رسوبات ایجاد شده از ذرات آلاینده موجود در روغن توربین بر روی لایه یاتاقان
اگر بار اعمال شده بر روی لایه یاتاقان، بسیار زیاد باشد روی این لایه رسوباتی ایجاد میشود و درصورتیکه این اتفاق بیش از اندازه تکرار شود میتواند به افزایش غیرقابل قبول دما و لرزش بیانجامد. این رسوبات عمدتاً ترکیبات ارگانیکی و محصولات جانبی فرایند اکسیداسیون میباشند، در روغن موتور نامحلول هستند، و میتوانند پیش ماده تولید رسوب باشند. در این مطالعه، پیش ماده تولیدکننده رسوب در روغن موتور با جزئیات مورد بررسی قرار گرفت و مکانیسم تولید رسوب نشان داده شد. علاوه بر این، تفاوت اثرات نوع روغن و شرایط لازم برای تشکیل رسوب نیز در نظر گرفته شده است.
1. مقدمه
با کار کردن موتور، روغن آن مستهلک میشود. استهلاک شدید روغن که در برخی موارد ممکن است در قسمتهایی از موتور رخ دهد، میتواند موجب تولید رسوب شود. تولید رسوب میتواند بر عملکرد سیستمها تأثیر بگذارد. مشکلات ناشی از ایجاد رسوبات روغنی که با گرفتگی خط لغزاننده میتوانند موجب روانسازی ضعیف عملکرد موتور گردند کاملاً شناخته شده اند. با این حال، این رسوبات هم ظاهر و ترکیب قابل رؤیت و هم غیرقابل رؤیت دارند. یکی از این رسوبات، رسوبات چسبنده تشکیل شده بر روی سطوح فلزی داغ هستند که با روغنهای روان کننده در تماس میباشند و شناخته شده ترین رسوبات هستند. این رسوبات را میتوان در خطوط روغنی و مخزن توربینهای گازی، حلقههای سیلندر موتورهای دیزلی، و خطوط روغنی توربوشارژرها (موتورهای شارژکننده توربینها) مشاهده کرد؛ تمامی این سطوح دارای دمایی بیش از 300 درجه سانتیگراد هستند. این رسوبات به دلیل واکنش چشمگیر اکسیداسیون حرارتی روغنها بر روی سطوح فلزی تولید میشوند و میتوان با انتخاب روغنهای مناسب با مقاومت بالا در برابر اکسیداسیون حرارتی و کاهش دمای سطح فلز، آن را کنترل کرد [1-4].
Under severe bearing conditions, deposits form on the loaded part of bearing pads and if this happens excessively, it could lead to unacceptable rises in temperature and vibration. Deposits are mainly organic compounds, formed as oxidation by-products, which are insoluble in lubricating oil and can be the precursor to deposits. In this study, the deposit precursor in lubricating oil was investigated in detail and the deposit production mechanism was demonstrated. Furthermore, the difference of oil type effects and the dependence of conditions on deposit formation are also considered.
1. Introduction
Lubricating oil deteriorates while in service. Severe deterioration, which can occur locally in some cases, can lead to a deposit problem. This could affect the functionality in systems. The problem caused by oil deposits that affects poor lubrication caused by clogging of the lubricant line has been known well. The deposits, however, have some kind of root and visual appearance and composition. Adhesive deposits forming on hot metal surfaces with which lubricating oils are in contact is one of them and the most well-known. They can be observed in the sump and oil lines of gas turbines, rings/liners of diesel engines and oil lines of turbochargers; all of which have surfaces at temperatures exceeding 300°C. Such deposits are due to the remarkable thermo-oxidation reaction of oils on hot metal surfaces and can be controlled by selecting proper oils with high thermo-oxidation stability and reducing the metal surface temperature [1-4].
1. مقدمه
2. دستور کار آزمایشات
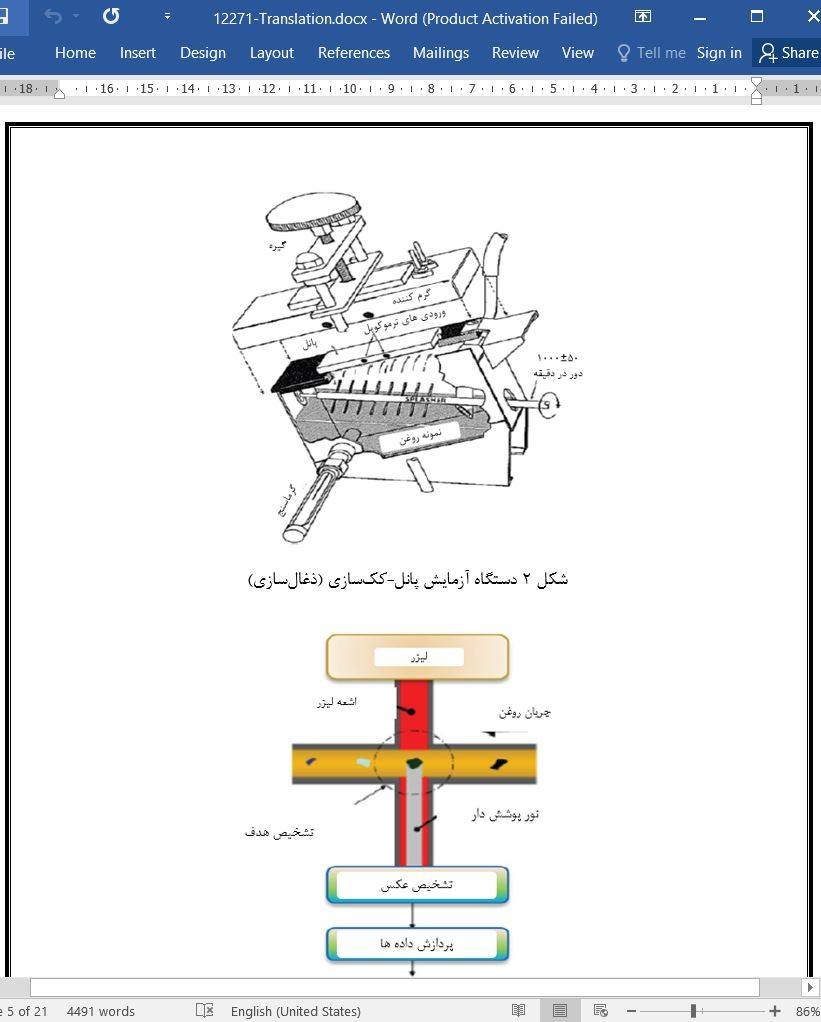
2.1. تجزیه و تحلیل رسوبات تشکیل شده روی بخش واقع بر پد برگردان یاتاقان کمپرسور (متراکم-کننده هوا) توربین واقعی
2.2. مشاهده ذرات آلاینده نامحلول در روغنهای فرسوده شده با گرمایش موضعی
2.3. تفاوت گروه روغن اصلی تولیدکننده ذرات آلاینده نامحلول
2.4. نمایش رسوب ایجادشده از ذرات آلاینده نامحلول در آزمون چرخش چهار ساچمه
3. نتایج
3.1. آنالیز رسوبهای تشکیل شده روی بخش واقع بر لایه مورب یاتاقان کمپرسور توربین واقعی
3.2. پراکندگی اندازه ذرات آلاینده نامحلول
3.3. تفاوت گروه روغنهای پایه/اولیه در تولید ذرات آلاینده نامحلول
3.4. شکل و شمایل(ظاهر) رسوب ایجادشده از ذرات
4. بحث
5. نتیجه گیری
منابع
1. Introduction
2. Experimental programs
2.1. Analysis of deposits formed on loaded part of tilting bearing pad in actual service compressor
2.2. Observation of particulate insoluble contamination in deteriorated oils made by localized heating
2.3. Base oil Group difference of particulate insoluble contamination
2.4. Demonstration of deposition by particulate insoluble contamination using rotating four-ball test The presumed deposition mechanism is based on the
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of deposits formed on loaded part of tilting bearing pad in actual service compressor
3.2. Particle size distribution of particulate insoluble contamination
3.3. Base oil Group difference of particulate insoluble contamination
3.4. Demonstration of deposition by particulate insoluble contamination using rotating four-ball test Conducting the four-ball test which was expected to
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه