تشخیص بیماری های قلبی مبتنی بر منطق فازی واسطه ای
چکیده
منطق فازی واسطه ای یک روش برای حل مشکل اطلاعات متناقض می باشد که راه حلی را برای رفع تناقضات ارائه می کند. هدف این مقاله ارائه کردن یک سیستم تخصصی مبتنی بر این نوع از منطق فازی برای تشخیص بیماری های احتمالی قلبی برای یک بیمار می باشد. سیستم پیشنهادی ما، حالت تعمیم یافته از کنترل کننده منطق فازی Mamdani بوده و شامل 44 قانون از نوع یک ورودی- یک خروجی می باشد. این سیستم با 11 متغیر به عنوان ورودی و یک متغیر به عنوان خروجی کار می کند..
1. مقدمه
عدم قطعیت در حالت های مختلف خودش را نشان میدهد و بر روی تصمیم گیری تاثیر می گذارد. معمولا، اطلاعات ممکن است ناقص، اشتباه، تکه تکه و یا غیر قابل اعتماد و مبهم باشد و یا گاهی ممکن است تناقض در اطلاعات وجود داشته باشد [1]. بیشتر این عدم قطعیت در اطلاعات را می توان با استفاده از منطق فازی نوع 1 [2]، منطق فازی نوع 2 [3و4] و یا منطق فازی شهودی [5و6] رفع کرد.
نظریه منطق فازی یک نظریه ریاضی را ارائه می کند تا بتوان عدم قطعیت مرتبط با فرآیند های ادراکی انسانی را درک کرد، مانند تفکر و استدلال. روش های متداول برای ارائه دانش، فاقد ابزار مناسب برای ارائه معنی مفاهیم فازی می باشد. در نتیجه، رویکرد های مبتنی بر منطق فازی اولیه، نمی توانند چارچوب مفهومی مناسبی را برای کار با ارائه دانش عقل سلیم فراهم کنند، زیرا این دانش به صورت ذاتی، ناقص و بدون دسته بندی می باشد. توسعه منطق فازی به انگیزه رفع نیاز برای چارچوب مفهومی صورت گرفت که این چارچوب بتواند مشکلات مرتبط با این ابهام مفهومی را حل کند.
6. جمع بندی
عدم قطعیت در حالت های مختلف خودش را نشان میدهد و بر روی تصمیم گیری تاثیر دارد. این روز ها، مدل های ریاضی مختلفی ارائه شده است که می توانند با این عدم قطعیت کار کنند. اما در صورتی که ما با مبنای دانشی کار کنیم که با زمان تغییر کند و اطلاعات متناقض را در اختیار ما قرار دهد که حالت تردید و یا تناقض ایجاد می کند و یا اگر ترکیبی از این شرایط وجود داشته باشد، ما باید از منطق فازی واسطه ای استفاده کنیم که بتواند اطلاعات متناقض را هم پردازش کند.
Abstract
Mediative fuzzy logic is an approach able to deal with inconsistent information providing a solution when contradiction exists. The aim of this paper is to design an expert system based on this type of fuzzy logic in order to diagnose a possible heart disease for a patient. Our proposed system is an extension of the standard Mamdani fuzzy logic controller and contains 44 rules of the type single input–single output. The system works with 11 variables as inputs and one variable as output.
1. Introduction
Uncertainty appears in different forms and affects decisions making. Frequently, information may be incomplete, imprecise, fragmentary, not fully reliable, vague, contradictory, or deficient in some other way [1]. Much of this uncertainty can be handle using Fuzzy logic type 1 [2], Fuzzy logic type 2 [3,4] or Intuitionistic fuzzy logic [5,6].
The theory of fuzzy logic provides a mathematical theory to capture the uncertainties associated with human cognitive processes, such as thinking and reasoning. The conventional approaches to knowledge representation lack the means for representing the meaning of fuzzy concepts. As a consequence, the approaches based on first order logic do not provide an appropriate conceptual framework for dealing with the representation of commonsense knowledge, since such knowledge is by its nature both lexically imprecise and non-categorical. The development of fuzzy logic was motivated in large measure by the need for a conceptual framework which can address the issue of lexical imprecision.
6. Conclusion
Uncertainty appears in different forms and. affects decision making. Nowadays, there are mathematical models to handle the uncertainty. But if we work with a knowledge base that changes with time, and with non-contradictory information that becomes doubtful or contradictory, or with any combination of these three situations then we need to use mediative fuzzy logic which is able to process inconsistent information.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. منطق فازی واسطه ای
3. ارائه دانش
4. سیستم فازی واسطه ای ارائه شده
4.1 متغیر های ورودی و خروجی
4.2 مبنای قوانین فازی
4.3 سیستم استدلال
4.3.1 سطح فازی سازی و فعال سازی
4.3.2 جمع بندی استنتاجی
4.3.3 غیر فازی سازی و نتیجه خروجی
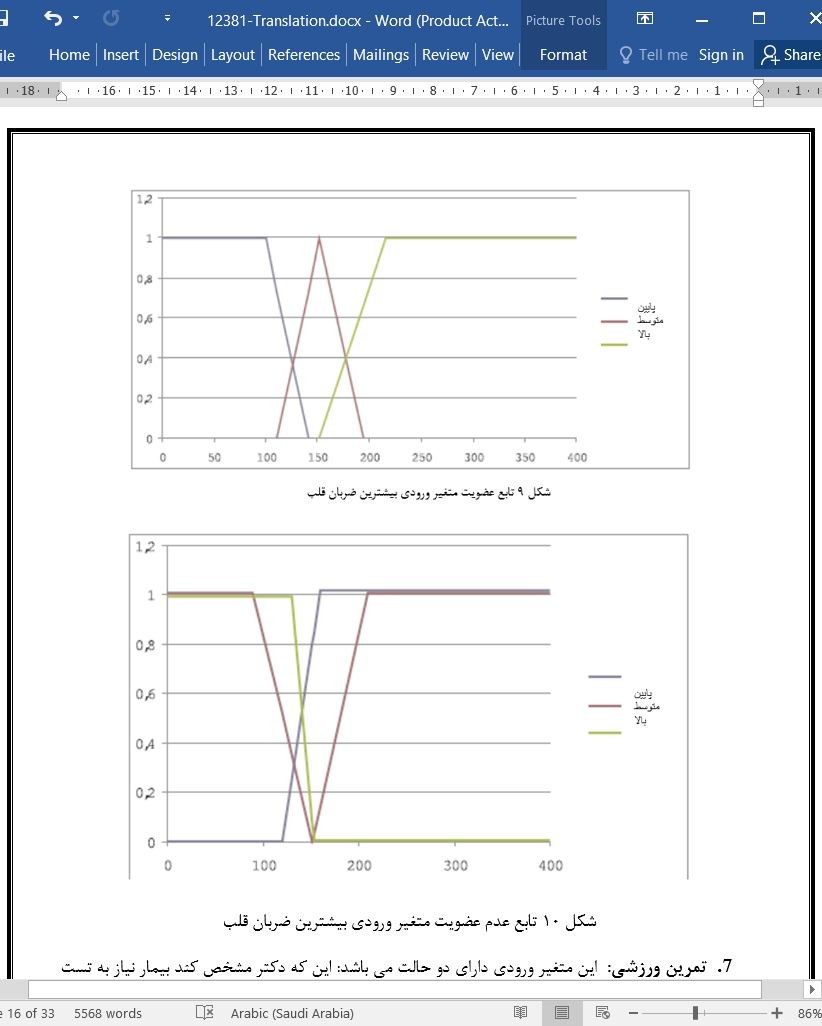
5. تست سیستم
6. جمع بندی
منابع
ABSTRACT
1. Introduction
2. Mediative fuzzy logic
3. Knowledge representation
4. Proposed mediative fuzzy system
4.1. Input and output variables
4.2. Fuzzy rule base
4.3. Reasoning system
4.3.2. Inferred conclusion
4.3.3. Defuzzification and output result
5. System testing
6. Conclusion
References
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه