compared with 41 features using C4.5 classifier.
Filter and wrapper based feature selection method was proposed by Wei et al. [20] and the experiments were conducted on KDD’99 data. In their work, instead of constructing a large number of features from massive network traffic, the authors aim to select the most prominent features and use them to detect intrusions in a fast and effective manner. They first employed feature selection based on filter method and wrapper method. Filter based feature selection uses the Information Gain to select important features based on relevance between an attribute and class and important attributes are selected based on rank. Wrapper based feature selection used some searching methods to select subset of the features and selected subset is evaluated using C4.5 and Bayesian network. However Siva et al. [26] used Genetic search as a searching strategy for wrapper based feature selection to select the optimal subset. But Lei Yu et al [12] created a filter based correlation model to select the features in faster manner without giving up the efficiency. The classifiers based on Support Vector Machines and neural network was used by Sung et al. [2] with selected 13 features. A parallel computing model and a nature inspired feature selection technique was attempted by Natesan et al. [27] proposing an efficient feature selection and classification in order to obtain optimized detection rate. Also Map Reduce programming model is used for selecting optimal subset with low computational complexity. IDS using Rough Set Theory (RST) along with SVM was constructed by Chen et al. where RST was used for selecting the important features [15]. The NSL-KDD dataset which is variation of the KDDCUP’99 was used by Dhanabal et al. [11] whose work differs from the others in terms of the data set usage.
III. DATASET DESCRIPTION
In this work, we used KDD CUP 99 data set [14], which consists of normal and attack types (22 different types).Each record of data is constructed from group of packets measured over 2 second window of a connection established to the same destination. Each data record has 41 features (34-numeric, 4- binary, and 3-nominal). First nine features represent the basic statistical information of the packets over a connection, next thirteen features represent the content of the packets, and another nine features represent the traffic information. The last nine features represent the host based features. There are different types of attack which are entering into the network over a period of time and the attacks are classified into the following four main classes. They are briefly described as follows:
• Denial of Service (Dos): Attacker tries to prevent legitimate users from using a service. Remote to Local (R2L): Attacker does not have an account on the victim machine, but tries to gain access.
• User to Root (U2R): Attacker has local access to the victim machine and tries to gain super user privileges.
• Probe: Attacker tries to gain information about the target host.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. کار مرتبط
3. توصیف DATASET
4. کار پیشنهاد شده
A. انتخاب ویژگی مبتنی بر فیلتر
B. انتخاب ویژگی های مبتنی بر پوشش
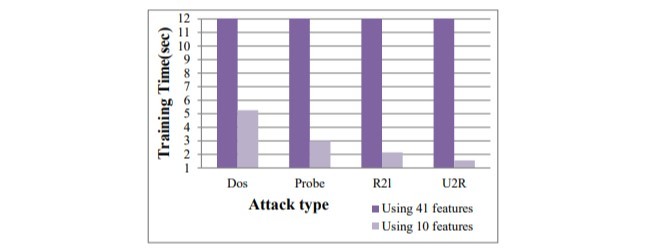
5. نتایج و بحث
A. آزمایشات مبتنی بر KDD CUP 99
A. نتایج کار پیشنهادی
6. نتیجه گیری و کار آینده
منابع
Abstract
1. INTRODUCTION
2. RELATED WORK
.3 DATASET DESCRIPTION
4. PROPOSED WORK
A. Filter based feature selection
B. Wrapper based feature selection
5. RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
A. Experiments based on KDD CUP 99
A. Results of proposed work
6. CONCLUSION AND FUTURE WORK
References
